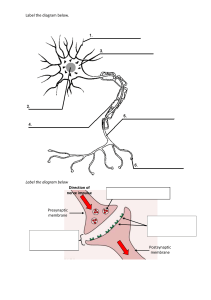
Practical lesson tasks (General Medicine, Pediatrics) Physiology of analyzers. Auditory, vestibular, gustatory, olfactory analyzers PART 1 Task №1. Analyzer parts. Fill in the table, specify the structures related to the relevant parts of these analyzers Parts Analyzer Peripheral Conduction Central Auditory sensory hair cells in organ Cochlear Spiral ganglion - cochlear temporal lobe of of Corti (located in internal nerve (part of cerebral cortex. ear). cranial nerve VIII) - medulla (cochlear nuclei) - auditory pathway - superior olivary nucleus - inferior colliculus - medial geniculate nucleus Vestibular – bony labyrinth located in – branches of vestibulocochlear postcentral gyrus, lower temporal bone (otolith nerve (cranial nerve VIII) part. organs and medulla (nucleus of Schwalbe, three semicircular canals) Bekhterev, Deiters, Manakov) spinal cord, cerebellum, midbrain (oculomotor nuclei), autonomic ganglions, reticular formation Olfactory Olfactory receptors Olfactory nerve - pierce the inner part of temporal are situated in olfactory cribriform plate of ethmoid bone lobe, hippocampus. mucus - olfactory bulb (second order membrane, which is the neuron) - olfactory tract (tractus modified olfactorius) mucus membrane that lines olfactory center. upper part of nostril. Taste Taste receptors – taste buds, Receptors – chorda tympani fibers postcentral gyrus, lateral each taste bud of facial nerve (VII), sulcus. contains 2-6 receptors and glossopharyngeal nerve fibers basal cells. (IX) -nucleus of tractus solitarius in Most of the taste buds are the medulla oblongata (first order present on the neuron) papillae of tongue. Taste medial leminiscus (second order buds are also situated neuron) - posteroventral nucleus of in the mucosa of epiglottis, thalamus (third palate, pharynx order neuron). and the proximal part of esophagus. Task №2. The structure and function of the ear. Fill the table Structures Outer ear auricle, external auditory canal, tympanic membrane Middle ear tympanic cavity, and its little bones auditory ossicles : malleus, incus, stapes and Function receives the sound waves then transmit it to tympanic membrane conduct sound vibration from tympanic membrane to internal ear 1 Inner ear Eustachian tube Labyrinth (cochlea)– bone canal makes of two and a half turn. Two membranes divide bone canal: Vestibular membrane (Reissner membrane) Basilar membrane Scalae of spiral canal of cochlea: Scala vestibular; Scala media; Organ of Corti is located basilar membrane of scala media. Scala tympani. pivotal roles in maintaining postural balance and visual focus on a single object (gaze fixation). Task №3. . Transmission of sound vibrations. find the correct sequence 1 sound 11 deformation of hair cells upon contact with the integumentary membrane 8 oscillations of the perilymph of the upper and lower channels 3 eardrum 12 occurrence of receptor potential 5 incus 13 AP 10 vibrations of the hair cells of the main membrane 9 middle channel endolymph oscillations 7 oscillation oval window 4 malleus 14 nerve fibers 2 external auditory canal 6 stapes Task №4. Vestibular apparatus. Fill the table Element of the vestibular apparatus Location Sensitive to ... Otolithic apparatus Both of them – otolith apparatus (receptor cells, particles of calcium carbonate) movements like linear acceleration and head tilts hair cells receptors Three semicircular canals, their end is enlarged - ampulla. In the ampulla – receptive hair cells Directional sensitivity of individual vertebrate hair cells to controlled deflection of their hair bundles Task №5. Taste disorders. Fill the table Name of the disorder Ageusia taste loss hypergeusia hypergeusia hypogeusia parageusia reduced taste sensitivity taste perversion Task №6. Disturbance of smell. Fill the table Name of the violation hyposmia hyposmia hyperosmia Anosmia paraosmia sensitization sensing odor susceptibility odor perception Description Description 2 PART 2. Solve cases and answer the questions Case 1. Galina Ivanovna is 30 years old. The functions of the hearing organs are normal. Sound signals were continuously turned on: the first with a frequency of 35,000 Hz, the second - 9 Hz, the third - 12,000 Hz. Which of the signal will Galina Ivanovna hear?Why? Answer: A 12,000 Hz sound wave will be audible to Galina Ivanovna. She won't be able to hear noises between 35000 and 9 Hz since humans only detect sounds between 16 and 20,000 Hz. Case 2. Two friends went to the lake