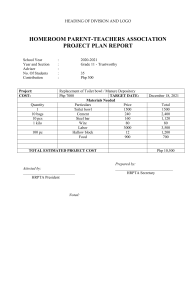
(~marketing-analytics.php) Product Validation MarketingMind BASES (https://www.addtoany.com/share#url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.ashokcharan.com%2FMarketingAnalytics%2F~pv(~marketingBASES.php&title=BASES%20%7C%20MM%20Marketing%20Mind%2C%20Research%20Analytics) analytics.php) (/#linkedin) BASES LinkedIn (/#twitter) Twitter (/#facebook) (/#whatsapp) WhatsApp (/#email) Email (Booz-AllenFacebook Sales Estimating System) is a STM which integrates consumer response data with manufacturers’ marketing plans to assess the volumetric potential of concepts and products prior to introduction. Product Validation The system was developed in 1977 by Lynn Y.S. Lin who at the time was with Burke Marketing Research. Lin was inspired by work on marketing simulators at Pillsbury where he was working prior to joining Burke. BASES was acquired by Nielsen in 1998. Product Validation (~pv- BASES Premise product-Consumers do not usually do what they claim to do; and often the difference between claims and validation.php) behaviours is very significant. This inconvenient truth, which complicates market research in general, must not be overlooked in product validation. Moments of Truth As with other STMs, BASES rides on the premise there exists a strong correlation between (~pv- that consumers’ claimed purchase behaviour and what subsequently transpires in the marketplace. While momentsconsumers overstate their intended purchase ofbehaviour, they tend to do so with consistency. truth.php) It has been observed that the level of overstatement varies by country, by culture, and by measure. With a database of about 200,000 concept tests (as of 2014), BASES is able to accurately estimate the adjustment factors required to deflate the respondents’ claims such that they closely reflect their behaviour. Launch Validation Methods (~pv- Model Structure validationmethods.php) Marketing Analytics Workshop In an analyticsdriven business environment, this analytics-centred consumer marketing workshop is tailored to the needs of consumer analysts, marketing researchers, brand managers, category managers and seasoned marketing and retailing professionals. What they SHOULD TEACH at Business Schools Simulated Test Markets (~pvSTM.php) BASES (~pv- Exhibit 11.5 BASES overview. An overview of the model is provided in Exhibit BASES.php) 11.5. BASES essentially takes consumer response data (what people say they will do), deflates it to adjust for overstatement, and adjusts for the impact of marketing activities to yield behavioural data (a forecast of what people will actually do). Controlled Store Data Collection Test (~pvCST.php) Product Launch Evaluation (~pvExhibit 11.6 Data collection at concept and product product-stage. launch- Online is the preferred and primary mode of data collection as it yields considerable savings in time evaluation.php) and cost of study. BASES has e-Panels in a ParfittCollins Model (~pv- number of markets in North America, Europe and Asia; the largest amongst these is the U.S. e-Panel, comprising 125,000. Where studies require face-to-face interaction (e.g. sniff or taste tests), mall intercept, controlled location tests and door to door methods are used for interviewing respondents. Is marketing education fluffy too? Experiential Learning via Simulators | Best Way to Train Marketers Marketing simulators impart much needed combat experiences, equipping practitioners with the skills to succeed in the consumer market battleground. They combine theory with practice, linking the classroom with the consumer marketplace. two stage interviewing process is depicted in parfitt- The Exhibit 11.6. The concept stage, where respond to questions on the product collins- respondents concept, yields information on product trial. model.php) In case of face-to-face interviews, those respondents who indicate they will not try the product (“definitely would not try”, “probably would not try”) are dropped from the product placement stage. For e-Panel surveys however, all respondents are moved to the product placement stage, and receive samples. After allowing respondents time to use the product samples, a post-usage interview is conducted to obtain information on respondents’ likelihood to repurchase the product. TRB Model (~pvTRBmodel.php) Bass Diffusion Model (~pvbassdiffusionExhibit 11.7 Example of a concept board (sourced model.php) from a student project, where ambrosia is a fictional beverage category). During the concept stage, either a concept board (like the one shown in Exhibit 11.7) or a commercial New Product Development is used for conveying the product concept and the (~np-newbrand’s positioning. The board contains the productdevelopment.php)information that will be communicated by Product Design advertising as well as details on prices, sizes