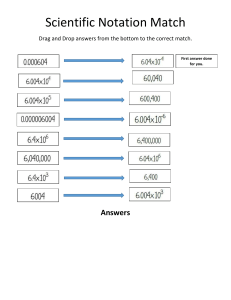
General Physics 1 First Quarter Name of Learner: ______________________________ Grade Level: __________________ Section: ______________________________________ Date: ________________________ Week: _____________ Address: _______________________________________________________________________________________ Date of Release: _______________________ Date of Submission: ______________ Date Received_______________ LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET NO. ______ Topic: Scientific Notation and Units I. Background Information for Learners Measurement- A quantitative observation Consists of 2 parts Number Unit – tells the scale being used A. Scientific Notation- Very large or very small numbers can be expressed using scientific notation. The number is written as a number between 1 and 10 multiplied by 10 raised to a power. The power of 10 depends on • The number of places the decimal point is moved. • The direction the decimal point is moved. • Left Positive exponent • Right Negative exponent Representing Large Numbers Representing Small Numbers To obtain a number between 1 and 10 we must move the decimal point. 0.000167 = 1.67 10−4 B. Units Units provide a scale on which to represent the results of a measurement. • There are 3 commonly used unit systems. • English • Metric (uses prefixes to change the size of the unit) • SI (uses prefixes to change the size of the unit) C. Measurements of Length, Volume and Mass • Volume Amount of 3-D space occupied by a substance Fundamental unit is meter3 (m3) • II. Mass Quantity of matter in an object Fundamental unit is kilogram Learning Competency with Code Solve measurement problems involving conversion of units, expression of measurements in scientific notation (STEM_GP12EU-la-1) III. Objectives/Learning Targets 1. Convert numbers into scientific notation; 2. Express length, Mass, time in SI units. 3. Solve Unit Conversion problems Detailed Directions/Instructions Read the instructions and answer the attached activities. Exercise/Activities 1. Activity 1 – Scientific Notation (45 min.) 2. Activity 2 – Conversion of units (45 min) 3. Activity 3 – Practice Solving (45 min) IV. V. VI. Rubric for Scoring Understanding (R)-1. Accuracy (A)-1. Evidence (C)-1. Explain (E)-1. Demonstrate understanding of the question. The student understood the question. The student answered the question accurately using factual information. The student use specific evidence to back-up answer. The student explains the answer thoroughly and logically. The student provides enough information to back-up the answer in a way that makes sense. Total of 4 points (can also be 1⁄2 for a total of 2) VII. VIII. Values Integration References/s for Learners www.boyertownasd.org Google.com https://chapworksheetfall.org ____________________________________________ Signature of Student ____________________________________________ Name and Signature of Parent/s Guardian Note: You can attach additional sheets if necessary Activity 1 Scientific Notation and Conversion of Units Worksheet – Scientific Notation Name: ________________________________________________Section: _______________ Date: ____________ I. Instruction: Convert the following numbers into scientific notation. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. II. 3,400 _______________________________ 0.000023 ____________________________ 101,000 _____________________________ 0.010 _______________________________ 45.01 _______________________________ 1,000,000 ___________________________ 0.00671 _____________________________ 4.50 ________________________________ Instruction: Convert the following numbers into standard notation: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. III. 2.30 x 104 _______________________________ 1.76 x 10-3 _______________________________ 1.901 x 10-7 ______________________________ 8.65 x 10-1 _______________________________ 9.11 x 103 _______________________________ 5.40 x 101 _______________________________ 1.76 x 100 _______________________________ 7.4 x 10-5 _______________________________ Instruction: Rewrite the following numbers in scientific notation, in simplest form. Include units. Use appropriate significant figures. 