Copy of Anatomy and Adaptations of Fish Body Plans Student Notes (1)
advertisement

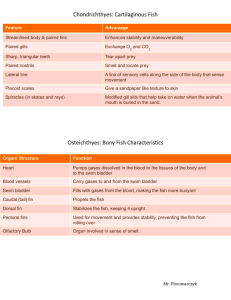
Anatomy and Adaptations of Fish Body Plans Function of Fish Anatomy & Fins Body Part or Fin Operculum Lateral Line Dorsal Fins Pectoral Fins Pelvic Fins Anal Fin Caudal Fin Function gill cover sensory organs found in fish, used to detect movement, vibration, and pressure gradients in the surrounding water. increase the lateral surface of the body during swimming, and thereby provide stability but at the expense of increasing drag. responsible for control of directional movement, up and down or side to side. help balance the fish, keep it level and prevent it from rolling from side to side. stabilizes the fish while swimming. moves, propels or pushes the fish through the water. Caudal Fin Shapes and Functions Example Description Rounded Truncated Adapted Function Good for acceleration and maneuvering not good for long distance Allows for quick turns and short bursts of speed Emarginate Least amount of drag; two lobes Forked 2 lobes; helps reduce turbulence Lunate Tend to be the fastest fishes; maintains speed Fish Body Shapes Example Description Flat Body Adapted Function bottom dweller Laterally Compressed ● leisurely swimmers ● enter crevices ● for quick bursts of speed live in narrow spaces and rocks Elongate Torpedo fast swimmers Mouth Shape and Functions Example Description Large Adapted Function surrounds and swallows prey whole Little mouth nibbling on small plants/animals Mouth Near Top (superior) Mouth in Middle (terminal) Mouth on Bottom (inferior) ● called superior ● Eating near surface or on prey above ● called terminal ● Eating prey directly ahead ● called inferior ● Eating off the bottom