Underground Excavation: Micro-Tunneling & Trenchless Tech
advertisement

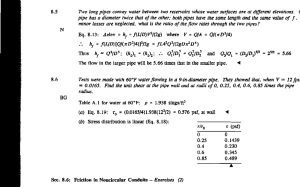
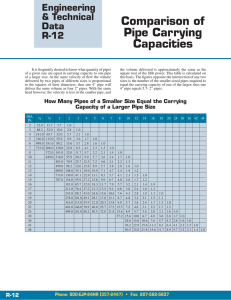
FOCUS www.EquipmentIndia.com Underground Excavation is Here to Stay Photo courtesy: Herrenknecht Asia Ltd Sub-terrain excavation and drilling to provide sustained connect for utilities, in urban spaces, is the essence of the challenge. It is adequately met by using micro-tunnelling and trenchless technologies. P ower, water and gas supply; modern high-tech electronic communications; Internet highways and connectivity linkages; provision of geo-sensitive alarms and signalling systems; safety connectivity; sewerage disposal and waste management facilities and many other such utilities are the undisputable essentials of modern urban and infrastructure development in the country. The above utilities need to be provided under the surface, in order to make them robust, reliable and sustainable, 56 under the most adverse climatic conditions and undisturbed from the numerous activities on the surface like traffic and other activities. Most developed countries have established norms, standards and laws governing the provisions of various utilities. However, in India, despite availability of sub-terrain drilling technologies, the implementation of the same has been highly self-discretionary so far. Going further, driven by the government’s impetus to modernising the utilities across the entire space of infrastructure and its plans to develop Smart Cities in India, it is safe to state that micro-tunnelling and trenchless construction is the need of the hour.Therefore, the government is bound to bring in regulatory statutes, making it mandatory by law in the country. Prashant Mehta, Director, Kem Tron Technologies, reinforces this view by commenting, “The oil & gas sector has planned to install 2,500 km of pipeline in the coming two-three years.With the strict environmental norms, there is a huge scope of using the recycling units for the river/highway/canal crossings to EQUIPMENT INDIA JULY 2016 Focus Lead - MIcro Tunelling & Trenchless-ok.indd 56 29-06-2016 5:48:23 PM FOCUS www.EquipmentIndia.com Photo courtesy: Kem Tron Technologies this equipment has been present for a long time, it is only now that a whole range of new markets have opened up, and the growth story is expected to continue for a long time to come. Coming to specifics as related to micro-tunnel boring machines, Anand Dwarkanath, South Asia Representative (Utility Division), Herrenknecht Asia Ltd, explains the challenges and the need for mitigation. He states, “Micro-tunnelling, as with all tunnelling, comes with construction risks that need mitigation during construction planning phase, equipment configuration and also during construction phase.The equipment supply business for micro-tunnelling is unlike other construction equipment businesses such as supply of excavators, dumpers, tower cranes, etc.” There is a major scope for trenchless equipment in the market. be installed where the use of bentonite slurry is required for operation. It has become mandatory to use our equipment for the same to avoid any environment issues and pollution.” Challenges and solutions To begin with, India has a long history of evolution of infrastructure development spanning over many centuries. At every stage, depending upon the comprehension of the implementers, available engineering, technologies and work methods, new systems were built many times over the existing facilities, and the older ones were made redundant and discarded in an as-is-where-is condition.There was no standardised approach, nor were the same documented, and the people involved are not alive anymore. This is one of the most significant and complex challenges involved in sub-terrain infrastructure development.Take for example cities like Kolkata, Mumbai, Chennai, New Delhi and other old cities on one side, and our first known national highway— Sher Shah Suri Marg — which was built much before the British era. Secondly, the geological uncertainties of unexplored sub-terrain conditions throw up many unforeseen, unpredictable and unprecedented challenges during construction. Modern imaging and soil investigating methods provide some relief. However, depending on the dimensions and shapes of small underground excavation required, different micro-tunnelling and trenchless equipment provide the best possible solutions in today’s world. In India, although “Micro-tunnelling comes with construction risks that need mitigation during construction planning phase, equipment configuration and construction phase.” Anand Dwarkanath, South Asia Representative (Utility Division), Herrenknecht Asia Ltd Micro-tunnelling option Dwarkanath, an expert in tunnelling, defines the term, “Micro-tunnelling is defined as a tunnelling method during which an unmanned tunnel boring machine is controlled remotely in pipe jacking from a control container on the surface. The process often involves active ‘face pressure’ control to keep the pressure in the machine excavation chamber balanced against the ground pressure and water pressure faced during excavation.” He