1. Altitude of summit of Mt. Ka‘ala (highest point on O‘ahu): 4020 ft = 2. Altitude of summit of Mauna Kea: 13,796 ft = 3. Thickness of a human hair: 0.015 cm = 4. Wavelength of reddish light: 0.0000007 m = 5. Height of your instructor: 1.80 m = 6. Number of galaxies in the universe: 1 trillion galaxies = 7. Age of the universe in seconds: 430,000,000,000,000,000 s = 8. Volume of a hydrogen atom: 0.000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 621 cm3 = IV. Instruction: --How many sig figs are in each of the following examples: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 926.9 707 123.06 0.0402 0.82610 338.00 Activity 2 Scientific Notation and Conversion of Units Worksheet – Conversion of Unit Name: ________________________________________________Section: _______________ Date: ____________ IX. Instructions: Convert the following metric measurements: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. II. 1000 mg =______g 160 cm =_______mm 109 dg = _______Kg 250 m = _______ Km 14 km = _______ m 1 L = __________mL 480 cm = ______ m 27 g = _________kg 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 198g = ________ Kg mL = __________uL 500 um = ______cm 5 L = __________mL 16 cm = _______ mm 65 g = _________mg 2500 m = ______ Km 355 mL = _______L 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 8 mm = ________ cm 6.3 cm = ________mm 5.6 m = _________cm 26,000 cm = _____ m 56,500 mm = _____km 27.5 mg = ________g 923 cm = _________m 0.025 Km = _______m Instructions: Identify the following abbreviations of the following units: milliliter_______ milligram_______ kilometer_______ centimeter_______ kilogram_______ millimeter_______ second_______ gram_______ meter_______ liter_______ decigram_______ micrometer_______ III. Instructions: Match each of the following length units to the distance that it is best or most frequently used to describe. Column A Column B A. Size of an ant _____ 0.1 nm = 1 Å B. Size of a person _____ 100 nm = 1000 Å C. Distances between neighboring stars _____ 100 µm D. Diameter of human hair _____ 1 mm E. Size of an atom _____ 100 cm = 1 m F. Size of viruses and small bacteria _____ 1 km G. Distances within our Solar System _____ 108 km H. Distances around Oahu _____ 1013 km Activity 3 Scientific Notation and Conversion of Units Worksheet – Practice Solving Name: ________________________________________________Section: _______________ Date: ____________ I. Instruction: Find the percent error for each problem below. 1. a. Starting with your age in years, calculate your age in days. (You do not need to be exact: forget about leap days, etc.) b. Approximately how many days long is your total life expectancy? 2. Use your weight in pounds (while standing on the surface of the Earth) to calculate your mass in kilograms and in grams. (1 kg weighs approx. 2.205 lb on the surface of the Earth) This is a useful thing to know, since almost every other country in the world uses kilograms! 3. Convert the speed 1.0000 m/s [meter/second] to mi/h [miles/hour], expressing your answer to 5 significant figures. (Useful info: 1 mile = 5280 feet exactly, and 1 inch = 2.54 cm exactly.) Answer Key Activity 1 Scientific Notation and Conversion of Units Worksheet – Scientific Notation Name: ________________________________________________Section: _______________ Date: ____________ I. 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) Instruction: Convert the following numbers into scientific notation. 