and (~pd-product- varieties. Other than that, no additional information design.php) about the brand or competitor’s products is Product Validation (~pv-product- provided. validation.php) Analysis and Forecasting Marketing Education How to Choose the Right Marketing Simulator (~arHow-to-Choosethe-RightMarketingSimulator.php) Self-Learners: Experiential Exhibit 11.8 Purchase intent — proportion of Learning to Adapt to the New Age ofrespondent across a 5-point rating scale. Marketing (~arThe concept and after-use surveys obtain self-learnersexperientialinformation for the purpose of volume forecasting. learning-to-copewith-the-new- This includes purchase intent, purchase quantity norms-of(i.e. the quantity respondents’ claim they will buy marketing.php) should they try the product), and the frequency of Negotiation Skills purchasing should they continue to buy. The new Training for product is rated on the factors that typically evoke Retailers, Marketers, Trade consumers’ desire to purchase, for instance, Marketers and novelty, likeability, credibility and affordability. Category Managers (~ar- Information is also obtained on product usage, its negotiationsskills-training.php)perception on key image and performance attributes, suggested improvement, drivers and Simulators becoming inhibiters, and the source of volume. essential Training Platforms (~ar- Purchase intent is measured on a 5-point rating marketingscale similar to the one shown in the example in educationsimulatorsExhibit 11.8. Considering that it pertains to becomingessential-training-respondents’ claimed intent to purchase, we need platforms.php) benchmarks to interpret this information. Whether What they the top 2 box scores of 41% and 81% for concept SHOULD TEACH and after-use purchase intent are good or bad at Business depends on how they compare with the BASES Schools (~arwhat-theybenchmarks. should-teach-atbusinessBASES database of about 200,000 tests is the schools.php) primary device used for interpretation. It serves as Experiential Learning through the source for benchmarks for all key measures, Marketing both at the concept and after-use phase. It is noted Simulators (~arthat while after-use purchase intent strongly experientiallearningcorrelates with in-market success, purchase intent marketingsimulators.php) at the concept phase is not as good a reflection of in-market success. Success targets accordingly are derived from the after-use scores obtained for products that were tested by BASES and that subsequently achieved in-market success. Should a new product score higher than the BASES targets, it will have a high chance for success. To generate a forecast BASES requires the following inputs on the marketing plan for the new product: Introduction dates Budget Distribution and out-of-stock across retail channels Advertising schedule Consumer promotion schedule Trade promotion schedule Retail sales for category and company’s internal sales data Seasonality To the extent that execution is not in sync with plan, actual sales volume would differ from the BASES estimates. It is however possible to revise volume estimates based on revisions to the marketing plan. Exhibit 11.9 Volume estimation. The volume is forecasted by decomposing total sales into trial and repeat volume, as depicted in Exhibit 11.9. The forecast which pertains to the first two years of launch, yields trial volume, repeat volume, and consumption in terms of average frequency of purchase and the average quantity per occasion. In terms of key deliverables, BASES provides an estimate of a new product’s volume potential. It also estimates the product’s source of growth — how much the new product will cannibalize the company’s brands, and how much it will gain from competitors. In addition research diagnostics reveal the strengths and weaknesses of the new product initiative, and insights on how to improve the product, its mix and the execution plan. Previous Next Note: To find content on MarketingMind type the acronym ‘MM’ followed by your query into the search bar. For example, if you enter ‘mm consumer analytics’ into Chrome’s search bar, relevant pages from MarketingMind will appear in Google’s result pages. add a NOTE/COMMENT ... (../Destiny/index.php) (../MarketingAnalytics/index.php) (../MarketingAnalytics/dm.php) (../Solutions/solutions.php) Contact (https://www.ashokcharan.com/Contact/contact.php) | Privacy Statement (https://www.ashokcharan.com/login/privacy.php) | Disclaimer: Opinions and views expressed on www.ashokcharan.com are the author’s personal views, and do not represent the official views of the National University of Singapore (NUS) or the NUS Business School | © Copyright 2013-2022 www.ashokcharan.com. All Rights Reserved. We deploy cookies to improve your experience. By continuing to use our site you consent to the use our cookies. Ok