adds,“Simply put, micro-tunnelling Micro-Tunnelling Applications • • • • • • Water supply pipelines, gravity sewer installation with different pipe materials such as vitrified clay, RCP, steel, composite, polycrete or even DI pipes River crossings for oil & gas pipes Railway crossings for multi-utility applications such as high-voltage cables Casing pipe installation for multiple carrier pipe applications Pedestrian subway installation using pipe-arch method Sea-water intake and effluent outfall applications for power plants and process plants. - Anand Dwarkanath JULY 2016 EQUIPMENT INDIA Focus Lead - MIcro Tunelling & Trenchless-ok.indd 57 57 29-06-2016 5:48:27 PM FOCUS www.EquipmentIndia.com Tunnel Alignment Methods • • • Electronic Laser System (ELS) comprising an active laser target (installed in the machine), a laser source (installed in the shaft), and a measurement wheel (length encoder) for pipe drive length measurement, together gives accurate straight or constant inclination tunnels for recommended distances up to 200 m. From tunnel length of 200 m to 400 m, length increases may begin to refract the laser beam upwards as a result of climatic conditions in the tunnel, thus affecting vertical deviation (grade) measurements. Therefore, in this case, millimetre level machine grade control is then achieved by a Hydrostatic Water Leveller (HWL) along with ELS. The HWL is a pressurised water tube that enables monitoring the elevation conferred pressure difference at the machine and shaft end. The difference in pressures indicates the actual elevation change of the machine. For over 400 m drive lengths, the laser beam turns weaker and diffused to a higher spot diameter that also ‘dances’ on the target. Therefore, a gyro device (which is a north-seeking gyrocompass) is used instead of a laser system.The gyro-compass is mounted on the machine to determine accurately the horizontal deviation of the latter. The elevation is checked with the help of the HWL system. Gyro is also used for curved drives. Operationally though, having advanced guidance systems does not absolve a contractor from having their surveyor crew personnel to do checks every day on the jacking shaft end. This is mainly to ensure that there have been no shaft movements due to high jacking forces, resulting in laser beam shifts, etc. For example, the laser mounted in the shaft should always be checked in relation to the survey points. - Anand Dwarkanath equipment are miniaturised versions of their large diameter counterparts, except that they involve ‘pipe-jacking’ in contrast to segmental lining. In other words, lower diameter shields, cylinders, slurry pumps, excavation transport components such as slurry pipes (for slurry machines), screw conveyors (in case of EPB machines) are all smaller in size compared to their large diameter counterparts.” Mehta defines the same, “Micro-tunnelling is a tunnelling process where the workforce does not routinely work in the tunnel. Micro-tunnelling is currently the most accurate pipeline installation method. Line and grade tolerances of one inch are the micro-tunnelling industry standard. This can be extremely important when trying to install a new pipeline in an area where a maze of underground utility lines already exists.” He adds, “Micro-tunnelling is an underground digging technique used to construct a tunnel for laying utility pipes lines like sewage, gas, water etc. Micro-tunnelling is a process that uses a remotely controlled Micro-tunnel Boring Machine (MTBM) combined with the pipe-jacking technique to directly install product pipelines underground “There will be major growth in trenchless equipment in the near future with the kind of infrastructure planned by the present government.” Prashant Mehta, Director, Kem Tron Technologies 58 in a single pass. This process avoids the need to have long stretches of open trenches for pipe-laying, which causes extreme disruption to the community at large.” What micro-tunnelling entails Dwarkanath explains, “Diameter difference also results in lesser number of cutting tools dressed on the cutting wheel/cutting head and creates the important difference of the location of the operator who sits on the surface outside inside the Control Container for micro-tunnelling machines, whereas he is inside the tunnel for large diameter machines.” He adds, “In addition, the tunnel lining method of precast segment installation necessitates a whole different set of equipment to transport, feed and erect the segments inside the tunnel in case of larger machines. In the case of pipe-jacking, these are usually clay, reinforced concrete pipes and steel pipes that are successively jacked in short lengths behind the machine, thus keeping the entire tunnel in constant motion until the machine reaches the exit shaft.” Thus, micro-tunnelling is different from segmental lining wherein the tunnel is static and each ring’s position is fixed as soon as it is erected. A large diameter tunnelling machine needs a segment erector to erect pre-cast lining, whereas the small diameter micro-tunnelling machine needs a ‘jacking station’ located at the entry shaft to push the pipes into