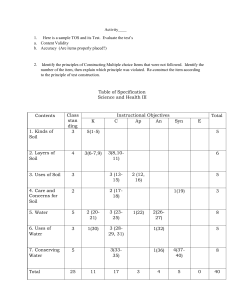
Soil 2.2.1 Chemical properties of soil Specifications 2.2.1 (a) examine the chemical features of soil including plant-available nutrients, pH and liming, cation exchange, and flocculation 2.2.1 (b) conduct an investigation into the chemical properties of soil to • demonstrate cation exchange capacity (CEC)* • show flocculation* • determine the pH* Examine consider an argument or concept in a way that uncovers the assumptions and relationships of the issue Conduct to direct in action or course; manage Ion An atom or a molecule that has a net electric charge Anion Negatively charged ion Cation Positively charged ion Soil colloids Small particles of soil clay and soil humus Flocculation The clustering together of soil particles to create larger structures called floccules Cation exchange The ability of soil particles (clay and humus) to attract, retain and release cations Cation exchange capacity (C.E.C.) The capacity of a soil to exchange cations between the soil surfaces and water (soil solution) pH A measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution Liming Spreading ground limestone on soil Milliequivalent (mEq) Amount of a substance that will react with a certain number of hydrogen ions Soil 2.2.1 Chemical properties of soil Chemical properties that are important in determining the characteristics of a soil: 1. Flocculation 2. Cation exchange 3. pH 4. Plant-available nutrients Ion Cation Anion An atom or a molecule that has a net electric charge Positively charged ion Negatively charged ion Soil colloids: smallest particles, soil clay and soil humus, most chemically active Flocculation The clustering together of soil particles to create larger structures called floccules 1. Chemical reactions form negative charges on soil colloids 2. Cations are adsorbed onto the surface 3. The colloids are linked together by polarized water to form a floccule 4. Floccules trap larger particles such as sand to form aggregates An aggregate is a substance formed by combining several separate elements Cations that promote flocculation and that are abundant in Irish soils: Al3+, Fe3+, Ca2+, Mg2+, H+, K+, Na+ Soil 2.2.1 Chemical properties of soil Cations are attracted to negatively charged humus and clay particles They are released into the soil through weathering Cation exchange: The ability of soil particles (clay and humus) to attract, retain and release cations. Constantly taking place. A cation with 2 +ve charges can replace two separate cations with 1 +ve charge. Cation exchange capacity (C.E.C.) The quantity of cations that a soil adsorbs or the capacity of a soil to exchange cations between the soil surfaces and the soil solution Factors affecting cation exchange capacity Humus content Clay content Soil texture Highest CEC value as colloidal humus has high number of –ve charges Higher CEC with a higher clay content in soil Fine textured soils have a higher CEC pH Low pH level (below 5) leads to fewer cations in the soil. pH can be increased by liming (increases Ca2+). Increasing pH leads to increase of –ve charges on soil colloids (greater CEC) Soil 2.2.1 Chemical properties of soil pH A measure of the concentration of the hydrogen ions in a solution . It can also be expressed as the negative log of the hydrogen ion concentration: pH = -log10[H+] pH scale 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Neutral Acidic 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 alkaline pH range of most soils pH for ideal agricultural soils 5.5 - 8.5 6.5 - 7.5 Acidic ions Alkaline ions Hydrogen and Aluminium Calcium and magnesium Hydrogen is derived from carbonic acids Aluminium is derived from granite or sandstone Derived from limestone and the application of lime Available soil nutrients Availability of certain nutrients is reduced if soils become increasingly acidic or alkaline Most nutrients are available between pH 6 – 7 Raising the pH by liming can improve the availability of nutrients in acidic soils Liming: Spreading ground limestone on soil Contains calcium and magnesium pH levels increase and acidic levels of the soil decreases Reduces acid leaching Medium-term activity (takes approx. 2 years for full effects) Ca 2+ and Mg2+ replace H+ and Al3+ ions Ground limestone that is used for agriculture must consist of the following: • • • • Crushed natural limestone that contains calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate Moisture no greater that 2.5% Total neutralizing value no less than 90% Pass through a 3.35 mm sieve and not less than 35% through a 0.15 mm sieve Soil 2.2.1 Chemical properties of soil Questions What are the chemically active particles in soil? Do humus and clay particles have a negative charge? List the chemical properties that are important in determining the characteristics of a soil What is flocculation? What are floccules also known as? Name two soil colloids What are soil colloids? How does flocculation occur? List three cations that promote flocculation What are cations? What are anions? What is cation exchange? What does C.E.C. Stand for? What is cation exchange capacity (C.E.C.)? How are cations released into soil? When does cation exchange take place? What factors affect cation exchange capacity? Define the term leachate What is pH? What is the pH value scale? What is the value given to a neutral pH? What do you describe a solution with a pH less than 7? What do you describe a solution with a pH more than 7? List two acidic ions List two alkaline ions Where are hydrogen ions derived from? Where are aluminium ions derived from? Where are calcium and magnesium ions derived from? Name the liquid used to determine the pH of a substance (soil) What is the optimum pH level for crop growth? What pH can reduce the availability of nutrients to plants? How can you increase the availability of essential nutrients in an acidic soil? What is liming? What does ground limestone contain? How does liming work? What are the advantages of liming? What must the moisture content of ground limestone for agriculture be? What must the total neutralizing value of ground limestone for agriculture be? What size sieve should ground limestone for agriculture pass through?