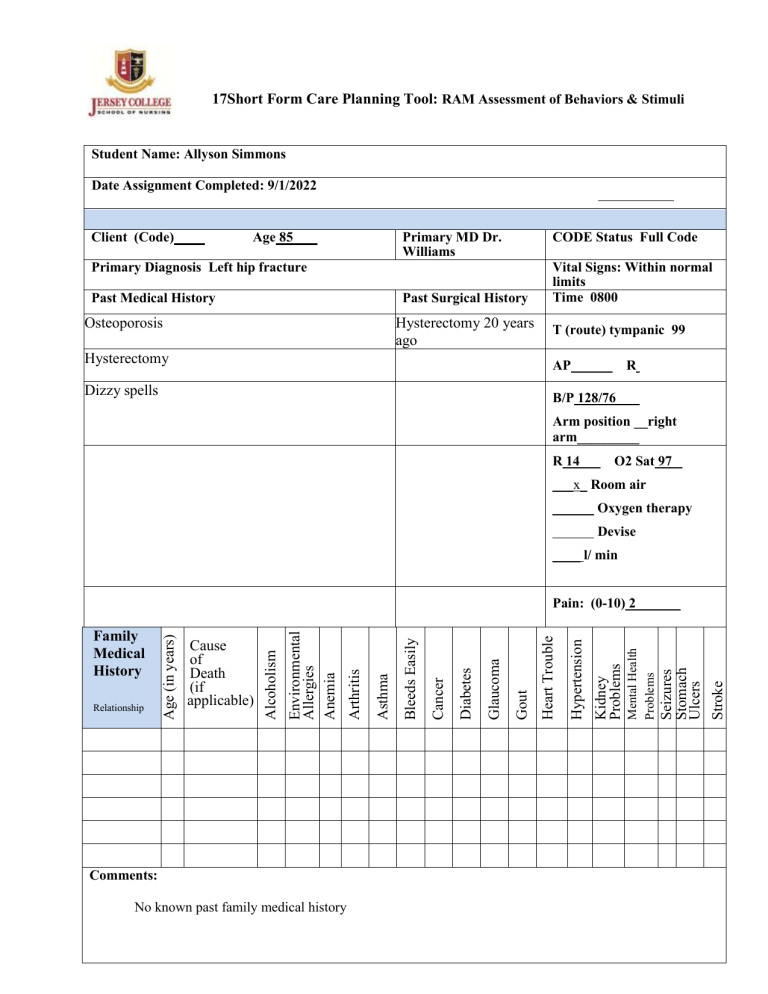
17Short Form Care Planning Tool: RAM Assessment of Behaviors & Stimuli Student Name: Allyson Simmons Date Assignment Completed: 9/1/2022 Client (Code) Age 85 Primary MD Dr. Williams CODE Status Full Code Primary Diagnosis Left hip fracture Past Medical History Past Surgical History Osteoporosis Hysterectomy 20 years ago Vital Signs: Within normal limits Time 0800 T (route) tympanic 99 Hysterectomy AP Dizzy spells B/P 128/76 R Arm position __right arm_________ R 14 O2 Sat 97 ___x_ Room air ______ Oxygen therapy Devise ____ l/ min Comments: No known past family medical history Seizures Stomach Ulcers Stroke Mental Health Problems Kidney Problems Hypertension Heart Trouble Gout Glaucoma Diabetes Cancer Bleeds Easily Asthma Arthritis Environmental Allergies Anemia Relationship Cause of Death (if applicable) Alcoholism Family Medical History Age (in years) Pain: (0-10) 2 Current Medications (Including Herbal & Over the Counter) Medication Route Dosage Frequency Enoxaparin Subcutaneously 40mg Daily Docusate PO 100mg Daily Morphine sulfate IV 4mg Every 4 hours prn for pain Raloxifene PO Not listed Daily Immunization History: All immunizations up to date Admission date: 9/1/2022 Height: 152 cm Weight: 47.5 kg (105 lb) BMI: 17.47 Allergies: (Including environmental, food and medications) NKDA Name of Agent Reaction System Review Findings GI/Nutrition Diet: Appetite 65% - - Normal Findings: Bowel sounds active in all quadrants Abdomen soft, non-distended, non-tender Receives and tolerates nutrition and fluids Absence of nausea, vomiting, cramping, diarrhea or Constipation No complaints of nausea, vomiting, or abdomen pain with palpation How did you assist the client with their diet? Asking what food, the patients likes to eat Asking what are the patients preferences Describe your Findings: Patients eats very little with no nutritional value Feeding tube (include size and type) Assess barriers to accessing nutritional food Intake: 575 ml Neurological Normal Findings: Alert and oriented x 3 Speech is clear Memory intact Follows commands and converses Absence of seizures Behavior appropriate to situation When upright: Balance steady Gross motor coordination intact Hand grasps strong/equal PERRLA, Foot presses and pulls strong and equal Gag, cough, blink reflexes intact Patient denies numbness tingling or other paresthesia of extremities Respiratory Normal Findings: Breath sounds clear and equal in all lobes. Respirations regular, non-labored, without use of accessory muscles Mucous membranes pink Chest excursion symmetrical Trachea midline If cough present, non-productive Sputum clear or absent Cardiovascular Normal Findings: Regular rhythm, heart sounds S1 S2 present Blood pressure baseline Denies chest pain Periorbital, sacral, pedal & generalized edema absent Skin warm & dry to slightly moist Nail beds pink, capillary refill< 3 sec Peripheral pulses palpable or present with doppler Skin Normal Findings: Color normal for ethnicity Temperature warm, dry to slightly moist Turgor normal, mucous membranes moist Skin intact without breakdown, rash, redness Describe your findings: Patient denies any dizziness and nausea at this time. Pupils are both 5mm in size, equal, round, reactive to light with constriction to 3mm. Mini- cog assessment was performed with patient verbalizing 3 words, filling out the clock correctly, and repeated 3 words mini- cog score of 5/5. GSC shows Spontaneous opening of eyes obeyed verbal commands conversed oriented GCS score 15 Describe your findings: Normal heart and lung sounds anterior and posterior Describe your findings: Normal findings on auscultation Describe your findings: Skin intact