the tunnel. The large diameter machine has no requirement for bentonite clay slurry to be injected surrounding the tunnel (in the annular gap), whereas micro-tunnelling equipment above 1 m diameter (pipe internal diameter) tend to have bentonite injection stations affixed in every 15 or so pipes that disburse bentonite in the annulus in order to reduce ground friction while pipe jacking. Micro-tunnelling created pipelines could be seen as ‘moving’, ‘floating’ pipelines that should be ideally jacked uninterrupted until the machine reaches its destination shaft. Thereby the risk in micro-tunnelling — pipe jacking is also higher even though drive lengths are EQUIPMENT INDIA JULY 2016 Focus Lead - MIcro Tunelling & Trenchless-ok.indd 58 29-06-2016 5:48:29 PM FOCUS Why machines get stuck underground • • • • Hard rock condition Soft soil collapse Very high discharge of underground water Improper tooling. shorter than in large diameter projects (100 m to 250 m average). Mehta mentions, “It is remotely operated small diameter tunnelling and is achieved by jacking pipes of concrete, or other suitable materials, behind a tunnelling machine, from a launch shaft into a reception shaft.” A typical micro-tunnel equipment spread consists of an MTBM matched to the expected subsurface conditions and the pipe diameter to be installed; a hydraulic jacking system to pipe jack the pipeline, a closed-loop slurry system to remove the excavated tunnel spoil; a slurry cleaning system to remove the spoil from the slurry water; a lubrication system to lubricate the exterior of the pipeline during installation; a guidance system to provide installation accuracy and an electrical supply and distribution system to power all of the above equipment. Top side equipment used to support the tunnelling operation usually includes a crane, pipe driving and dewatering equipment for shaft construction; backhoe and front end loaders for shaft www.EquipmentIndia.com excavation and spoil handling, and truck transport for equipment movement. Operational challenges & mitigation As mentioned earlier, micro-tunnelling entails what we might describe as a moving and floating tunnel that under ideal conditions, should have a fairly smooth passage from the entry shaft to exit shaft. It is a time-bound methodology where interruptions and waittimes, more than what would be reasonable, could translate quite rapidly to a failed drive, whereby the machine and the pipeline behind it can no longer be pushed further. In other words the drive is “stuck”. Following from this potential eventuality, these are all the risk-mitigation measures that need to be observed in order to ensure a successfully completed drive. Having said that, drive completion is also not the only measure of success. Equally important is the accuracy of installation, effect of the passage of the TBM on nearby ground strata thereby eliminating non-permissible levels of ground disturbance, settlements and the counter-measures taken such as annular grouting. Also important is site organisation efficiency that allows contractors sufficient width in time as well as cost savings, to meet the above operational challenges. In short, micro-tunnelling operation- Mitigating operational challenges • • • • • • 60 The main job of the operational person would be laying the pipelines within the tolerance limit. Practically, a lot of demanding situations are faced at the jobsite. Detailed geological study should be conducted before the start of the tunnelling process to identify the ground conditions. When crossing railway lines, gas and power lines tunnelling process should be carefully monitored so that existing infrastructure will not be affected. The pipe is attached behind the machine, after every pipe advance, a new pipe would be joined at the back side, forming a continuous tunnel. Here the whole tunnel is pushed by a jacking rig which has limited capacity.When the tunnel length increases, so does the frictional force. To overcome the frictional force along the line, lubrication fluid should be pumped on the periphery of the pipe. This helps to reduce the jacking load. With through knowledge of the area where work is to be undertaken, (through municipal and other official help of layout drawing of existing facilities), certain hurdles on the job are taken care of. - Prashant Mehta On surface support facilities • • • • • • • • • Mud recycling unit Mud mixing/preparation tank Shaker Baskets with wedge type screens Bentonite pumping unit Centrifugal pumps Cranes and lifting tools DG Set for power supply Jacking Frame High pressure water jet pumps Prashant Mehta al challenges are not all about the equipment. In fact, a major aspect of success in micro tunnelling operations is site preparation, readiness, efficiency of site logistics etc., that are called in to support the pipe-jacking process. Delays caused due to diesel supply, mobile crane availability, lack of readiness of jacking shafts, receiving shafts, lack of jacking pipes, inter-jack stations etc., can lead to a drive failure irrespective of how good the machine is. In contrast, laser guidance systems that are a feature of micro-tunnelling