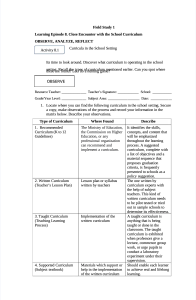
Field Study 1 Learning Episode 8. Close Encounter with the School Curriculum OBSERVE, ANALYZE, REFLECT Activity 8.1 Curricula in the School Setting Its time to look around. Discover what curriculum is operating in the school stheettsien ga.reRfeocuan lldt?heLetytspedso oaf hcuunrrtin cu glu gm amm e?entioned earlier. Can you spot where OBSERVE Resource Teacher: Teacher’s Signature: School: Grade/YearLevel: Subject Area: Date: 1. Locate where you can find the following curriculum in the school setting. Secure a copy, make observations of the process and record your information in the matrix below. Describe your observations. Type of Curriculum 1. Recommended Curriculum (K to 12 Guidelines) 2. Written Curriculum (Teacher’s Lesson Plan) 3. Taught Curriculum (Teaching Learning Process) 4. Supported Curriculum (Subject textbook) Where Found Describe The Ministry of Education, the Commission on Higher Education, or any professional organization can recommend and implement a curriculum. It identifies the skills, concepts, and content that will be emphasized throughout the learning process. A suggested curriculum, complete with a list of objectives and a material sequence that proposes graduation criteria, is frequently presented to schools as a policy suggestion. The one written by curriculum experts with the help of subject teachers. This kind of written curriculum needs to be pilot tested or tried out in sample schools to determine its effectiveness. A taught curriculum is anything that is being taught or done in the classroom. The taught curriculum is exhibited when professors give a lecture, commence group work, or urge pupils to conduct a laboratory experiment under their supervision. Should enable each learner to achieve real and lifelong learning. Lesson plan or syllabus written by teachers Implementation of the written curriculum Materials which support or help in the implementation of the written curriculum 5. Assessed Curriculum (Assessment Process) Activity 8.2 6. Learned Curriculum (Achieved Learning Outcomes) 7. Hidden Curriculum (Media) To determine the extent of teaching or tell if the students are progressing What students learned This may be partially in what is not taught inside a school's formal curriculum. Series of evaluation are being done by extent of teaching or if the student are progressing. Learning outcomes can be used to determine how competent students should be at the end of a class. A learning result can be defined by what students can do or do in their cognitive, emotional, or psychomotor domains. The test results indicate the learning outcome, which students can achieve through learning objectives. The hidden curriculum refers to the unexpected or unwanted curriculum that plays an essential role in learning. It is made up of procedures, norms, and values. See the threeminute video below for further information. ANALYZE Which of the seven types curriculum in the school setting is easy to find? Why? The K-12 curriculum is the most recent and has been adopted by DepEd; it is also the easiest to locate in a school setting when compared to the other curricula. Which is difficult to observe? Why? A curriculum that is hidden due to the fact that it is the most difficult to observe. Are these all found in the school setting? How do curricula relate to one another? The curriculum is organized in such a way that the outcomes build on one another. This ensures that students have the skills they need to succeed in the next unit or class lev Draw a diagram to show the relationship of one curriculum to the other. OBSERVE Make a reflection on the diagram that you have drawn. The authorized curriculum informs the written curriculum, and the written curriculum informs the taught curriculum. Supported curricula are comparable to taught curricula, but they typically include support sessions, labs, peer-to-peer comprehension, and other activities. The assessed curriculum is based on the written and taught curriculum. We get at the learnt curriculum after examining the written, taught, and assessed curriculum. The majority of inadvertent or unplanned curriculum is buried. However, it continues to play an important role in education. Values, standards, and processes can all be part of it. The Miniscule School Curriculum : The lesson, A closer look Teacher’s Signature: School: Grade/YearLevel: Subject Area: Resource Teacher: Date: REFLECT This activity requires a full lesson observation from Motivation ro Assessment. Procedure: 1. Secures permit to observe one complete lesson in a particular subject, in a particular grade/ your level. 2. K leseseopna close watch on the different components of the miniscule curriculum: the 3. Follow the three major components of a curriculum (Planning, Implementing and Evaluating/Assessing). Observe and record your observation. Observe and Record Observation on the Following Aspects Major Curriculum Components A. Planning Key Guide for Observation (Carefully look for the indicators/behavior of the teacher along the key points. Write your observation and description in your notebook.) 1. Borrow the teacher’s lesson plan for the day. What major parts so you see? Request a copy for your use. Answer the following questions: a. What are the lesson objectives/learning outcomes? Use simple present tense of verbs in a sentences. Appreciate the use of simple present tense b. What are included in the subject matter? Simple Present Tense of Verbs c. What procedure or method will the teacher use to implement the plan? She uses teaching centered approach d. Will the teacher assess or evaluate the lesson? How will this be done? B. Implementing By precise execution of the lesson plan, finding truthful and trustworthy references on the internet, and by her confidence. Now its time to observe how the teacher implemented the prepared lesson plan. Observe closely the procedure. a. How did the teacher begin the lesson? She goes over the daily routines with the students. The teacher first requested one of the students to lead the prayer. Then inquired of the monitor about her classmates' attendance. She then went through the lesson she had covered the day before. b. What procedure or steps where followed? The Developmental activities follow the Preliminary activities (daily routines, review, incentive, and greetings). c. How did the teacher engaged the learners? The teacher started witha motivation activity for students as a warm up for their background knowledge. d. Was the teacher a guide at the side? Yes e. Where the learners on task?