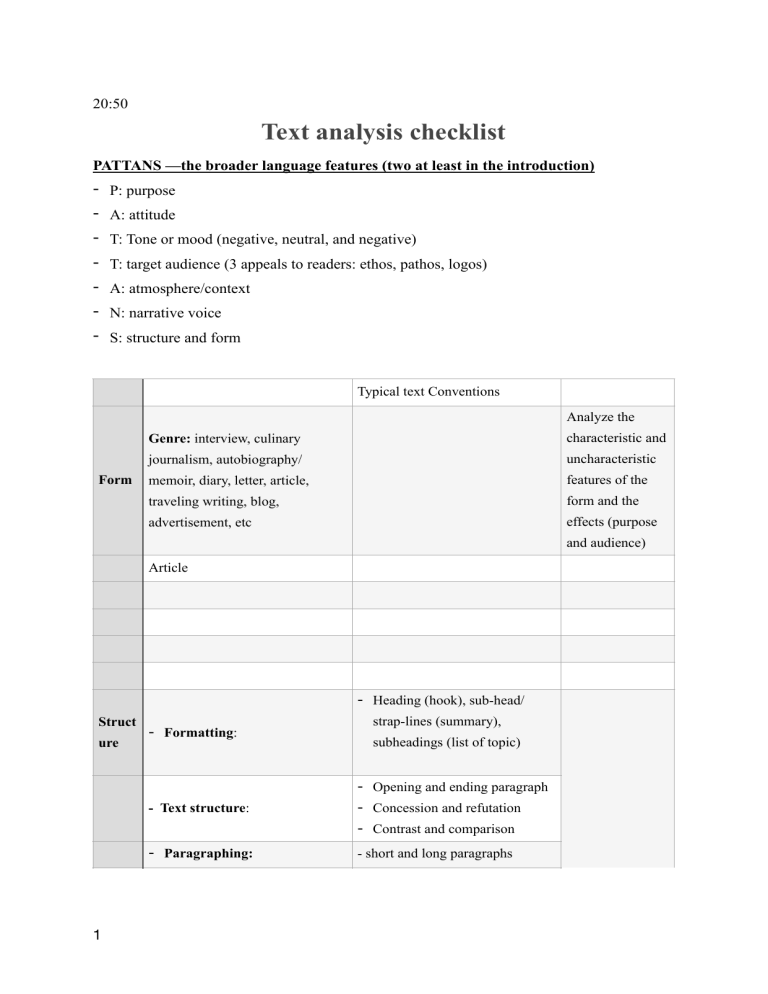
20:50 Text analysis checklist PATTANS —the broader language features (two at least in the introduction) - P: purpose A: attitude T: Tone or mood (negative, neutral, and negative) T: target audience (3 appeals to readers: ethos, pathos, logos) A: atmosphere/context N: narrative voice S: structure and form Typical text Conventions Analyze the Form Genre: interview, culinary characteristic and journalism, autobiography/ uncharacteristic memoir, diary, letter, article, features of the traveling writing, blog, form and the advertisement, etc effects (purpose and audience) Article - Heading (hook), sub-head/ Struct ure 1 - Formatting: strap-lines (summary), subheadings (list of topic) - Text structure: - Opening and ending paragraph - Concession and refutation - Contrast and comparison - Paragraphing: - short and long paragraphs - Transition: - progress of an argument (flow of ideas) - Patterns in tone Analyze the - chronologically, non- Sequence: features and the chronologically, forwards in specific and time, backwards in time, overall effects flashback. - shift - on focus/time/space/perspective - Syntax: sentence type/form, sentence variety, sentence Lang uage structure, including punctuation - Diction: vocabulary (part of speech, jargon, colloquialism) - Figurative language: figure of speech, imagery Summary of key points for an effective analysis • • • • • 1) Get the overview of the given text • What overall view or sense of the text do you get from reading it? • Is there a speci c message or core theme/ motif? 2) Identify the distinctive features of form, structure and language • What do you notice about the language used (e.g. voice and lexis)? • What do you notice about the form, structure, patterns and chronology? 3) Focus on effects • What speci c effects do these choices of form, structure and language have? • Why have these speci c words, phrases or structures been chosen? • Are they positive, negative, or neutral in their effect? 4) Explain, explore and evaluate • What is the reader told explicitly? • What is revealed or what can be inferred? (What do we have to guess about?) • What valid interpretations can be made? 5) Check for changes or contrasts • 2 Is the text consistent in its message, or in the mood or tone conveyed? • Are there shifts in tone or focus? • If it does change, where does it happen structurally? • Are there elements in the text that are ambiguous, or that contrast or contradict each other? Tips of writing structure: - 5 or 6 paragraphs commentary, including the introduction and conclusion - 10 to 12 annotations (broad coverage of the whole contexts ), 2 or 3 in each paragraphs - Use accurate terminology: annotations into syntax, diction, figurative languages, audience appeals (ethos, pathos, logos) - Introduce effect-statements, effects on meaning, style, purpose, and readers. 2 or 3 comments on characteristic and uncharacteristic features of form 2 or 3 comments on overall structure PEEEE (Point, evidence about form, structure and language, explanation of denotation, exploration of connotation/implication and evaluation its specific and overall effects). 3