and pilot tube guided auger boring result in straight lines, smooth bores and tight gradient control. Drive accuracies better than ±1 inch are normal. The ground strata and its interplay with the pipe-jacking process, accumulation of fines in the annular gap, leaking tunnel pipes (bentonite leaks), site delays and interruptions that would in unstable ground end in the ground ‘catching’ the pipeline are broad reasons that equipment get stuck in the tunnel. Sometimes, parts of the pipeline can be freed up by injecting large volumes of bentonite or additives surrounding identified areas of the pipeline and the jacking can continue. This is where advanced bentonite injection station systems come into play, on their own. The ones from Herrenknecht are normally installed every 15 m of the pipeline and the bentonite can be injected in time as well as volumetric measure. Other mitigating measures a site project manager could take, is to invest in inserting an Inter-jack Station (IJS) for introducing supplementary pushing EQUIPMENT INDIA JULY 2016 Focus Lead - MIcro Tunelling & Trenchless-ok.indd 60 29-06-2016 5:48:29 PM FOCUS www.EquipmentIndia.com Used equipment options Trenchless Method Horizontal Directional Drill (HDD) equipment is used for underground construction. It is a trenchless method of installing a pipe in the ground at variable angles using a guidable drill head.The technology is a preferred trenchless method for installing underground pipes, cables (OFC and power cables) ranging from large size pipeline river crossings to small diameter cable conduits and railway signalling cables. HDD is a proven, environment-friendly method, which apart from being cost-effective, also imposes minimal disruption to the community and surrounding infrastructure. Depending on pipeline installation parameters such as length, diameter, pipe material, geotechnical strata information, depth of pipeline, ground water levels etc., it may be possible to choose alternative methods to micro-tunnelling. One can even consider methods that are close to micro-tunnelling such as the Pilot Tube Auger Guided Boring Method. Competitive trenchless methods including Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD), pipe bursting, pipe ramming etc., can also be looked at. However, the pros and cons, capabilities and limitations of trenchless methodologies should be studied in detail before any method is finalised. Pilot tube auger boring, for example, could be an economic accurate gravity sewer installation solution for small diameters in the range of 150 mm to 600 mm.The advantage is in ease and economy of operation. Also PVC, HDPE pipes can be installed in this way. Moreover, there are now ways to install pipes at these diameters in up to 20 Mpa strength ground using our front steer system in hard rock up to 140 Mpa using front steer with air hammer up to 100 m with high accuracy. However, there are bound to be some limitations to technology use. On the other hand, HDD is suited for pumped sewerage and water supply pipelines, but is not considered a suitable method for gravity sewers. The drill hole is much bigger than the pipe it carries. In homogenous ground, it is difficult to ensure a smooth bore, resulting in undulating inverts, and drill bit deflections often result in a deviated path lying between point A and B. - Parth Patel, Director, Apollo Techno Equipments force available for use along the pipeline. Factors inducing IJS installation are primarily the total length of the tunnel influencing the sum of ground friction expected along the pipeline, along with other predicted ground strata-related risks such as soil/rock permeability resulting in loss of bentonite to the nearby ground, presence of structures above or near the pipeline such as a concrete foundations, manholes etc., that can weigh on a pipeline and increase the overall jacking forces. However, if the pipeline refuses to move despite all good efforts, then the only practical option usually is to excavate a rescue pit and pull the machine out with a mobile crane. It may be possible to convert the rescue pit into an intermediate shaft/manhole and drive into it from the other end based on project design. “Apollo Techno Equipments is the first in the country to manufacture Horizontal Directional Drill equipment.” Parth Patel, Director, Apollo Techno Equipments 62 While it is true that second-hand/ used equipment are often available, they are also often poorly maintained or not in working or warranty-worthy conditions when they put up for sale by an owner/contractor. Often, the equipment is sold ‘as-is’ and this is not convenient for the buying party from India, who would have greater expectations of performance from the equipment set. This is especially true for projects with risky tunnel layouts, topography, location (either in hinterland or built-up areas) and most importantly where geotechnical conditions (ground strata) are complex or less predictable. From a cost perspective too, prices for ‘as-is’ equipment could be unrealistically high in relation to its condition. The above would provide some insight as to why surplus equipment lying around