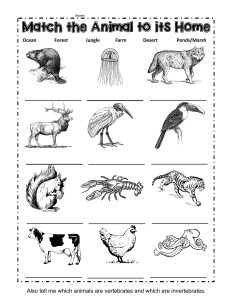
Text No. 1 - Vertebrates and Invertebrates Animals can be classified into two main groups: vertebrates and invertebrates. The main difference between vertebrates and invertebrates is that invertebrates, like insects and flatworms, do not have a backbone or a spinal column. Examples of vertebrates include humans, birds, and snakes. Differences in Physical Characteristics Invertebrates have no backbone, while vertebrates have a well-developed internal skeleton of cartilage and bone and a highly developed brain that is enclosed by a skull. A nerve cord is enclosed by vertebrae — individual bones that make up a vertebrate's spine. Vertebrates have well-developed sensory organs, a respiratory system with either gills or lungs, and a bilateral symmetry with an advanced nervous system that further distinguishes them from invertebrates. Differences in Habitat Both types of animals live in a variety of habitats, but vertebrates can essentially suit themselves in all habitats easily. The highly developed nervous system and internal skeletons of vertebrates allow them to adapt to land, sea, and air. Nevertheless, invertebrates are also found in a vast range of habitats, from forests and deserts, to caves and seabed mud. Population of Vertebrates vs. Invertebrates To date, nearly 2 million species of invertebrates have been identified. These 2 million species make up about 98% of the total animals identified in the entire animal kingdom, i.e., 98 out of 100 types of animals in the world today are invertebrates. On the other hand, vertebrates only form 2% of the animal species. Human beings are vertebrates. Adaptation to the Environment In contrast to invertebrates, vertebrates have a highly developed nervous system. With the help of their specialized nerve-fiber system, they can react very quickly to changes in their surroundings, giving them a competitive edge. Compared to vertebrates (animals with backbones), most invertebrates have simple nervous systems, and they behave almost entirely by instinct. This system works well most of the time, even though these animals are often incapable of learning from their mistakes. Moths, for example, repeatedly flutter around bright lights, even at the risk of getting burned. Notable exceptions are octopuses and their close relatives, which are thought to be among the most intelligent animals in the invertebrate world. Similarities Between Vertebrates and Invertebrates The feature uniting all chordates (all vertebrates and some invertebrates) is that at some stage in their lives, all have a flexible supporting rod, a notochord, that runs through the length of their bodies. In a majority of chordates, the notochord is replaced by a series of interlocking bones called vertebrae which appear during early development. The presence of these bones is what determines whether an animal is a vertebrate (has vertebrae) or invertebrate (does not have vertebrae).