Periodic Table & Electron Configuration: High School Chemistry
advertisement

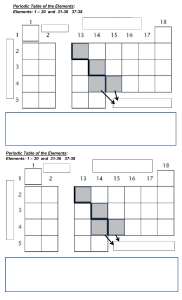
The Periodic Table of Elements Electrons in an Atom In the modern periodic table of elements, the elements are arranged according to the increase of proton number (Z) There are three types of elements in the periodic table: metals (on the right side and in the middle of PTE), nonmetals (on the left side) and semimetals or metalloids (just between metals and nonmetals) Rows in the periodic table are called periods and they are numbered from 1 to 7 Columns in the periodic table are called groups. The 18 columns of the periodic table are assigned the numbers 1-18, beginning with the column farthest to the left. Names of some groups in the periodic table have the origin in the characteristic properties of elements in that group. Also, some groups are named after the first element in that group. 1st Group of elements: Alkali Metals 2nd Group of elements: Alkaline earth elements 3rd -11th group - Transition metals 13th Group – Boron group 14th group – Carbon group 15th group – Nitrogen group 16th group – Chalcogen group (Chalcogens) 17th group – Halogen group (Halogens) 18th group – Noble gases Every electron is moving very fast around the nucleus and has characteristic energy state called shell. The lowest energy has a shell that is closest to the nucleus. There are 7 possible shells and they are labeled with the letters K, L, M, N, O, P and Q or with the numbers n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 – the rows in the periodic table correspond to that 7 shells of atom Important notice: • We can not know exactly where some electron in an atom is at the particular moment. Because of that, we are describing electrons in an atom as an electron cloud. Every shell can be filled with determined amount of electrons The greatest number of electrons that can take place in one shell is 2n2 n = shell number Electrons fill the shells from the one that is at the lowest energy (closest to the nucleus) to higher ones.