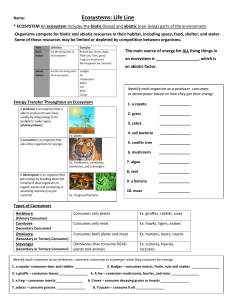
The environment means a surrounding where we meet, we live and we breathe. It is one of the basic essential things for living beings. The word Environment includes all biotic and abiotic things which are present around us. It provides fundamental things like air, water, food, and land which is very important for our well-being. It’s a gift given by God to human beings which helps in nurturing human life. Importance of Environment It plays a vigorous role in keeping living things hale and hearty. It helps in maintaining the ecological balance. It provides food, shelter, air and accomplishes all human needs. n addition to this environment is the source of natural beauty which is necessary for maintaining physical and mental health. Impact of Human Activities on the Environment There are various types of human activities which are directly contributing to environmental disasters such as acid rain, acidification of oceans, change in the climate, deforestation, depletion of an ozone layer, disposal of hazardous wastes, global warming, overpopulation, pollution, etc. Components of Environment The components of the environment are: Biotic Components: It includes all biotic factors or living forms like plants, animals, and microorganisms. Abiotic Components: It includes non-living factors like temperature, light, rainfall, soil, minerals, etc. It comprises the atmosphere, lithosphere, and hydrosphere. Biotic Environment The biotic components of the environment are the living organisms present in the ecosystem that includes plants, animals, and microorganisms (Bacteria and Fungi). These components can be classified into three main groups based on their roles in the ecosystem. These are as follows. Producers like plants, algae, and bacteria take in energy from sunlight and use it to transform carbon dioxide and oxygen into sugars and energy. They form the base of the food web and are the largest group of living beings in the ecosystem. They also establish an interrelationship with the abiotic components of the ecosystem by absorbing the inorganic carbon and nitrogen from the atmosphere. Consumers like herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores in the ecosystem get their energy from consuming other organisms. For example, Herbivores eat producers, carnivores eat other animals and omnivores eat both. Along with producers and decomposers, consumers are part of the food chain and food webs, where energy and nutrients are transferred from one level to another. Decomposers like earthworms, dung beetles, and many species of fungi and bacteria break down waste material and dead organisms. They create a vital recycling task of returning nutrients integrated into dead organisms to the soil from where plants can take them up again.