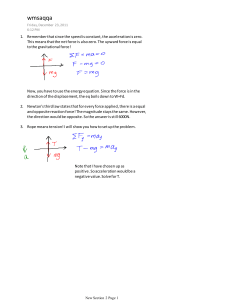
ST. JOSEPH SCHOOL OF LAWANG BATO, INC. Mulawinan St., Lawang Bato, Valenzuela City Learning Module in Science 8 Reference: Vibal Science and Technology 8 Pages 4-12 Prepared by: Ms. Jolina R. De Vera ST. JOSEPH SCHOOL OF LAWANG BATO, INC. Mulawinan St., Lawang Bato, Valenzuela City MODULE 1 MOTION Duration: 2 days II. Introduction Motion is the phenomenon in which an object changes its position over time. III. Overview This module teaches the students the relationship between the amount force applied and the mass of an object to the amount of change in the object’s motion. IV. Objectives: At the end of the lesson, the student will be able to: 1. Discuss the three laws of motion. 2. Explain the relationship of mass and acceleration. V. Pre-Test: Write TRUE if the statement is correct and FALSE if it is not. Write your answer on the space provided before the number. ________1. Friction is a force that opposes motion. ________2. Acceleration is not related to mass. ________3. Greater force means greater motion. ________4. Isaac Newton is the father of motion. ________5. A rolling ball implies motion. VI. Instructions to the users: MODULE 1 MOTION LEARNING STEPS 1. Answer Pre-test (do not browse yet the content of the module) 2. Newton’s Laws of Motion 3. Answer Test Yourself 1 RESOURCES Pre-Test Information Sheet 1 Test Yourself 1 for Information Sheet 1 NOTE: For Test Yourself, Formative Assessment and Valuing, please write your answer on a sheet of long bond paper. Instructions to the Parents: Dear Parents: Due to the pandemic that we are currently facing I am asking your help to please guide your son/daughter in answering the activities in the module. Kindly follow the time allotment for each activity. Kindly submit the activities every Friday. Thank you for your cooperation and guidance. God bless and keep safe always. Information Sheet 1 VII.NEWTON’S LAWS OF MOTION Keywords Net force - It is capable of changing the state of motion of an object. Acceleration -It is the rate of change in velocity of a moving object per unit time. Velocity – It is the description of the motion of an object in terms of both the speed and direction. Balanced forces- Refer to the equal forces acting in opposite directions; thus they have zero net force. Unbalanced forces- Have a nonzero net force; thus, it produces acceleration. Mass- It is the measurement of the amount of matter something contains. It SI quantity is Kg. Weight- It is the measurement of the pull of gravity. Its SI quantity is Newton 1.1 LAW OF INERTIA Inertia is a property of the body that tends to resist a change in its state of motion. The greater the mass, the greater its inertia and the greater the inertia, the harder it is to change the motion of that body. It also states that an object at rest will remain at rest unless acted upon by external force and an object in uniform motion will remain in uniform motion unless acted upon by unbalanced force. Examples: Seatbelts tighten in a car when it stops quickly Leaves falling down when the branches of the tree are shaken The continued swirling of milk after the stirring stopped 1.2 LAW OF ACCELERATION It states that the acceleration is inversely proportional to the mass. And directly proportional to force. 1.2.1 Force and Acceleration The greater the unbalanced force, the greater the acceleration of the body being acted upon. Look at figure 1 below. 1.2.2 Mass and Acceleration It shows us the effect of the mass of an object to the acceleration produced when a force act on it. Look at figure 2 below. Figure 1: force and acceleration Figure 2: mass and acceleration Problem sample 1: An object has a mass of 18.22 kg and an acceleration of 14.06 m/s/s. What is the force on the object? Given: m= 18.22 kg a= 14.06 m/s2 Find: Force Formula: F=ma Solution: F= 18.22 kg (14.06 m/s/s) F= 256.17 N Problem sample 2: An object with a mass of 11.20 kg experiences a force of 11.12 N. What is the acceleration of the object? Given: m= 11.20 kg Newton F= 11.12 N can also Find: acceleration be Formula: F=ma or written as Solution: 11.12 N= 11.20 kg a kg. m/s/s = a=0.99 m/s/s or 0.99 m/s2 a=0.99 m/s/s or 0.99 m/s2 Problem sample 3: An object with a force of 16.01 N on it is accelerating at 19.50 m/s/s. What is the mass of the object? a=0.82 kg Given: a= 19.50 m/s/s F= 16.01 N Find: mass Formula: F=ma or Solution: 16.01 N= m 19.50 m/s/s = m=0.82 kg 1.3. LAW OF INTERACTION It states that when a body A exerts a force on body B, body B will exert an equal but oppositely directed force or commonly known as “to every action, there is an equal but opposite reaction force.” Examples: Figure 3: law of interaction example 1 Figure 4: law of interaction example 2 VIII.TEST YOURSELF 1 for Information Sheet 1 Time Allotted: 45 minutes A. Imagine that you are holding a ball of 6 N at rest on the palm of your hand. Complete the following statements. 1. A downward force of 6N is exerted on the book by the ______________. 2-3.The reaction to this force is an upward force of 6N exerted by the _____________ on the ______________. 4-5. An upward force of ________________ is exerted on the _______________ by the hand. 6-9. The reaction to the force in letter c is a force of ________N, acting ___________ exerted by the ____________ on the ______________. B. Solve for the following problems. Show your solution. 10-14. How much force is needed to kick 2 kg ball in 8.64 m/s2? 15-20. a force of 5 N accelerates a mass by 2 m/s2. What will be the acceleration if the force and mass were increased to twice their original values? C. Using your knowledge about the laws of motion, develop a written plan of “Newton’s Olympics” (an Olympics involving cars made out of balloon and cars). VIII. Formative Assessment: Answer Review A (1-4) and B (5-7) on pages 20-21 of your Vibal Science and Technology 8 IX. Post-Test A. Fill in the table by citing 5 examples of Laws of Motion that you encounter every day. On the first column, write the activity. On the second column, identify the laws of motion involved and on the third column, explain why do you consider such activity/activities to be under that specific law/laws of motion. ACTIVITIES THAT YOU ENCOUNTER EVERY DAY LAWS OF MOTION INVOLVED EXPLANATION 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. X. Valuing Answer the question briefly. 1. How are different laws of motion used in road safety? XI. References Rabago, Lilia M. et.al. Science and Technology 8. Quezon City: Vibal Publishing House, 2019 Ramos, John Donnie A. et.al. Exploring Life through Science Series Second Edition The New Grade 8. Quezon City: Phoenix Publishing House, 2018