3,400 0.000023 101,000 0.010 45.01 1,000,000 0.00671 4.50 II. 3.4 x 103 2.3 x 10-5 1.01 x 105 1.0 x 10-2 4.501 x 101 1 x 106 6.71 x 10-3 4.50 x 100 Instruction: Convert the following numbers into standard notation: 2.30 x 104 23,000 1.76 x 10-3 0.00176 1.901 x 10-7 0.0000001901 8.65 x 10-1 0.865 9.11 x 103 9,110 5.40 x 101 54.0 1.76 x 100 1.76 7.4 x 10-5 0.000074 III. Instruction: Rewrite the following numbers in scientific notation, in simplest form. Include units. Use appropriate significant figures. 1. Altitude of summit of Mt. Ka‘ala (highest point on O‘ahu): 4020 ft = 4.02 × 103 ft (or 4.020; it is unclear whether the final zero is significant) 2. Altitude of summit of Mauna Kea: 13,796 ft = 1.3796 × 104 ft 3. Thickness of a human hair: 0.015 cm = 1.5 × 10–2 cm 4. Wavelength of reddish light: 0.0000007 m 7 × 10–7 m 5. Height of your instructor: 1.80 m = 1.80 m (this is the same as writing 1.80 × 100 m) 6. Number of galaxies in the universe: 1 trillion galaxies = 1 × 1012 galaxies (or simply: 1012 galaxies) 7. Age of the universe in seconds: 430,000,000,000,000,000 s =4.3 × 1017 s (or 4.30, or 4.300, etc., although there are probably only 2 sig. figs) 8. Volume of a hydrogen atom: 0.000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 621 cm3 = 6.21 × 10–25 cm3 IV. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Instruction: --How many sig figs are in each of the following examples: 926.9 has 4 Significant Figures (SF) 707 has 3 SF 123.06 has 5 SF 0.0402 has 3 SF 0.82610 has 5 SF 338.00 has 5 SF Activity 2 Scientific Notation and Conversion of Units Worksheet – Conversion of Unit Name: ________________________________________________Section: _______________ Date: ____________ I. Instructions: Convert the following metric measurements: 1000 mg = 1 g 198g = 0.198 Kg 8 mm = 0.8 cm 160 cm = 1,600 mm 75mL = 75,000 uL 6.3 cm = 63 mm 109 dg = 0.0109 Kg 500 um = 0.05 cm 5.6 m = 560 cm 250 m = 0.250 Km 5 L = 5,000mL 26,000 cm = 260 m 14 Km = 14,000 m 16 cm = 160mm 56,500 mm = 0.0565 Km 1 L = 1,000 mL 65 g = 65,000 mg 27.5 mg = 0.0275 g 480 cm = 4.8 m 2500 m = 2.5 Km 923 cm = 9.23 m 27 = 0.027 kg 355 mL = 0.355 L II. 0.025 Km = 2,500 cm Instructions: Identify the following abbreviations of the following units: milliliter___mL____ milligram___mg____ kilometer__km____ centimeter___cm___ kilogram___kg___ millimeter___mm___ second___s____ gram__g_____ meter____m___ liter____L___ decigram___dg___ micrometer__um____ III. Instructions: Match each of the following length units to the distance that it is best or most frequently used to describe. Column A Column B A. Size of an ant E 0.1 nm = 1 Å B. Size of a person F 100 nm = 1000 Å C. Distances between neighboring stars D 100 µm D. Diameter of human hair A 1 mm E. Size of an atom B 100 cm = 1 m F. Size of viruses and small bacteria H 1 km G. Distances within our Solar System G 108 km H. Distances around Oahu C 1013 km Activity 3 Scientific Notation and Conversion of Units Worksheet – Practice Solving Name: ________________________________________________Section: _______________ Date: ____________ I, Instruction: Find the percent error for each problem below. 1. a. Starting with your age in years, calculate your age in days. (You do not need to be exact: forget about leap days, etc.) Answer: Assuming an age of 20. years: (20. y) × (365 d / 1 y) = 7300 d b. Approximately how many days long is your total life expectancy? Answer: Assuming an 80.-year life expectancy: (80. y) × (365 d / 1 y) = 29,000 d (rounded to 2 significant figures) 2. Use your weight in pounds (while standing on the surface of the Earth) to calculate your mass in kilograms and in grams. (1 kg weighs approx. 