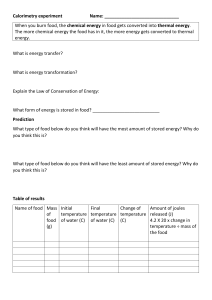
Forms of Energy Student Notes I. What is Energy? A. Energy is the ability to cause change. B. Energy moves from one place to another. C. Different things can happen due to different forms of energy. II. Kinetic Energy A. Kinetic energy – the energy of motion. III. Thermal Energy A. Heat (q) – the energy transferred when a change in temperature occurs. i. Unit is joules, J B. Thermal energy – the energy due to the random movement of particles. i. Heat cannot be directly measured, but temperature can. C. Temperature – a measurement of the average kinetic energy of particles. i. Change in temperature indicates transfer of thermal energy. IV. Potential Energy A. Potential energy – the energy stored due to physical position, electrical charge, or chemical composition. B. Potential energy can be converted to kinetic energy when stored energy is released. V. Chemical Energy A. Chemical energy – the energy stored in chemical bonds (AKA chemical potential energy). B. Chemical potential energy can be converted into different forms of energy. VI. Other Forms of Energy A. Light Energy is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye. B. Electrical Energy is energy available from the flow of electrical charges. C. Sound Energy is energy associated with the vibration or disturbance of matter. D. Nuclear Energy is energy release from the fusion or fission of the nucleus of an atom. E. Solar Energy is radiant energy from the sun. F. Gravitational Potential Energy is stored by objects that are above Earth’s surface. G. Elastic Potential Energy is energy stored by something that can stretch or compress. VII. Conservation of Energy A. Law of Conservation of Energy – the law that states that energy cannot be created or destroyed i. Based on principle that there is a fixed amount of energy in the universe. B. Energy of a system plus the energy of the surroundings equals the total energy of the universe i. System – the substance(s) undergoing chemical or physical change ii. Surroundings – everything in the universe except the substance(s) undergoing a chemical or physical change C. Energy can be converted from one form to another D. Example: In a power plant, chemical potential energy stored in the coal is converted into electrical energy. E. Example: When an explosive detonates, chemical potential energy is converted into heat, light, motion, and sound. Forms of Energy Student Notes I. What is Energy? A. Energy is the ability to cause change. B. Energy moves from one place to another. C. Different things can happen due to different forms of energy. II. Kinetic Energy A. Kinetic energy – the energy of motion. III. Thermal Energy A. Heat (q) – the energy transferred when a change in temperature occurs. i. Unit is joules, J B. Thermal energy – the energy due to the random movement of particles. i. Heat cannot be directly measured, but temperature can. C. Temperature – a measurement of the average kinetic energy of particles. i. Change in temperature indicates transfer of thermal energy. IV. Potential Energy A. Potential energy – the energy stored due to physical position, electrical charge, or chemical composition. B. Potential energy can be converted to kinetic energy when stored energy is released. V. Chemical Energy A. Chemical energy – the energy stored in chemical bonds (AKA chemical potential energy). B. Chemical potential energy can be converted into different forms of energy. VI. Other Forms of Energy A. Light Energy is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye. B. Electrical Energy is energy available from the flow of electrical charges. C. Sound Energy is energy associated with the vibration or disturbance of matter. D. Nuclear Energy is energy release from the fusion or fission of the nucleus of an atom. E. Solar Energy is radiant energy from the sun. F. Gravitational Potential Energy is stored by objects that are above Earth’s surface. G. Elastic Potential Energy is energy stored by something that can stretch or compress. VIII. Conservation of Energy A. Law of Conservation of Energy – the law that states that energy cannot be created or destroyed i. Based on principle that there is a fixed amount of energy in the universe. B. Energy of a system plus the energy of the surroundings equals the total energy of the universe i. System – the substance(s) undergoing chemical or physical change ii. Surroundings – everything in the universe except the substance(s) undergoing a chemical or physical change C. Energy can be converted from one form to another D. Example: In a power plant, chemical potential energy stored in the coal is converted into electrical energy. E. Example: When an explosive detonates, chemical potential energy is converted into heat, light, motion, and sound.