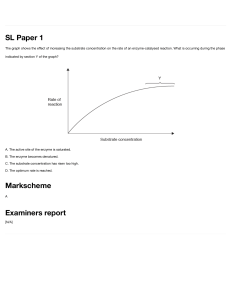
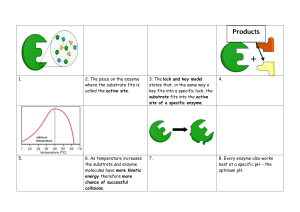
CHAPTER 4 : ENZYMES 4.2 MECHANISM OF ENZYME ACTION AND ENZYME KINETICS Back Next Contents : Mechanism of Enzyme Action The lock-and-key hypothesis The induced-fit hypothesis Back Enzyme Kinetics Michaelis-Menten equation Effects of enzyme concentration, substrate concentration, temperature and pH on the Rate of an enzyme catalysed reaction Next Michaelis-Menten Equation A reaction model was proposed by Leonor Michaelis and Maud Menten in 1913 to account for enzymecatalysed reaction Back Next The Relationship between The Rate of an EnzymeCatalysed Reaction and The Substrate Concentration Back Next Lineweaver-Burk Plot Back Next The Significant of Vmax - Vmax : Maximal Velocity The velocity of an enzyme-catalysed reaction when there is a saturating level of substrate -Vmax show the turnover number ( catalytic constant ) of an enzyme. This is the number of substrate molecules that can be converted into product molecules by the catalytic site of one enzyme molecule per unit time (second) Back Next The Significant of Km - Michaelis-Menten Constant (Km) : Substrate concentration that produces one half Vmax - Km provides a measure of the substrate concentration required for significant enzyme reaction to occur - Km values also provide a measure of the affinity of an enzyme for its substrate - Different enzymes have different Km values Back Next Assumptions of Michaelis-Menten Kinetics Substrate concentration > Enzyme concentration Vmax is obtained when the catalytic sites of enzymes are saturated with substrate The reverse reaction of an enzyme and product is negligible Back The total of enzyme substrate remains constant The uncatalysed rate of conversion of substrate to product wuthout enzyme is negligible Enzyme is not allosteric and not cooperative Next Effects of Enzyme Concentration, Substrate Concentration, Temperature and pH on the Rate of an Enzyme Catalysed Reaction The Concentration of the Enzyme The Concentration of the Substrate pH Back Temperature Presence pf Competitive and Non-Competitve Inhibitors Next Enzyme Concentration 01 The company You can enter a subtitle here if you need it Back The rate of an enzymecatalysed reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the enzyme if substrates are present in excess and no other factors are limiting When substrates are not in excess, there is no increase in reaction because the substrates concentration become the limiting factor Next Substrate Concentration At low substrate concentration, the rate of an enzyme reaction increases directly proportion to increasing substrate concentration As the substrate concentration increases, more active sites are involved in the binding of substrate molecules At a certain point, increasing the substrate concentration does not increase the net reaction rate Back Next Effects of Temperature At low temperature, an enzyme-catalysed reaction occurs very slowly. Increasing the temperature increases the kinetic energy of reactants At suboptimal temperatues, the Q10 reactions is approximately 2 Back Next Effects of pH Most enzymes are effective only within a narrow pH range. The optimum pH is the pH at which the maximum rate of reaction occurs Different enzymes have different pH optima Back Next Example of Enzymes Optimum pH $100 Describe your product or your service here ● Characteristic ● Characteristic Basic Back $220 Describe your product or your service here ● Characteristic ● Characteristic Pro $300 Describe your product or your service here ● Characteristic ● Characteristic Premium Next Arigatou Gozaimasu :) Back Next