2.205 lb on the surface of the Earth) This is a useful thing to know, since almost every other country in the world uses kilograms! Answer: Assuming a weight of 150. pounds: (150. lb) × (1 kg / 2.205 lb) = 68.0 kg 3. Convert the speed 1.0000 m/s [meter/second] to mi/h [miles/hour], expressing your answer to 5 significant figures. (Useful info: 1 mile = 5280 feet exactly, and 1 inch = 2.54 cm exactly.) Answer: . a. 1.0000 m/s = 2.2369 mi/h, or 1.0000 mi/h = 0.44704 m/s For Teachers Bukidnon Association of Catholic Schools (BUACS), Inc Dioceses of Malaybalay Stella Matutina Academy General Physics 1 First Quarter LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET NO. 14 Topic: Scientific Notation and Units I. Background Information for Learners Measurement- A quantitative observation Consists of 2 parts Number Unit – tells the scale being used A. Scientific Notation- Very large or very small numbers can be expressed using scientific notation. The number is written as a number between 1 and 10 multiplied by 10 raised to a power. The power of 10 depends on • The number of places the decimal point is moved. • The direction the decimal point is moved. • Left Positive exponent • Right Negative exponent Representing Large Numbers Representing Small Numbers To obtain a number between 1 and 10 we must move the decimal point. 4 Units Units provide a scale on which to represent the results of a measurement. • There are 3 commonly used unit systems. • English • Metric (uses prefixes to change the size of the unit) • SI (uses prefixes to change the size of the unit) Measurements of Length, Volume and Mass • Volume Amount of 3-D space occupied by a substance Fundamental unit is meter3 (m3) • Mass II. Quantity of matter in an object Fundamental unit is kilogram Learning Competency with Code Solve measurement problems involving conversion of units, expression of measurements in scientific notation (STEM_GP12EU-la-1) III. Objectives/Learning Targets 4. Convert numbers into scientific notation; 5. Express length, Mass, time in SI units. 6. Solve Unit Conversion problems IV. Detailed Directions/Instructions Read the instructions and answer the attached activities. V. Exercise/Activities 1. Activity 1 – Scientific Notation (45 min.) 2. Activity 2 – Conversion of units (45 min) 3. Activity 3 – Practice Solving (45 min) VI. Rubric for Scoring Understanding (R)-1. Accuracy (A)-1. Evidence (C)-1. Explain (E)-1. Demonstrate understanding of the question. The student understood the question. The student answered the question accurately using factual information. The student use specific evidence to back-up answer. The student explains the answer thoroughly and logically. The student provides enough information to back-up the answer in a way that makes sense. Total of 4 points (can also be 1⁄2 for a total of 2) VII. Values Integration VIII. References/s for Learners www.boyertownasd.org Google.com https://chapworksheetfall.org Urone et al., (2015) General Physics 1. Vibal Publishing Inc. pp4-7 ____________________________________________ Signature of Student ____________________________________________ Name and Signature of Parent/s Guardian Note: You can attach additional sheets if necessary Activity 1 Scientific Notation and Conversion of Units Worksheet – Scientific Notation Name: ________________________________________________Section: _______________ Date: ____________ V. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. VI. Instruction: Convert the following numbers into scientific notation. 3,400 _______________________________ 0.000023 ____________________________ 101,000 _____________________________ 0.010 _______________________________ 45.01 _______________________________ 1,000,000 ___________________________ 0.00671 _____________________________ 4.50 ________________________________ Instruction: Convert the following numbers into standard notation: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. VII. 2.30 x 104 _______________________________ 1.76 x 10-3 _______________________________ 1.901 x 10-7 ______________________________ 8.65 x 10-1 _______________________________ 9.11 x 103 _______________________________ 5.40 x 101 _______________________________ 1.76 x 100 _______________________________ 7.4 x 10-5 _______________________________ Instruction: Rewrite the following numbers in scientific notation, in simplest form. Include units. Use appropriate significant figures. 