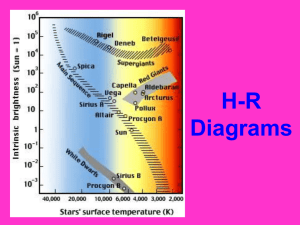
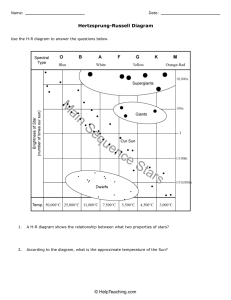
Name: Class: Date: SPECIAL TOPIC - THE HERTZSPRUNG-RUSSEL DIAGRAM About 100 years ago, two astronomers working independently made the same discovery. Both Ejnar Hertzsprung in Denmark and Henry Russell in the U.S. made graphs to find out if the temperature and the absolute brightness of stars are related. They plotted the surface temperature of stars on the x-axis and their absolute brightness on the y-axis. The points formed a distinct pattern. The graph they made is called the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, or H-R diagram. Astronomers use the H-R diagram to classify how stars change over time. Most of the stars in the H-R diagram form a diagonal line called the main sequence. More than 90% of stars, including our Sun, are main-sequence stars. In the main-sequence, as temperature increases, absolute brightness increases. Thus, hot bluish stars are located on the left and cooler, reddish stars are located on the right. The brightest stars are located near the top of the H-R diagram, while the dimmest stars are located on the bottom. Giant and supergiant stars are very bright and can be found near the top right of the diagram. White dwarfs are hot, but not very bright, so they appear at the bottom left of the diagram. SPECIAL TOPIC - THE HERTZSPRUNG-RUSSEL DIAGRAM 1. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram shows the relationship between the temperature of stars and what? 2. What is measured on the x-axis? What is measured on the y-axis? x-axis: _______________________ y-axis: _______________________ 3. The area on the H-R diagram that runs from the upper left to the lower right and includes more than 90% of all stars is called the _____________________________. 4. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true based on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. a. The Sun is a main-sequence star. b. The absolute brightness of a white dwarf is greater than supergiant stars. c. Polaris, a yellow supergiant, is hotter than Sirius B, a blue-white dwarf. d. The absolute brightness of Polaris would be greater than the Sun. 5. Use the H-R diagram below to answer the following questions High A Brightness B C D E Low F High Temperature Low a. Which star has the greatest brightness? ______ b. Which star has the hottest surface? _______ c. Stars C and D have the same brightness. What 2 things are different about them? d. Which star is most likely a supergiant? _______ e. Which star is most likely to be blue-white in color? ________