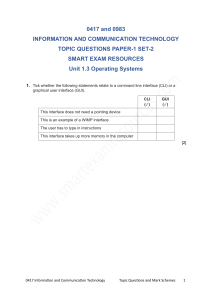
Grade 8 Name: Date: ICT Final Extra Practice Worksheet AHISR ICT Department Hardware and Software A computer system consists of hardware and software. Define: 1. Hardware: is a general term of physical components that make up computer system. 2. Software: is a general term for programs that controls the computer system. Give Examples of system software. Compiler-linkers-device driver-operating system-utilities Give examples of Application Software. Word processor-spreadsheet-database-control and measurement software-appsphoto editing-video editing software-graphics manipulation software Give examples of internal hardware. Motherboard-random access memory (Ram)-read only memory (Rom)-video cardssound cards. Give examples of external hardware. Keyboard-mouse-printer-camera-microphone-flash memory-external hdd Write the full form of RAM and ROM, and compare and contrast between them. RAM: - Random access memory is an internal chip where data is temporary stored, it's often referred to as a volatile that lost its contents when power of computer turned off. ROM: - Read only memory is a memory used to store information that need to be permanent, its often referred to non-volatile. List the types of the hard disk, the main storage of the computer. 1. HDD (internal hard disk drive) 2. SDD (solid state drive) 1 Define the Operating system. To enable computer systems function and allow user to communicate with computer systems, special software known as operating system (OS) List four tasks of the operating system. 1. Control of the operation of the input, output, and storage devices. 2. Dealing with errors that occur in application programs. 3. Maintaining security of the whole computer system. 4. Allowing communication between the user and the computer system. What does CLI and GUI stand for? CLI: Command line interface GUI: Graphical user interface Explain the WIMP technology which the GUI use. WIMP (windows icon menu and pointing device), it's one of the most common technology which was developed for use on personal computers. Here a mouse is used to control a cursor and icons are selected to open/run windows. List the advantages and disadvantages for CLI and GUI interfaces. Interface CLI Advantages The user is in direct communication with the computer The user is not restricted to a number of options. It's possible to alert computer configuration system. 2 Disadvantages The user needs to learn a number of commands to carry out basic operations. All commands needs to typed in, which takes time. Each command must be typed in using the correct format. It's more difficult to edit once commands are entered. GUI The user doesn’t need to learn any command. It's more user friendly. A pointing device(mouse) is used to click on an icon to launch the application It uses up more computer memory than a CLI interface. The user is limited to the icon provided on the screen. It needs an operating system such as windows to operate, which uses up considerable memory. Types of computers. Select the most appropriate computer type for the following. Desktop Computers (PC) - Laptops-Tablets-Smartphones- Smart watches -Mainframe Computers Not easily carried around since they are made up of separate components. desktop Have limited battery life. laptop The keyboard and pointing devices can sometimes be awkward to use. laptop Have sensors like touch screen, and voice recognition like Siri. Tablets Fully portable. Tablets Fixed in one location so less likelihood of them being damaged. desktop Allows normal phone calls to be made. smartphones The small screen makes pages difficult to read. smartphones Allow users to wear mini-computers on their wrists. Smart watches Fitness and health monitoring capabilities. Smart watches Used to run commercial applications like banking and insurance. smartphones Can have Several CPUs. Mainframe List four main features of mainframe computers. 1. They can have several CPUs. 2. They have very fast processor speed. 3. They can support multiple operating systems. 4. They have huge internal memories. 3 File Management State what the following file extensions are short for. 1. .csv: comma separated value 2. .txt: text 3. .rtf: rich text format 4. .gif: graphics interchange format 5. .jpg: joint photographic expert group 6. Pdf: portable document format 7. .png: portable network graphics 8. .mp4: moving picture expert group layer 4 9. .css: cascading style sheet 10. Html: hypertext markup language Mention two reasons (or advantages) for reducing the file size. 1. It is important when sending files as email attachments, the larger the size the more time it takes to transmit. 2. Because all computer systems have a limited storage. Images Explain the text wrapping options used with an image. 1. In line with text: place the image as a line graphic and is treated as a text character with in a line of text. 2. Square: place image on the page and the text wrap around it. 3. Tight: place image on the page and the text wrap around it like a square. 4. Through: place image on the page and the text wrap around the image. 5. Top and bottom: place image on the page and the text wrap above and below the image. 6. In front of text: this places an image over the top of the text. 7. Behind text: this places an image behind the text. 4 5