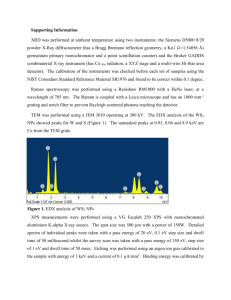
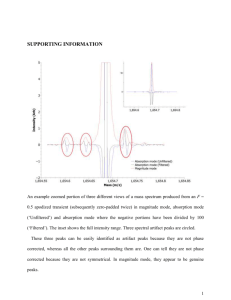
Midterm 2 Practice Problems 1. Give at least one technique to describe how you would characterize each of the following samples. Describe what the technique measures and why it would be useful. a. CaMnO3 at low temperature where it is antiferromagnetically ordered. b. LixFePO4 where you want to know the oxidation state and coordination environment of Fe ions c. NiPd alloy microparticles where you want to know elemental composition and distribution d. Cs2AgBiBr6 doped with 10% Tl, where you want to know if Tl prefers the Ag or Bi crystallographic site. e. The lead content of paint in your house. f. An oxide material that emits a different color light when it is irradiated with visible light. 2. Describe the differences between EDX, EELS, and XRF. Draw a diagram with Xrays/electrons interacting with a sample and/or its electronic states, followed by an output (photon, electron, etc.) that is measured. 3. How does magic-angle spinning in solid-state NMR solve the issue of broadening due to dipolar coupling and chemical shift anisotropy? 4. Give the intercepts and Miller index for the following plane, assuming this cubic unit cell: 5. Given an orthorhombic crystal, with a = 4 Å, b = 3 Å, and c = 5 Å, calculate the dspacing for the (835) plane. Then give the expected 2θ position of that diffraction peak. 6. Based on the following “PXRD pattern”, where blue lines represent measured peaks and orange lines represent expected (predicted) positions for peaks associated with a particular material, what could be two possible explanation for why there are some extra peaks present? 7. What is the wavelength of a neutron that is at a temperature of 400 K? 8. If you want to obtain scattering data over a wide range of Q (i.e., the scattering vector), what are two ways to accomplish this? 9. What do PDF and EXAFS have in common in terms of their output? 10. The following questions are about synchrotrons: a. What is a synchrotron? b. Name at least 4 techniques that are ideally performed at a synchrotron. c. Synchrotrons give off a broad range of X-rays. Describe one way to monochromate those X-rays. 11. What are the two main types of X-ray interaction with matter? 12. What is the difference between Bragg scattering and diffuse scattering? What technique combines both? 13. Give one example each of methods for characterizing local/defect structure, average crystal structure, nanostructure, and microstructure. 14. Here is a cyclic voltammogram. Mark which peaks are reduction peaks and which are oxidation peaks: 15. In the above CV, what is the electrochemical reference? 16. Here is a character table. Which vibrational modes are IR active? Which ones are Raman active? 17. What leads to Stokes and Anti-Stokes Raman? How does this relate to EELS? 18. Describe the main selection rules for UV-Vis spectroscopy 19. Which is faster, fluorescence or phosphorescence and why? Hint: see the previous question.