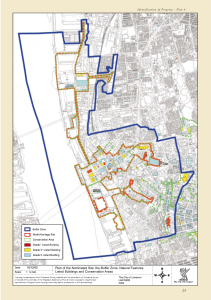
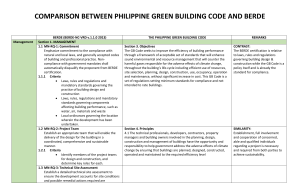
DESIGN 5 RSW SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT Sustainable development is the broad concept that all human undertakings should increase the longevity of the Earth and its inhabitants. Architects refer to as the "built environment" should not harm or deplete the Earth's resources. Builders, architects, designers, community planners, and real estate developers work hard to develop structures and communities which don't consume natural resources or harm the Earth's functioning. The goal is to meet today's needs with renewable resources while also providing for future generations' needs. Sustainable development seeks to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, slow global warming, protect natural resources, and create communities that enable people to fulfill their full potential. Sustainable development has also been referred to as green architecture, eco-design, eco-friendly architecture, earth-friendly architecture, environmental architecture, and natural architecture in the field of architecture. SUSTAINABLE ARCHITECTURE Sustainable architecture is defined as a building designed and built to considerably limit harm to the health of its people and the environment. A sustainable building is important because it uses less energy and water over time and is constructed with fewer chemically toxic materials. Characteristics of Sustainable Architecture Concentrate on lowering human impact on the environment. Renewable energy sources such as solar panels and natural heating, cooling, and ventilation systems reduce wasteful and harmful energy consumption. Buildings that generate at least as much energy as they consume, resulting in a net zero effect. Water conservation systems, such as rainwater collection and gray water recycling. Renewable materials such as bamboo, hemp, cork, flax, and soy are used. Replacement of traditional materials such as concrete with sustainable alternatives such as hempcrete (made from hemp, lime, and water) or conventional plastics with innovative bioplastics derived from algae. Utilization of recycled and upcycled materials. Adaptable, modular spaces, many of which are made of natural materials that can be easily disassembled, repurposed, or recycled. Tiny houses, micro-apartments, and other small structures help meet the demand for more sustainable housing while consuming less land and energy. Alternative housing solutions, such as homes and apartment buildings made from recycled shipping containers and floating architecture on waterways worldwide, are helping to address housing shortages in densely populated coastal areas. Incorporating plants and nature into existing buildings through living walls, tree-covered residential towers, and green roofs help cool them and create healthy biophilic environments for humans. GREEN BUILDING CODE The Philippine Green Building Code aims to improve building performance efficiency by implementing measures that promote resource management efficiency and site sustainability while minimizing buildings' negative impact on human health and the environment. The Code proposes a set of guidelines for resource efficiency, site selection, planning, design, construction, use, occupancy, operation, and maintenance. The Green Building Code shares the following principles: 1. The technical professionals, developers, contractors, property managers, and building owners involved in the planning, design, construction, and management of buildings have the opportunity to help the government address the adverse effects of climate change by ensuring that buildings are planned, designed, constructed, operated and maintained to the required efficiency level. 2. Resources must be used efficiently to equitably meet the developmental and environmental needs of the present and future generations. 3. Occupants of green buildings will benefit from improved indoor environmental quality, promoting higher productivity and better comfort. BERDE AND LEED The LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification is the most extensively used green building rating instrument in the world, designed by the US Green Building Council (USGBC). Certification represents excellence in design and construction at the highest level of sustainability. It deals with global issues like energy production and greenhouse gas emissions. It ensures lower carbon emissions, lower utility costs, and healthier environments by taking a holistic approach to building operations performance, developmental microclimate impact, and human behavior from facilities provided. On the other hand, the BERDE (Building for Ecologically Responsive Design Excellence) certification was developed by the Philippine Green Building Council (PHILGBC) as an appropriate response to the Philippine building industry's need to proactively address the adverse effects of climate change in the property sector. It addresses local issues such as transportation and the indoor environment's quality, air quality, light quality, and thermal comfort. It assesses and validates building performance that goes above and beyond existing mandatory building and environmental regulations and standards.