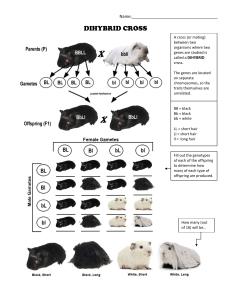
Biology 30: Unit 3 Name: _________________________ Mark: ____ / 30 Genetics Quiz Multiple Choice: Please answer the following questions on the scantron sheet provided. 1. Among Mendel’s laws is inheritance is the law of segregation which states: a. genes are carried in pairs and separate during meiosis to be distributed into different sex cells. b. the dominant form of a trait will appear in every generation. c. The probability of two or more independent events occurring together is the product of the individual probabilities. d. members of different pairs of genes behave independently during meiosis. 2. A gene exists in two different forms (A and a). If an individual is homozygous recessive, which type(s) of gametes can it produce? a. Aa c. a b. A d. A and a 3. If the genotype of the parents are SS and ss, then the F2 will be a. All Ss c. ½ ss and ½ Ss b. ½ Ss and ½ SS d. ¼ SS, ½ Ss and ¼ ss 4. Familial intestinal polyposis results in multiple finger-like growths (polyps) from the lining of the large intestine. It is inherited as a dominant trait. Let N represent the allele producing polyps and n represent the normal allele. One parent is Nn and the other nn. If the couple has 4 children, how many would be expect o have the familial polyposis phenotype? a. 1 c. 3 b. 2 d. 4 5. If ¾ of the offspring from any experimental cross showed only the dominant phenotypic characteristics, the parents of those particular offspring were a. Both homozygous dominant b. Both heterozygous c. One homozygous dominant, one homozygous recessive d. One heterozygous, one homozygous dominant 6. If an organism of genotype AA mates with an organism of genotype Aa and 150 offspring were produced, the number of offspring with the genotype Aa will be closest to a. 120 c. 30 b. 70 d. 0 7. The ratio 9:3:3:1 usually results from a a. dihybrid cross and is the genotypic ratio b. dihybrid cross and is the phenotypic ratio c. monohybrid cross and is the genotypic ratio d. monohybrid cross and is the phenotypic ratio Use the information below to answer the following two questions. BS BS Q Bs U bS Y bs H Bs R V Z I bS S W F J bs T X G K Black hair (B) is dominant to white hair (b), and straight hair (S) is dominant to curly hair (s). Each pair of alleles sorts independently. Letters in the Punnett square represent offspring. 8. The phenotype of organism “K” would be a. black straight hair b. black curly hair c. white straight hair d. white curly hair 9. The individual showing only one recessive trait is a. U b. H c. Z d. F 10. Incomplete dominance occurs when a. one gene prevents the expression of another gene b. one gene is masked by the presence of another gene c. a mixture of traits is expressed when the genes occur together d. the traits occur randomly when the genes occur together 11. In short-horned cattle, if a red bull (RR) is crossed with a white cow (WW), all the offspring are roan (RW) (calf has white & red hair). A cross between 2 roans should yield offspring in the ratio of a. 3 white : 1 red c. 1 red : 2 roan: 1 white b. 3 red : 1 white d. 3 roan : 1 white 2 12. A certain strain of Drosophila raised at 25⁰C have curly wings. If they (P1) are allowed to breed at 16⁰C, the wings of the offspring (F1) will be straight. If the offspring are returned to 25⁰C and allowed to breed, the next generation (F2) will have curly wings. This is an example of a. sex-linked characteristics b. codominance c. influence of the environment on genetic traits d. Pleiotrophic genes 13. In humans, what is the probability that a couple’s first child will be a boy, and that their second child will be a boy, respectively? a. 1 and ½ c. ½ and ½ b. ¾ and ¼ d. ½ and ¼ 14. A female with blood type AB and a male with blood type O have several children. The phenotypic ratio for these children would be a. ½ type A and ½ type B c. ¼ type O, ½ type AB and ¼ type A b. ½ type AB and ½ type O d. ¼ type O and ¾ type A 15. ABO blood type is controlled by how many genes in any one individual? a. one c. three b. two d. four 16. A particular sex-linked recessive disease in humans is usually fatal. Suppose a man with the disease and a woman heterozygous for the trait have a daughter. What is the probability that the daughter will have the disease? a. 0 c. 0.50 b. 0.25 d. 1 17. Based on the following combination frequencies, determine the order of the genes along the chromosomes. A-B = 14 map units; A-C = 17 map units; A-D = 6 map units; B-C = 31 map units, and B-D = 8 map units. a. A-C-D-B c. B-A-C-D b. C-A-B-D d. C-A-D-B 18. In fruit flies, gray body (B) is dominant over black body (b). Two gray flies were mated and produced 158 gray flies and 49 black flies. The parents genotype was a. BB x BB c. BB x Bb b. Bb x Bb d. Bb x bb 19. A man who carries a sex-linked gene on his Y chromosome will transmit this gene to a. ½ of all his male offspring c. all of his female offspring b. ½ of his female offspring d. all of his male offspring 3 20. Meiosis can produce gametes with a. new combinations of chromosomes b. variation c. half the chromosomes of the parent d. all of the above Short Answer: Please answer the following questions on this sheet. 1) You are a genetics researcher and study inheritance patterns in Drosophila (fruit flies) to map genes. When you breed flies heterozygous for both wing length (A long) and body color (B gray) with a test cross fly (vestigial-winged, black-bodied), you obtain the following results: /5 702 705 long winged and gray bodied vestigial winged and black bodied 45 30 long winged and black bodied vestigial winged and gray bodied Based on the data above, answer the following: a) State the genotypes of the 2 parents: _________________ x __________________ b) What are the likely genotypes of the following offspring: __________________ ____________________ _______________________ long wing/black body – vestigial wing/gray body – vestigial wing – black body 2) In Martians, one gene is responsible for antennae. Martians who are homozygous recessive (aa) have no antennae, whereas those carrying the dominant allele (A) have antennae. A separate gene is responsible for the size of their eyes. The dominant allele (B) results in bulging eye, while the homozygous recessive genotype (bb) results in normal-sized eyes. A Martian homozygous for both bulging-eyes and antennae is mated to a Martian with normal eyes and no antennae. a) What are the genotypes of the parents? (1 mark) b) In the F1 generation, what is the chance of a baby Martian having bulging eyes and antennae? (1 mark) /5 c) What would be the genotypes of the individuals you would cross to get the F2 Generation? (1 mark) d) In the F2 generation, what is the chance of getting a Martian with bulging eyes and antennae? (2 marks) 4