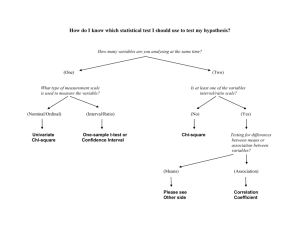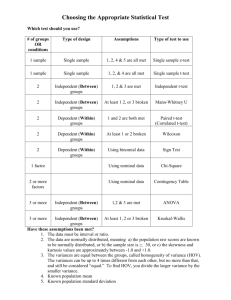
Paired-Samples T-Test measure the same group of people twice. Assumptions of the paired-samples t-test § § § § interval or continuous independent. normally distributed. equal variances. T-Value § The t-test produces a value, simply known as ‘t’, which can only be used to determine statistical significance. § It does not say anything about the size of the difference between the two mean scores (i.e., the effect size). § Researchers have to run a separate effect size calculation to obtain Cohen’s d. The Effect Size for the pairedsamples t-test § Cohen’s d is an effect size index for t-tests. § Cohen’s d-value = (Mean 1 – Mean 2) ÷ pooled standard deviation. § To determine effect sizes, researchers either have to compute them by hand or use a web-based calculator, such as Becker’s at http://www.uccs.edu/~lbecker/ Steps to Perform a pairedsamples t-test § Step 1: Examine and evaluate the descriptive statistics of the data from two groups and the reliability of the research instrument(s) being used. § Step 2: Check whether the statistical assumptions for the particular t-test are met. Levene’s test for equality of variances can be used to determine whether the two means have equal variances (SPSS can perform this statistical test; see below). Paired-Samples T-test in SPSS § Click the Analyze menu. Go to Compare Means and then PairedSamples T Test § On clicking Paired-Samples T Test, a dialog box opens § First, select the variables ‘implicature score’ and ‘routines score’. Make sure they are paired up as Variable 1 and Variable 2. § Click Continue and OK. Cohen’s d