9. Altitude of summit of Mt. Ka‘ala (highest point on O‘ahu): 4020 ft = 10. Altitude of summit of Mauna Kea: 13,796 ft = 11. Thickness of a human hair: 0.015 cm = 12. Wavelength of reddish light: 0.0000007 m = 13. Height of your instructor: 1.80 m = 14. Number of galaxies in the universe: 1 trillion galaxies = 15. Age of the universe in seconds: 430,000,000,000,000,000 s = 16. Volume of a hydrogen atom: 0.000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 621 cm3 = VIII. Instruction: --How many sig figs are in each of the following examples: 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 926.9 707 123.06 0.0402 0.82610 338.00 Activity 2 Scientific Notation and Conversion of Units Worksheet – Conversion of Unit Name: ________________________________________________Section: _______________ Date: ____________ IX. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. IV. Instructions: Convert the following metric measurements: 1000 mg =______g 160 cm =_______mm 109 dg = _______Kg 250 m = _______ Km 14 km = _______ m 1 L = __________mL 480 cm = ______ m 27 g = _________kg 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 198g = ________ Kg mL = __________uL 500 um = ______cm 5 L = __________mL 16 cm = _______ mm 65 g = _________mg 2500 m = ______ Km 355 mL = _______L 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 8 mm = ________ cm 6.3 cm = ________mm 5.6 m = _________cm 26,000 cm = _____ m 56,500 mm = _____km 27.5 mg = ________g 923 cm = _________m 0.025 Km = _______m Instructions: Identify the following abbreviations of the following units: milliliter_______ milligram_______ kilometer_______ centimeter_______ kilogram_______ millimeter_______ second_______ gram_______ meter_______ liter_______ decigram_______ micrometer_______ V. Instructions: Match each of the following length units to the distance that it is best or most frequently used to describe. Column A Column B A. Size of an ant _____ 0.1 nm = 1 Å B. Size of a person _____ 100 nm = 1000 Å C. Distances between neighboring stars _____ 100 µm D. Diameter of human hair _____ 1 mm E. Size of an atom _____ 100 cm = 1 m F. Size of viruses and small bacteria _____ 1 km G. Distances within our Solar System _____ 108 km H. Distances around Oahu _____ 1013 km Activity 3 Scientific Notation and Conversion of Units Worksheet – Practice Solving Name: ________________________________________________Section: _______________ Date: ____________ II. Instruction: Find the percent error for each problem below. 4. a. Starting with your age in years, calculate your age in days. (You do not need to be exact: forget about leap days, etc.) b. Approximately how many days long is your total life expectancy? 5. Use your weight in pounds (while standing on the surface of the Earth) to calculate your mass in kilograms and in grams. (1 kg weighs approx. 2.205 lb on the surface of the Earth) This is a useful thing to know, since almost every other country in the world uses kilograms! 6. Convert the speed 1.0000 m/s [meter/second] to mi/h [miles/hour], expressing your answer to 5 significant figures. (Useful info: 1 mile = 5280 feet exactly, and 1 inch = 2.54 cm exactly.) Answer Key Activity 1 Scientific Notation and Conversion of Units Worksheet – Scientific Notation Name: ________________________________________________Section: _______________ Date: ____________ V. 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) Instruction: Convert the following numbers into scientific notation. 