with normal elasticity Wounds Normal Findings: Edges approximated and clean Surrounding tissues free from signs & symptoms of infection Dressing dry & intact: drainage absent IV Site (If applicable) Peripheral IV: Site Size Date Inserted Fluids infusing yes/ no • Type • Amount If no fluid, last time flushed Central Access Device: • Type of Device • Date inserted Fluids infusing- yes/no Type Amount Mobility/Functional Ability Normal Findings: Active ROM of all extremities within physical limitations Tolerates prescribed activity order If ambulatory, gait steady Able to complete ADL's Able to transfer (with/without assistance) List assistive device(s) Determine if assistive devices are used correctly Neurovascular assessment for client with cast or traction GU/Elimination Normal Findings: Urine clear, straw to amber no unusual odor Urine output within established parameters Bladder non distended Continent or incontinent of urine If urinary devise is used, list (indwelling urinary catheter, external female catheter, condom catheter, suprapubic catheter, straight catheter) Wounds: (yes/no?) Findings: NO IV/ Central line (yes/no?) Describe your findings: IV intact and patent Right hand 18 gauge 9/1/2022 Lactated Ringers 84 ml/hr Describe your findings: Limited ROM reduced muscle strength unable to move or transfer independently Patient has a walker and cane that she does not use Gait unsteady Describe your findings: Patient is continent uses bedpan due to hip fracture Output: 600ml Psycho-Social Normal Findings: Participates in two way conversation, care and treatment plan Able to communicate his/her needs Coping mechanisms intact (client and family) Mood/affect/behavior appropriate to situation Assess client’s definition of health Assess client’s understanding of current illness What are the client’s resources for healthcare access, access to housing and food, ability to afford medications/ services and transportation to follow-up and future healthcare visits? Pain, Comfort, Rest and Sleep Normal Findings: Rates pain ( may use numeric scale 1-10, WongBaker faces pain scale, FLACC scale, CRIES scale, color analog scale, etc) States and appears rested Rests/sleeps during shift Slept well during night Obstetrics (If applicable) Assess Maternal status Description of uterine activity Assessment of Fetal status Description of findings on vaginal exam, if performed, including cervical dilation and effacement, fetal station, change in status of membranes, and progress since last exam Postpartum (If applicable) Describe your findings and identify scale used: Initial pain was 8/10 the pain decreased to 2/10 after pain medication given Describe your findings: Post Hysterectomy 20 years Describe your findings: N/A Assess Postpartum status Assess the breasts Assess Uterus (firm or boggy) What is the fundal height Is there bleeding (color and presence of clots) Inspect the dressing and incision if C- Section Assess Lochia (color, amount, number of pads used) Inspect the episiotomy ( redness or drainage) Has the client voided (amount, color) Has the client had a bowel movement Assess bonding Newborn Assessment (If applicable) Describe your findings: Socially withdrawn Assess Newborn status APGAR ( Appearance, pulse, grimace, activity and respirations) Weight/Length Head and abdominal circumference Skin (color, texture, nails, presence of rashes) Head and neck (molding) Fontanels Genitals and anus (passage of urine and stool) Describe your findings: N/A Pediatric Assessment (If applicable) Safety: Describe your findings: Describe your findings: N/A Assess Pediatric status Assessment triangle (general appearance, work of breathing and circulation of the