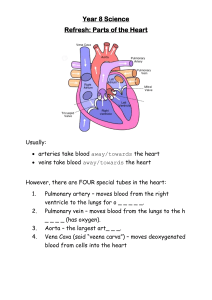
Chaper 38 Cardiac output is calculated by multiplying the heart rate in beats per minute Preload- the amount of blood and pressure in the ventricle at the end of diastole Afterload- the resistance has to be exceeded for the ventricle to eject the blood during systole. Myocardial infarction- or heart attack Copd-chronic obstructive pulmonary disease- group of disorders characterized by impaired airflow in the lungs Emphysema- one of the disorders and is characterized by enlargement of gas exchange airways and damage to the alveolar walls in lungs Chronic bronchitis- another disorder associated with COPD. Inflammation of the larger airways, increased productions of mucus and chronic cough. Asthma- produces symptoms of dyspnea, intermittent cough, chest tightness exertional wheeling heard on auscultation and prolonged expiration. Pneumonia- infection in the lungs. Fever cough increased secretions, difficulty breathing. Atelectasis- blockage or collapse of air passages in at least one lobe of the lungs Hemoptysis- presence of blood in the sputum. Characteristics of blood—weather it occurs as flecks, streaks, frank bleeding Pulmonary function test- look in patients chart and see what the results are from the radiologist. Complete blood count- differential provide information regarding oxygen and carbon dioxide transport capabilities and status of the immune response Basic metabolic panel- renal function, glucose level, electrolyte status Arterial blood gases- determines if someone gets put on a ventilator Statin- cholesterol medicine.. you want to watch the liver enzyme. Cardiac enzymes- troponin and CK levels Ck-mb levels. CK- breakdown of muscle Pneumothorax- air in the pleural cavity Pleural effusion- excess fluid accumulation in the pleural cavity Pericardial effusion- fluid around the heart Chest x-ray should be priority—the lungs on the Xray need to be black- because that means they are filled with air.. white cloudy means there is an infection.. white patches all over the lungs—CHF—fluid Diagnostic tests are intermediate Electrocardiogram (ecg also EKG)- graphic representation of the electrical activity that occurs in the heart ST segment is where the heart attack happens. Very vulnerable to electric impulses Atrial fib- need to be on the anticoagulant. To prevent a PE.. this is when you take the radial pulse and it is irregular, so you take the apical pulse for a full min. because the heartbeat is irregular Pulmonary embolismArrhythmias- abnormal rhythms of the heart Echocardiogram- ultrasound of the heart. Shows the movement of the blood through the heart and it is used to measure cardiac output. (Congenital heart defects, pericardial effusion, disorders of the heart valves, heart size, and effectiveness of cardiac output) Cardiac Catheterization- uses contrast and long flexible catheter to visualize the heart chambers, coronary arteries, and great vessels. Evaluate chest pain, locate the region of coronary artery occlusion and determine the effects of valvular heart disease. Inserted into the femoral or brachial artery to view the left side of the hear and inserted into the antecubital or femoral vein to see the right side of the heart. Education on oxygen at home, need to know Petroleum products are flammable, teach oxygen patients this. Hypoxemia- low level of oxygen in the blood Cyanosis- a bluish discoloration of the skin related to deoxygenation of hemoglobin, a decreasing oxygen saturation level, and a feeling of distress Hypercapnia- may have respiratory depression when supplemental oxygen levels are too high.. high level of carbon dioxide in the blood Don’t over oxygenate a COPD patient Fraction of inspired oxygenYou need an order for oxygen. However, if you patient needs oxygen you can usually use 2 liters on a cannula, until you can get an order On nclex, all answers are presumed that you have order Nebulizers and humidifiers may have bacterial contamination leading to infection Mask delivery system- gather and store oxygen between patients breath. Reservoir masks- valve system Patient needs a more precise airflow usually a % venti mask Compare and contrast before and after you initiate oxygen Wait 15-30 then check to see if anything has changed by doing a focused assessment When you switch a flow rate you have to change the oxygen device. Nasal cannula can only put out so much oxygen until you have to switch to a mask—chart oxygen cannula 2L/min don’t chart a percent Venturi mask- % Room air is 21% every liter you give raises it 3% Masks should be anywhere from 6-8L.. Nasal cannula should be anything below 6 L Any patient that is on oxygen is a high risk patient Bag-valve mask device- or ambu bag- used to ambulate a patient Pharyngeal airways Nasopharyngeal airway- placed nasally Pharyngeal airway- placed into the mouth Endotracheal tubes- are semirigid curved tubes with a cuff at the distal end that seals to prevent aspiration of gastric contents into the lung, allow positive pressure for ventilation (youtube placement video) If patient is gagging, they don’t need an airway. Take it out. Assess the mucous membrane, make sure it is not cut or bleeding Document if you gave oral care to the patient Tracheostomy tube- placed directly in the trachea to control the airway. Medication for pulmonary diseaseBronchodilators- increase the diameter of the bronchi and bronchioles which decreases wheezing and improves oxygenation Olol drugs-atenolol ACE inhibitor for hypertension drug cards Diuretics- study these drugs Postural drainage- therapeutic way to position a patient to use gravity to help mobilize respiratory tract secretions. Know the complications of postural drainage therapy.. slide 43 Chest tube- when we put a tube in we disrupt the If your caring for someone with a chest tube and it pops out you need to put an occlusion bandage over it because you want to seal the chest from room air.. because it will create a vacuum Predict and manage Chest tubes help drain fluid or blood and excessive air from the pleural space Coumadin ** INR thereaputic levels Antiembolism hose And sequential compression device questions will be in this chapter. Collaboration and delegation—study this portion Care of a chest tube must not be delegated UAP can report any changes in vital signs.. or difficulties presented with the patient You should tape it three sides so that way the air can escape and room air can not go in when the breathe in. If its taped in all four corners you have to eventually let the air out manually. Stay with the patient. Have everything ready for the doctor so that way they can walk in and put the chest tube in