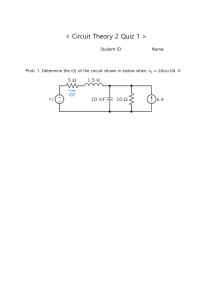
Electrical Circuit Theory (1) First Year Electrical Engineering : Presented by Dr. Eltaib Ibrahim IEEE Member 1 Course objectives • Introduction about Electrical Circuit The electric circuit is a mathematical model that approximates the behavior of an actual electrical system. As such, it provides an important information for learning-in your later courses and as a practicing engineer. the details of how to design and operate systems such as those just described. The models, the mathematical techniques, and the language of circuit theory will form the framework for your future engineering skills. 2 Course objectives • Understand the main basic of electrical circuit • To measure circuit parameters; power, energy, voltage and current • To understand DC circuit analysis • To understand AC circuit analysis • To measure the impedance circuit • To have the basic concept of magnetic element • To gain the student for the next course material of electrical circuit 2 3 Course contents ❑ Circuit variables, elements and simple resistive circuits ❑ Techniques of DC circuit analysis and DC Circuit Theorems ❑ Inductance and capacitance and mutual inductance ❑ AC circuit and steady state analysis ❑ Techniques of AC circuit analysis and AC Circuit Theorems ❑ Transformer ❑ Steady state power calculation ❑ Introduction about three phase circuit ❑ Introduction about resonance circuit ❑ Introduction about magnetic 4 This week ❑ Circuit variables, elements and simple resistive circuits ❑ Techniques of DC circuit analysis and DC Circuit Theorems ❑ Inductance and capacitance and mutual inductance ❑ AC circuit and steady state analysis ❑ Techniques of AC circuit analysis and AC Circuit Theorems ❑ Transformer ❑ Steady state power calculation ❑ Introduction about three phase circuit ❑ Introduction about resonance circuit ❑ Introduction about magnetic 5 International system of units ❑ Units ❑ References: ❑ James W. Nilsson- Susan A. Riedel “ Electric circuits” 8th edition Pearson Education 6 Techniques of DC circuit analysis ❑ Describing circuit ▪ • • • • Describing Node Voltage Example Node Voltage and dependent source Special cases 7 Techniques of DC circuit analysis ❑ Describing circuit ▪ • • • • Describing Node Voltage Example Node Voltage and dependent source Special cases 8 Techniques of DC circuit analysis ▪ • • • • Describing Node Voltage Example Node Voltage and dependent source Special cases 9 Techniques of DC circuit analysis ▪ • • • • Describing Node Voltage Example Node Voltage and dependent source Special cases 10 Techniques of DC circuit analysis ❑ Example ▪ • • • • Describing Node Voltage Example Node Voltage and dependent source Special cases 11 Techniques of DC circuit analysis ❑ Example ▪ • • • • Describing Node Voltage Example Node Voltage and dependent source Special cases • That the circuit has two essential nodes; we need to write a single node voltage • Select the lower node as the reference node • define the unknown node voltage as V1 12 Techniques of DC circuit analysis ❑ The Node-Voltage Method and Dependent sources ▪ • • • • Describing Node Voltage Example Node Voltage and dependent source Special cases 13 Techniques of DC circuit analysis ❑ The Node-Voltage Method : some special cases there is only one unknown node voltage (V2). Solution of this circuit ▪ • • • • thus involves only a single node voltage equation at node 2. Describing Node Voltage Example Node Voltage and dependent source Special cases 14 Techniques of DC circuit analysis ❑ The Node-Voltage Method : some special cases ▪ • • • • Describing Node Voltage Example Node Voltage and dependent source Special cases 15