3,400 0.000023 101,000 0.010 45.01 1,000,000 0.00671 4.50 VI. 3.4 x 103 2.3 x 10-5 1.01 x 105 1.0 x 10-2 4.501 x 101 1 x 106 6.71 x 10-3 4.50 x 100 Instruction: Convert the following numbers into standard notation: 2.30 x 104 23,000 1.76 x 10-3 0.00176 1.901 x 10-7 0.0000001901 8.65 x 10-1 0.865 9.11 x 103 9,110 5.40 x 101 54.0 1.76 x 100 1.76 7.4 x 10-5 0.000074 VII. Instruction: Rewrite the following numbers in scientific notation, in simplest form. Include units. Use appropriate significant figures. 9. Altitude of summit of Mt. Ka‘ala (highest point on O‘ahu): 4020 ft = 4.02 × 103 ft (or 4.020; it is unclear whether the final zero is significant) 10. Altitude of summit of Mauna Kea: 13,796 ft = 1.3796 × 104 ft 11. Thickness of a human hair: 0.015 cm = 1.5 × 10–2 cm 12. Wavelength of reddish light: 0.0000007 m 7 × 10–7 m 13. Height of your instructor: 1.80 m = 1.80 m (this is the same as writing 1.80 × 100 m) 14. Number of galaxies in the universe: 1 trillion galaxies = 1 × 1012 galaxies (or simply: 1012 galaxies) 15. Age of the universe in seconds: 430,000,000,000,000,000 s =4.3 × 1017 s (or 4.30, or 4.300, etc., although there are probably only 2 sig. figs) 16. Volume of a hydrogen atom: 0.000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 621 cm3 = 6.21 × 10–25 cm3 VIII. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Instruction: --How many sig figs are in each of the following examples: 926.9 has 4 Significant Figures (SF) 707 has 3 SF 123.06 has 5 SF 0.0402 has 3 SF 0.82610 has 5 SF 338.00 has 5 SF Activity 2 Scientific Notation and Conversion of Units Worksheet – Conversion of Unit Name: ________________________________________________Section: _______________ Date: ____________ X. Instructions: Convert the following metric measurements: 1000 mg = 1 g 198g = 0.198 Kg 8 mm = 0.8 cm 160 cm = 1,600 mm 75mL = 75,000 uL 6.3 cm = 63 mm 109 dg = 0.0109 Kg 500 um = 0.05 cm 5.6 m = 560 cm 250 m = 0.250 Km 5 L = 5,000mL 26,000 cm = 260 m 14 Km = 14,000 m 16 cm = 160mm 56,500 mm = 0.0565 Km 1 L = 1,000 mL 65 g = 65,000 mg 27.5 mg = 0.0275 g 480 cm = 4.8 m 2500 m = 2.5 Km 923 cm = 9.23 m 28 = 0.027 kg 355 mL = 0.355 L XI. 0.025 Km = 2,500 cm Instructions: Identify the following abbreviations of the following units: milliliter___mL____ milligram___mg____ kilometer__km____ centimeter___cm___ kilogram___kg___ millimeter___mm___ second___s____ gram__g_____ meter____m___ liter____L___ decigram___dg___ micrometer__um____ XII. Instructions: Match each of the following length units to the distance that it is best or most frequently used to describe. Column A Column B A. Size of an ant E 0.1 nm = 1 Å B. Size of a person F 100 nm = 1000 Å C. Distances between neighboring stars D 100 µm D. Diameter of human hair A 1 mm E. Size of an atom B 100 cm = 1 m F. Size of viruses and small bacteria H 1 km G. Distances within our Solar System G 108 km H. Distances around Oahu C 1013 km Activity 3 Scientific Notation and Conversion of Units Worksheet – Practice Solving Name: ________________________________________________Section: _______________ Date: ____________ I, Instruction: Find the percent error for each problem below. 4. a. Starting with your age in years, calculate your age in days. (You do not need to be exact: forget about leap days, etc.) Answer: Assuming an age of 20. years: (20. y) × (365 d / 1 y) = 7300 d b. Approximately how many days long is your total life expectancy? Answer: Assuming an 80.-year life expectancy: (80. y) × (365 d / 1 y) = 29,000 d (rounded to 2 significant figures) 5. Use your weight in pounds (while standing on the surface of the Earth) to calculate your mass in kilograms and in grams. (1 kg weighs approx. 2.205 lb on the surface of the Earth) This is a useful thing to know, since almost every other country in the world uses kilograms! Answer: Assuming a weight of 150. pounds: (150. lb) × (1 kg / 2.205 lb) = 68.0 kg 6. Convert the speed 1.0000 m/s [meter/second] to mi/h [miles/hour], expressing your answer to 5 significant figures. (Useful info: 1 mile = 5280 feet exactly, and 1 inch = 2.54 cm exactly.) Answer: . a. 1.0000 m/s = 2.2369 mi/h, or 1.0000 mi/h = 0.44704 m/s