skin) Psychological, psychosocial and physical development aligned with age Normal Findings: The physical environment is safe. • Physical layout of client area • Alarms • Bed, IV If Restraints used : Describe care Normal findings call bell within reach Current order for restraints Identify Focal Stimuli (Focal stimuli, according to Roy (1983) are those stimuli that immediately confront the individual in a particular situation. Example: Individual needs, the level of family adaptation, and changes in the family environment. Patient lives alone and is socially withdrawn. Struggles with independence and refuses help from family members Identify Contextual Stimuli (Contextual stimuli, according to Roy (1983) are internal or external factors that influence the ability to respond to the focal stimulus and contribute directly to adaptation but are not the focus of attention and energy.) Example: Other stimuli that may influence the situation- Coping mechanisms, diagnosis, symptom severity and co-morbidities. History of osteoporosis unsteady gait recent dizzy spells Identify Residual Stimuli (Residual stimuli, according to Roy (1983) are the additional environmental factors present within the situation but whose effect on the client is unclear. Example: Beliefs, behaviors and personal experiences. Age, weak bones, refusing to use assistive devices, resistive to assistance Diagnostic Testing/Laboratory Data (CBC, UA, Chemistry, Drug levels, Cultures, X-Rays, CT, MRI, etc.) HTC 42% WBC 18 Platelets 195 X-rays show left intertrochanteric hip fracture Teaching Needs Identified during the assessment (Behavior & Stimuli): Assessment of readiness to learn will be completed as part of the Teaching Plan. What teaching was reinforced during interactions with the client? Use of walker and cane / Dietician consulted SBAR Report Situation Patient having bouts of dizzy spells with an unsteady gait Patient had a fall resulting in a left hip fracture Background History of osteoporosis patient lives alone and refuses help from family Assessment Poor nutritional values patient feels loss of independence and refuses to use assistive devices Recommendation Consultation with a dietician and rehabilitation and provide information for social groups geared to patients age Professional Nursing Care Plan The following table provides information to utilize in developing your nursing care plans. Each column in the care plan form should include the appropriate information related to the Nursing Diagnosis. You are expected to develop 3 Nursing Diagnoses with the supporting documentation as noted on the page below. The Nursing Diagnoses are then labeled in priority order where 1 would be the highest priority. (Nursing Diagnosis Priority # ) Any questions that you have concerning the nursing care plans should be directed to your instructor. (I) Data Collection Related to the Nursing Diagnosis Subjective (Nonobservable) Objective (Observable) Subjective data should be clear, concise and specific to the Nursing Diagnosis Objective data should be clear, concise and specific to the Nursing Diagnosis Subjective Data: Objective Data : What the patient or family relates, states, or reports. (Nonobservable) What is observed or measured. May include the client’s behavior, vital signs, lung sounds, urine output, laboratory data, diagnostic testing (etc.) as related to the specific nursing diagnosis. (Observable) 1. 2. 3. 