elsewhere doesn’t automatically translate into a great purchase opportunity for Indian contractors. In the end these equipment need to ripped apart in a qualified facility, critical items need to be checked for the life-worthiness, hydraulic and electrical parts need replacing, the equipment needs to be put together and tested to be working together as a unit worthy enough of re-warranty. It is for this peace of mind that a buyer should be willing to part with his precious dollars. The question of going in for an imported or local make is a completely different one. This usually relies on the ability of the equipment manufacturer to source a niche, repetitively reliable supply chain that helps them determine a high build quality. On the other hand, India has been waiting since long on independency of indigenous Horizontal Directional Machines for laying telecom OFC, power cables, gas line connectivity, water and sewer pipes, and other utilities. Indian contractors now have better opportunities to procure machines in the least possible time with the availability of spare parts and engineer support to contractors across the nation. Patel says, “Apollo Techno Equipments is the first in the country to manufacture Horizontal Directional Drill equipment. EQUIPMENT INDIA JULY 2016 Focus Lead - MIcro Tunelling & Trenchless-ok.indd 62 29-06-2016 5:48:29 PM FOCUS www.EquipmentIndia.com Advantage Trenchless • • • • • • • • • • • Pipes can be installed either in straight lines or curved to avoid any obstacles. Working area is confined to the points of entry and exit only, causing less disruption and aiding. No disruption to road, river or rail traffic and less impact on landscapes. Short, medium or long lengths of pipe can be installed without the need for intermediate pits. Horizontal Directions Drilling is a much quicker process and in many cases has lower overall costs due to fewer workmen required. It’s unaffected by surface obstacles. Can be used to install pipes in changeable ground system. Flexibility (can be used anywhere). Less soil contamination (reduces damage to valuable resources). Optimises safety and hygiene at work. Reduces impact on environment. -Prashant Mehta tions and are also put through more number of work cycles. The models on offer for Indian markets are A400 to A800 with pulling force ranging from 12 to 20 tonne and torque from 5,500 to 6,500 NM, thereby providing a viable alternative to Indian buyers against using used equipment.” Market size & drivers Micro-tunnelling equipment is ver- Photo courtesy: Apollo Techno Equipments The world-class Horizontal Directional Drilling equipment is ideally suited for the unique Indian working conditions. The company offers various types of HDD equipment. Apollo Techno Equipments’ HDD machines are the perfect testimony to the ‘Make in India’ capabilities, offering unmatched performance. Every aspect of the machine has been made for India where such equipment need to take on tough working condi- Apollo Techno Equipments’ HDD machines are the perfect testimony to the ‘Make in India’ capabilities. 64 satile and suitable for various grounds, covering many different cities of India. Their biggest use is for creating underground sewerage and water transmission pipelines. In many cases, these sewerage pipelines are gravity flow based, therefore high accuracy in gradient is required. Micro-tunnelling machines with their advanced guidance features have a big role to play in such projects. Smart Cities are also by definition meant to be environmentally sustainable cities. Therefore it goes with the assumption that infrastructure such as sewer lines, cable lines, multi-utility pipelines and water pipelines are already laid out to cover the needs of future generations right from the beginning. Once the roads have been surfaced and infrastructure by way of above-ground structures is cemented, re-laying and re-digging defeats the purpose and creates huge environmental costs. We have several examples of this situation all over India and abroad. From a futuristic angle, investors (government or private) can create tunnel infrastructure that can be rented out to interested parties in the future. This may require slightly larger pipes or one large pipeline crossing the city with tapping points in between. That is why railway corridors have been crucial when it comes to cutting across already built-up infrastructure in cities like Mumbai. Private Internet providers etc, have benefited from these arrangements in the past. Smart Cities would substantially drive demand only if the planners take into account the capabilities of modern micro-tunnelling equipment. Mehta says, “There is a major scope for trenchless equipment in the market. Almost all authorities are required to adopt this technique for the safety of the utility installed and also minimum hindrance to the above-ground services. There will be major growth in this field in the near future with the kind of infrastructure planned by the present government.” EI The future lies underground! - SHANKAR SRIVASTAVA EQUIPMENT INDIA JULY 2016 Focus Lead - MIcro Tunelling & Trenchless-ok.indd 64 29-06-2016 5:48:30 PM