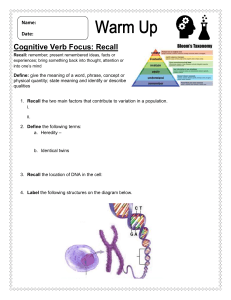
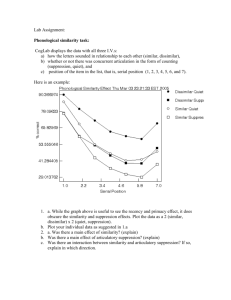
Research Support Topic:Working memory model Name Landry and Bartling Aim To investigate whether or not articulatory suppression would influence recall of a written list of phonologically dissimilar letters in sequential recall. Sample The participants consisted of thirty-four undergraduate psychology students. Method ● The participants were tested individually. In the experimental group, participants first saw a list of letters that they had to recall while saying the numbers '1' and '2' at a rate of two numbers per second (an articulatory suppression task). The control group saw the list of letters but did not carry out the articulatory suppression task. ● There were ten lists each consisting of a series of 7 letters randomly constructed from the letters F, K, L, M, R, X and Q. These letters were chosen because they don't sound similar. The experimenter presented one letter series at a time. The participants received an answer sheet with seven blanks in each row. Before the experiment started, each participant viewed one practice list in order to become acquainted with the procedure. Results The results showed that the scores from the experimental group were much lower than the scores from the control group. The mean per cent of accurate recall in the control group was 76% compared to a mean of 45% in the experimental group. Although the difference in the means was large, the standard deviations were nearly identical with SD = 0.13 for the control group and SD = 0.14 for the experimental group. A T-test was calculated and found a significant difference of p ≤ 0.01. Conclusion The results supported the experimental hypothesis as the mean per cent of accurate recall in the control group was higher than the mean percent of accurate recall in the experimental group. In line with the Working Memory Model, articulatory suppression is preventing rehearsal in the phonological loop because of overload. This resulted in difficulty in memorising the letter strings for participants in the experimental conditions whereas the participants in the control condition did not experience such overload. Strengths Weaknesses P P E E A A L L