4. (II) Complete NANDA Nursing Diagnosis (IV) Nursing Interventions (V) Scientific Rationales Best Evidence with References (VI) Evaluation of Patient Goals/ Outcomes Choose a NANDA approved diagnosis. The statement should list only one diagnosis and listed in the following format, i.e., problem followed by "Related to (R/T) the disease process Manifested by: (signs and symptoms) is not part of nursing diagnoses and should be written as a separate line. Example: Coping, ineffective family: R/T Temporary family disorganization and role changes. Manifested by significant other's limited personal communication with client. Each statement should be supported by a rationale Should be: 1. Concise 2. Clear 3. Specific 4. Individualized 5. Accomplishable to client and/or family, significant other. 1. Rationale should address how interventions are going to solve the problem and/or attain the outcomes. 2. Rationale should be specific to the interventions, i.e., why giving morphine 10 mg IV, why the client is being turned and positioned in proper alignment every 4 hours. 3. Rationale can be summarized in own words and/or quoted verbatim from sources. 4. For every nursing intervention, there needs to be a rationale. Should address: 1. If the expected revised, state how would revise intervention. 2. What was the client's response to interventions? (III) Goals/Outcomes (Long and Short term) Including timelines/timeframes 1. Could have both short term and long term outcomes throughout Nursing Care Plan (NCP), but each client should have one long term goal as part of the NCP. Definitions: Short-term goals: Those goals that are usually met before discharge or before transfer to a less acute level of care. Long-term goals: Those goals that may not be achieved before discharge but require continued attention by client and/or significant others as indicated. 2. Each diagnosis, if appropriate, could have short-term goals and long-term goals. 3. Statements: Specific - relates to nursing diagnosis. Measurable - tells what to see, hear, or smell. Achievable - realistic for patient. Clear and Concise - don't use “increase” or “decrease” without giving baseline range of data. 4. Timelines (timeframes) for achievement of goals: Should be realistic and specific. Give a date or time at which the expected outcome and nursing interventions are achieved and/or evaluated. Should specific as "by discharge date" or "on going." Student Name: Allyson Simmons Client Code: Full Code Instructor: _____Mrs. Loesch ___________________________ Date: 9/30/2022 Nursing Diagnosis Priority # Grade: Professional Nursing Care Plan (I) Data Collection Related to the Nursing Diagnosis Subjective (Non-observable) Unable to move or transfer independently Difficulty using the incentive spirometer (II) Complete NANDA Nursing Diagnosis (IV) Nursing Interventions Objective (Observable) Vital signs B/P 130/80 Temp 97.2 SPO2 94% at room air HR 85 bpm Capillary refill 2 sec Pedal pulses within normal limits Impaired Physical Mobility Risk for impaired gas exchange Teach patient or assist with active and passive ROM exercises Encourage the use of isometric exercises of affected and unaffected extremities Assist with incentive (III) Goals/Outcomes spirometer (Long and Short term) Including timelines/timeframes Patient will regain mobility at the highest possible level by 10/5/2022 Patient will Maintain position of function by 10/5/2022 Patient will be successful using the incentive spirometer by 9/31 (V) Scientific Rationales Best Evidence with References Increase blood flow to muscles and bone to improve Muscle tone, preserve joint mobility, and to prevent contractures or atrophy Isometrics contract muscles without bending joints or moving limbs and help maintain muscle strength and mass Increases available supplemental oxygen for optimal tissue oxygenation (VI) Evaluation of Patient Goals/ Outcomes Patient able to ambulate with minimal assistance No signs or symptoms of pneumonia