for swimming. Answer: Someone on the coast will hear it. Suddenly there was a strong sound, just like a gun shot. Since the sound often travels to one ear At that time, one of the friends was under water, the before the other, a person may readily detect second on the boat. They tried to determine the direction the direction of the sound source. The brain of its source. detects this minute difference in time and Who can more easily determine the direction of the sound minute variation in sound intensity and uses source? Why? these to estimate the direction of the sound source. Air is less dense than water. Sound travels more rapidly in a more crowded space. As a result, there will be less of a delay between the arrival of sound in the left and right ears than in the air. Inferring the direction of sound is thus simpler in the air than in water. Case 3. It is known that conduction of sound occurs by Answer: air conduction and bone conduction. Air conduction and bone conduction both In case of damage of air conduction, can bone conduction have a role in how sounds are perceived. For be maintained? What does this indicate? instance, when there is hearing loss, the auditory ossicles' natural movement is compromised, which affects air conduction. Bone conduction might, however, continue. You need to place a sounding item on a section of the head to confirm this (preferably on the mastoid process). Case 4. В The examination revealed that the patient had Answer: damaged the semicircular canals of the inner ear. Yes, it is possible since the inner ear's Can he detect the linear acceleration of his body in semicircular channel receptors pick up on space? changes in the body's movement speed. Receptors found in the vestibule sacs sense how the head is positioned in space. Case 5. Seasickness is a feeling of nausea and dizziness Answer: due to monotonous fluctuations. The pathological condition of seasickness is In which case does a person endure the symptoms of brought on by rolling of the sea. It shows Seasickness — on the ship’s deck or in the cabin? Explain symptoms like nauseousness, the reason for this phenomenon. lightheadedness, cephalgia, vomiting, malaise, emotional deviations (apathy/excitement), dropping blood pressure, and arrhythmia. Reasons: intense nature of the pitching, alcohol intake, fatty foods, overeating, chronic diseases, etc. Case 6. The man complained that sometimes he has Answer: decreased taste sense of the food he is having. The components of the taste sensation He also noticed that this occurs if he has a great system are as follows: 1) the flavor substance excitement. in the mouth; 2) the substance's dissolution by saliva; 3) the penetration of dissolved 3 Is his decreased taste sense associated with his great excitement? Explain your answer. particles of the substance to the taste receptors; 4) irritation of the taste receptors; and 5) the perception of taste. When contrasting a person's calm demeanor with a condition of intense emotional arousal, it is important to focus on the second factor, which is the saliva's role in the substance's disintegration. Salivation is known to be hindered by intense emotional arousal due to norepinephrine's action (a mediator of the postganglionic link of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system). Because of this, in the dry oral cavity, the taste sensations will be noticeably weakened. Case 7. The patient was diagnosed with bilateral lesion of Answer: loss of taste and dysfunction of the lingual nerve. salivary gland. What kind of failure occurs in such a condition, and why? The anterior two-thirds of the tongue supply sensory innervation to the lingual nerve. It has fibers from both the face nerve and the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3) (CN VII). Trigeminal nerve fibers are responsible for touch, pain, and warmth (general feeling), whereas face nerve fibers are responsible for taste (special sensation). Case 8. The person who entered the room felt the sharp Answer: smell of flowers. After a while he stopped feeling the A person becomes addicted to the scent of an smell. odorous chemical after repeatedly irritating Why do people who have been in this room for a long their smell receptors, and they stop sensing time stop feeling the smell? it. Contrast, mutual weakening of scents in a combination of odorous substances, and combining the odors of many substances into one that has a qualitatively different smell are all conceivable effects of odors. 4