/Or were they participating in the class activity? They're both focused on their work and participating in class activities. f. Was the lesson finished within the class period? The teacher are 5 minutes advance to end the class period. C. Evaluating/Assessing Did learning occur in the lesson taught? Here you make observations to find evidence of learning. a. Were the objectives as learned outcomes achieved? Indeed b. How did the teacher assess/evaluate it? Short quizzes are used to assess students. c. eviden Wh ce was at shown? Get pieces of evidence? The answer sheet of the students. ANALYZE Write a paragraph based on the data you gathered using these key questions? How does the teacher whom you observed compare to the ideal characteristics or competencies of global quality teachers? The instructor is showing off his ability to "engage students in learning about the world and their position in it." 1. Was the lesson implemented as planned? Describe. Yes, due to the pupils' cooperation and the teacher's trust in her ability to carry out the plan and it's orderliness of the discussion.. 2. Can you describe the disposition of the teacher after the lesson was taught? Happy and eager? Satisfied and contented? Disappointed and exhausted? Satisfied and contented because the students already cope up the lesson 3. Can you describe the majority of student’s reactions after the lesson was taught? Confused? Happy and eager? Contented? No reactions at all. Happy and eager because they already know how to proper used of simple present tense of verb in a sentence. Based R onEy oT bservations and tasks in Activity 2 how will you prepare your lesson Fo LuErC plan? Make a short paragraph on the topic. It takes time, effort, and knowledge of your students' goals and abilities to create an effective lesson plan. The goal is to encourage students to absorb and remember as much knowledge as possible, as is the case with all instruction. First, decide what you want to accomplish. At the start of each lesson, make a note of your lesson plan aim. It should be quite easy to understand. It's essentially what your students will be able to do once y woaun'tvetofignoisthheedatdedaicthioingalth meim le!(D thersocurgibhevhidoewo,thgeaymm esi,gehttcg.)o. about it if you Activity 8.3 Constructive Alignment of the Components of a Lesson Plan Resource Teacher: Teacher’s Signature: Grade/YearLevel: School: Subject Area: Date: OBSERVE Using the diagram below fill up the component parts of a lesson plan I. II. III. Title of the Lesson: Simple present tense of verb Subject area: English Grade Level: 7 o Outcomes Use simple present tense of verbs in a sentences. Appreciate the use of simple present tense Assessment Teaching Method There will be lectures and discussion , then group activity.. Short quiz with only a few questions are given throughout the session and are graded. ANALYZE Answer the following questions based on the diagram. 1. Are the three components constructively aligned? Explain. Yes, since the instructor establishes the learning objectives first, then implements them using a teaching and learning-centered approach. The teacher then conducts an activity bee for groups of pupils to test their lem dgees b oef tahcehim ali.th the teaching methods used? Why? 2. Will thekn oo uw tco evaetedriw A teaching method refers to the concepts and procedures that teachers use to help students learn. The subject matter taught, impact the students and it can be observed in the students accessment in their short quiz and group activity. 3. What component would you tell if the outcomes have been achieved? In the assessment, the students' evaluations are used. REFLECT What lessons have you learned in developing or writing a lesson plan? It usually includes a goal (what students should learn), a method for achieving the goal (delivery and procedure), and a system for determining if the objective was reached (usually through homework assignments or testing). Learning outcomes, learning activities, and assessments are all part of a lesson plan. What value will it give to the teacher if the three components are aligned? The alignment of activities and assessments helps students focus on abilities that are relevant to the learning objectives, reducing wasted time. Link theory to practice Choose the correct answer from the options given. 1. When we say school curriculum it refers only to the K to 12 curriculum. A. This statement is True. B. This statement is not True. C. This statement is half True. D. This statement is silly. 2. A professional teacher should possess the following skills to address the need for a curricularist EXCEPT one. Which one is NOT? A. Knower of the curriculum B. Believer of the curriculum C. Implemented of the curriculum D. Writer of the curriculum 3. The influence of multimedia, peers, community, tradition, advancement in technology, though not deliberately taught in the lesson, will influence the curriculum. This is referred to as . A. Written curriculum B. Recommended curriculum C. Implemented curriculum D. Hidden curriculum 4. Which two components of the lesson plan (as a miniscule curriculum) should be aligned? I. Outcomes and Assessment II. Assessment and Teaching Methods III. Outcomes and Teaching Methods A. I only C. III only B. II only D. I, II, and III 5. What is the most important reason why there should be constructive alignment of the components of the curriculum? A. For ease of correcting by the school principal. B. To assure that each component contributes to the attainment of the learning outcomes. C. As a required template when starting to write a lesson plan. D. As a model of other lesson plans written and published. SHOW Your Learning Artifact Learning Artifacts for Activity 1-3 Present an artifact for Activity 1, 2, and 3. Activity 1 Artifact 1. Present an evidence for each kind of curriculum operating in the school setting. This can be in pictures, realia, documents or others. Activity 2: Artifact 1. Present a sample curriculum in a form of a Lesson Plan. Activity 3: Artifact 1. Present a matrix to show the constructive alignment of the three components of a lesson plan. a. Example: IV. Lesson Title: Simple Present Tense of Verb Subject Area: English Grade Level: 7 Lesson Outcomes Teaching Methods Evaluation Use simple present tense of verbs in a There will be lectures and Short quiz with only a few sentences. Appreciate the use of simple present tense discussion, then group activity. questions are given throughout the session and are graded.