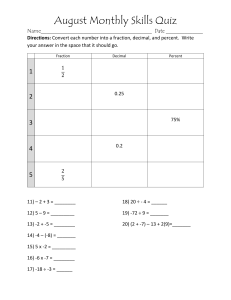
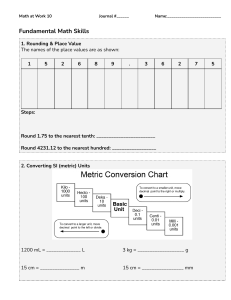
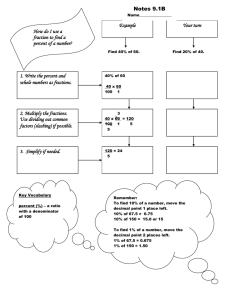
Daily Lesson Plan Technology and Livelihood Education In Mechanical Drafting G7 & G8 Quarter: Week: I. OBJECTIVES A. Content Standard B. Performance Standard C. Learning Competency/ Objectives (Write the LC code) II. CONTENT Subject matter Integration (Learning area) Strategies III. LEARNING RESOURCES A. References 1. Teacher’s Guide pages 2. Learner’s Materials pages 3. Textbook pages 4. Additional Materials from Learning Resources (LR)portal B. Other Learning Resources C. Materials IV. PROCEDURES Daily Routine Reviewing previous lesson or presenting the new lesson Day: Time allotment:60 mins. Conversion of fraction to decimal or decimal to fraction - Conversion results of fraction to decimal are accurate up to 2 decimal places. - Conversion results of decimal to fraction are accurate to the nearest standard measurement - Convert fraction to decimal and vice versa. Subtask: - Solve problems and exercises correctly in: a. converting fraction to decimal or decimal to fraction. - Solve problems and exercises correctly in: converting fraction to decimal or decimal to fraction - Show patience in solving the problem. Conversion of Fraction and Decimal. Math 4As 13 Kto12 Mechanical Drafting Learning Module pp.52-55 - Greetings - Prayer - Checking of Attendance - Arrangement of chairs - Checking of garbage under the chairs Guide questions? - Do all groups perform the activity in Storing/Keeping of drafting measuring instruments? - What problems did you encounter while doing the activity? Activity Analyze Abstraction The next lesson you will be able to apply the basic mathematical operation as what you did in Math subject Do you have an idea why you will apply the basic mathematical operation? Let us determine how much you already know about the conversion of fraction to decimal and decimal to fraction. Take this test. Directions: Convert the following. Write your answers on a separate sheet of paper. TEST I. - A. Convert fractions into decimals. 1. ¼ to decimal 2. ¾ to decimal 3. 7/16 to decimal 4. 3/8 to decimal 5. 1/8 to decimal B. Convert decimals into fractions. 6. 0.35 7. 0.24 8. 0.75 9. 0.125 10. 0.150 Check if your answers are correct by comparing them with those in the Answer Key. If you got 90-100% of the items correct, that means you already familiar with the lesson covered by Learning Outcome No. 3. However, you may still study the lesson to refresh your memory and learn new concepts. If you missed a lot of items, do all the activities to gain knowledge and skills required for mastery. CONVERSION OF FRACTION AND DECIMAL Changing Fractions to Decimals Any rational number can be changed from fractional form to decimal form. This is done by simply dividing the numerator by the denominator. Rounding Off Decimals Metric measurements in decimals are often long numbers. They must often be rounded to a convenient number of digits. In this text most metric dimensions are either whole millimeter or two-places decimals that have been rounded off. To help you round off your own calculation, rules of rounding are discussed below. 1. If the first number to be eliminated is less than 5, simply drop it (and the number to the right of it) and let the last significant digit stand. Conversion of Decimals to Fractions A decimal is changed to a fraction by using 10 or any power of 10 as denominator of the given decimal. Then change to lowest term when possible. Millimeters Equivalent of Decimals and Fractions of an Inch. Application Show that you learned something by doing this activity. After learning the procedure in converting fraction to decimal; 1. inform your teacher that you are ready to solve problems in converting metric measurement to decimal and vice versa. 2. convert the following measurements from fractions to decimal. a) 5/16 b) 1/3 c) 3/16 d) 7/8 e) 5/32 3. When you finish answering, check your work again before submitting it to your teacher for verification and recording. If your work passes the required output, you are now ready to proceed to the next activity. If not, make the necessary corrections then submit your work again. Finding practical applications of concepts Making generalizations and abstractions about the lesson Evaluation Answer key: A. 1.) . 25 2.) .75 3.) .0.4375 4.) .375 5.) .125 B. 1.) 13.76 2. )38.61 3.) 41.01 4.)8.62 5.)7.25 C. 1.) 1/5 2.) 4/5 3.) 21/25 4.) 7/50 5.) 6/25 6.) ¾ 7.) 1/8 8.) 3/20 9.) 13/20 10.) 3/8 How Much Have You Learned? Directions: A. Convert fractions into decimals. Write your answer on a separate sheet of paper. 1. ¼ to decimal 2. ¾ to decimal 3. 7/16 to decimal 4. 3/8 to decimal 5. 1/8 to decimal B. Round off the following numbers to their nearest hundredths. 1. 13.7556 2. 38.614 3. 41.009 4. 8.6245 5. 7.2532 C. Convert decimals into fractions. Write your answers on a separate sheet of paper. 1. 0.2 2. 0.8 3. 0.84 4. 0.35 5. 0.24 6. 0.75 7. 0.125 8. 0.150 9. 0.65 10. 0.375 Agreement Remarks Reflection Reflect on your teaching and assess yourself as a teacher. Think about your students’ progress this week. What works? What else needs to be done to help the students learn? Identify what help your instructional supervisors can provide for you so when you meet them, you can ask them relevant questions. A. No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation B. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation who scored below 80% C. Did the remedial lessons work? No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson D. No. of learners who continue to require remediation E. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did these works? F. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve? G. What innovation or localized materials did I use/discover which I wish to share with other teachers? JONAS D. ACASO DLP WRITER, VALENCIA NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL