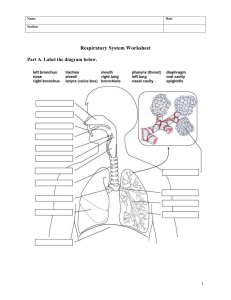
Pre-test: Multiple Choice. Choose the letter of the best answer. Write the chosen letter on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What body system is responsible for supplying oxygen to the body? A. skeletal system C. respiratory system B. circulatory system D. excretory system 2. Which major part of the respiratory system performs the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide with air from the atmosphere? A. Mouth B. Lungs C. diaphragm D. bronchi 3. What is the function of the alveoli? A. It allows the gas exchange in lungs B. It serves as passageway of air into the lungs. C. It is the organ through which air enters and then filtered. D. It is in charge of supplying oxygen into the lungs. 4. What is the role of the pharynx in the respiratory system? A. It transfers the gases from the airways to the blood B. It enables air from the nasal passage to enter the trachea C. It enables air to enter the nasal passage. D. It filters and purifies the air 5. What is the name of this structure that serves as channel where air enters the body; warmed, cleaned, and moistened? A. nasal passage B. mouth C. trachea D. lungs 6. What structure of the circulatory system transports the blood throughout the body? A. Artery B. Heart C. blood vessel D. pipe 7. What is the role of the heart in the circulatory system? A. It pumps the oxygen-rich blood throughout the body B. It carries the blood throughout the body C. It carries materials throughout the body D. It decreases the amount of oxygen in the blood 8. How many chambers does a human heart have? A. 3 B. 4 C. 5 D. 6 9. What are the functions of the atria of the heart? A. They are the pumping chambers, moving the blood to the lungs and into the body. B. They are the receiving chambers of the heart, accepting blood from the body and from the lungs. C. They force the blood out into the arteries. D. They control movement of the blood into the heart chambers and out of the aorta and the pulmonary artery. 10. Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? A. Arteries B. Veins C. capillaries D. arteries and capillaries The respiratory system is made up of the organs in the body that help us to breathe. Breathing is just one of the functions that the respiratory system carries out. Respiration, the process of gas exchange, is another important function performed by the respiratory system. It includes all of the mechanisms involved in getting oxygen to the cells of your body and getting rid of carbon dioxide. Phases of Respiration 1. Breathing – the act of taking air in (inspiration) and out of the lungs (expiration). 2. External respiration – exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air and the blood within the lungs. 3. Internal respiration – exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood and body cells. 4. Cellular respiration – the process of using oxygen to break down sugar in food, producing energy (ATP) in cells and releasing carbon dioxide as a waste product. Parts and Its Functions KEY CONCEPT: The air we breathe goes through the nose, nasal passages, and then through trachea or windpipe, which separates into two branches, called bronchial tubes or bronchi, one entering each lung. The bronchi subdivide many times inside the lungs, analogous to the branching pattern of grapes, finally becoming hairlike tubes called bronchioles. In the last part of the terminal bronchioles are tiny bubble-like bunch of structures called alveoli or airsacs. The circulatory system is the life support structure that nourishes your cells with food and oxygen. It also carries away the waste products. The following are the three major parts of the circulatory system, with their roles: 1. Heart – pumps the blood throughout the body. 2. Blood vessel – carries the blood throughout the body. Arteries - carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the cells, tissues, and organs of the body Veins – carry deoxygenated blood to the heart Capillaries - the smallest blood vessels in the body, connecting the smallest arteries to the smallest veins - the actual site where gases and nutrients are exchanged 3. Blood – carries the materials throughout the body. CIRCULATION TYPE OF CIRCULATION DESCRIPTION DIAGRAM 1. Pulmonary Circulation Movement of blood from the heart to the lungs, and back to the heart. 2. Coronary Circulation Movement of blood through the tissues of the heart. 3. Systemic Circulation Movement of blood from the heart to the rest of the body, excluding the lungs Effects of Lifestyle on the Functioning of Respiratory and Circulatory System Respiratory disease are conditions that affects your airways and lungs Some of these are discussed below. 1. Asthma – is a condition when a person experiences difficulty in breathing as a result of the narrowing and swelling of the bronchial airways. 2. Common Cold – disease affecting the upper respiratory tract (nose and throat). It is transmitted by virus infected airborne droplets or by direct contact with infected secretions. 3. Pneumonia – is the infection of the lungs caused by viruses and bacteria wherein the alveoli in the lungs are inflamed and become filled with liquid and pus making it difficult for the lungs to transfer oxygen to the blood. 4. Influenza – is caused by the influenza virus that attacks your throat, nose and lungs. It is a highly contagious disease and can spread directly through air droplets. 5. Bronchitis - is the inflammation or swelling of bronchial tube lining. Person with bronchitis may experience breathing difficulty because of the mucus or phlegm forms in the airways obstructing the flow of oxygen into the lungs. 6. Tuberculosis (TB) – is a bacterial infection of the lungs caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis. 7. Coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) - infectious disease caused by a new strain of coronavirus that infect both people and animals. The virus passes through the nose, sinuses, and throat and reached the lungs. Circulatory Disease is an interruption, blockage, or diseases that affect how you heart or blood vessels pump blood. Here are some of the common conditions affecting the circulatory system: 1. Atherosclerosis – is a condition that develops when a substance called plaque builds up in the walls of the arteries making it harder for blood to flow through. The risk factors for these diseases are smoking, eating food high in fats, excessive alcohol intake, diabetes and increased stress. 2. Stroke – occurs when it damages the brain when a blood vessel gets blocked or leaked usually from a blood clot. Some risk factors for stroke include smoking, high blood pressure, excessive alcohol intake and diabetes. 3. Hypertension –known as the silent killer due to the fact that people with hypertension usually have no symptoms. The causes of this disease include obesity, diabetes, lack of fruits and vegetables in the diet and high salt intake. 4. Heart attack – occurs when the blood flow to the part of the heart is blocked by blood clot, the heart muscle supplied by the artery begins to die. The causes for the heart attack are atherosclerosis, diabetes, and high-blood pressure. The following are some ways to prevent respiratory and circulatory diseases: 1. Good nutrition, good sleep and rest enhances your immune system that helps the body to resist infections. And avoid eating high cholesterol and fatty foods. 2. Do not smoke. Cigarettes contain harmful substances that can be fatal to your body. 3. Exercise regularly. It improves the health of your lungs and heart. 4. Observe strict personal hygiene. Always keep your body clean because it will reduce the risk of catching any diseases. 5. Avoid crowds. Avoid direct contact with person suffering from respiratory diseases. Activity 1: Name Me (Human Respiratory System Activity 2: Complete me! As shown in the diagram, the parts of the Respiratory System are labelled 1, 2, 3 etc. Below the diagram is a table with three columns. The first column refers to the labelled parts on the diagram, the second column (A, B, C, etc.) are the parts of the respiratory system and lastly (r, s, t, etc.) are the functions. Your first task is to unscramble the letters of each word found in the second column. Then, match the first column to the second column and to the third column by writing the letter/s for each number. Write your answer on a separate sheet of paper. Below is a simplified path of the blood flow inside our body. You are asked to identify first the parts of the heart indicated by A-D. Also, name the two arrows labelled as E and F which represents the pathways. By looking at the diagram, fill in the blanks on How blood flows through the heart. Write your answer on a separate sheet of paper. Example: 1. C. NASAL CAVITY– w How blood flows through the heart? PARTS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM A. MAIDGRAPH B. CHEATAR C. ALSAN VACITY D. SNUGL E. VIALOLE F. BONRICH G. SCHOOLBRINE H. XYLARN I. HAXYNRP FUNCTIONS r. also called windpipe; a hollow tube that serves as passageway of air into the lungs s. also called bronchial tubes; two branching tubes that connect the trachea to the lungs t. also called air sacs; allow the gas exchange in lungs u. Located behind the nasal cavity and above the larynx. Food as well as air passes through it v. associated with the production of sound; is situated in the neck of mammals and plays a vital role in the protection of the trachea w. the organ through which the air enters and is filtered x. the finer subdivisions of bronchi; hair like tubes that connect to alveoli y. either of the paired respiratory organs, situated inside the rib cage, that transfer oxygen into the blood and remove carbon dioxide from it z. muscular wall below the rib cage that contracts when we exhale Blood from the body travels into the (A) _________, moves into the (C)__________, and is finally pushed into the lungs in the pulmonary (E)_____________. The blood then picks up oxygen and travels back to the heart into the (B)_______________through the pulmonary (F)__________. Then it travels through to the (D) and exits the body through the aorta. Activity 3: Prevention is Better than Cure! Make an infographic disseminating information on effective ways of taking care of respiratory and circulatory system. RUBRIC CATEGORY Presentation Creativity and Originality 5 The infographic clearly communicates the main idea and strongly promotes awareness All of the graphics used 4 The infographic communicates some of the important ideas and slightly promotes awareness Most of the graphics used 3 The infographic indirectly communicates the idea and hardly promotes awareness The graphics 2 The infographic does not sufficiently communicate any idea that can promote awareness The graphics lacks 1 The infographic does not communicate any idea at all that can promote awareness The graphics were not Accuracy and Relevance of the Content Required Elements on the poster reflect an exceptional degree of student ingenuity in their creation. All graphics in the infographic are accurate and related to the topic. on the poster reflect student ingenuity in their creation. The infographic includes all required elements as well as additional information All required elements are included. Most graphics in the infographic are accurate and related to the topic. were made by the student but were copied from the designs or ideas of others. Some graphics in the infographic are accurate and related to the topic. originality and does not reflect student ingenuity in their creation made by the student. The graphics in the infographic are neither accurate nor related to the topic. Few required elements are included. Required elements are missing All graphics in the infographic does not make sense and not related to the topic. All elements does not relate to the topic. ASSESSMENT: Choose the letter of the best answer. Write your answers on a separate sheet of paper. 1. Which are the organs of the respiratory system? A. Lungs, heart, and blood. B. Rib cage, diaphragm, and lungs. C. Nose, lungs, heart, and diaphragm D. Lungs, throat, and passageways that lead to the lungs 2. What happens in the diaphragm when we exhale (breathe out)? A. The diaphragm relaxes and moves upwards. B. The diaphragm contracts and moves upwards. C. The diaphragm relaxes and moves downwards. D. The diaphragm contracts and moves downwards. 3. What will happen if the epiglottis does not close the entrance of airways? A. The larynx will be blocked with food particles. B. The pharynx will have difficulty in swallowing. C. The food particles will block the opening of the trachea and a person will have difficulty in breathing. D. The food particles will block the bronchioles thus making it difficult to breathe in and breathe out. 4. What important activity takes place in the lungs? A. Food is digested. B. Liquid waste is filtered from the blood. C. The trachea is exchanged for the larynx. D. Oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide. 5. Which statement is true about the human circulatory system? A. It makes blood cells. B. It transports oxygen and nutrients. C. It breaks down food and releases nutrients. D. It is the first line of defense against bacteria. 6. Which blood vessel carries blood back to the heart? A. Artery B. Blood vessel C. Capillary D. Vein 7. Which is NOT a function of the circulatory system? A. Deliver oxygen and nutrients to cells. B. Break down carbohydrates into glucose. C. Transport other materials through body. D. Remove carbon dioxide and wastes from cells. 8. If a rupture occurs in the pulmonary artery, which passageway is affected? A. The passageway of blood going to aorta. B. The passageway of blood going to lungs. C. The passageway of blood going to vena cava. D. The passageway of blood going to right atrium. 9. What type of circulation carries oxygenated blood to the body? A. Bodily Circulation C. Pulmonary Circulation B. Coronary Circulation D. Systemic Circulation 10. How do the respiratory and circulatory systems work together? A. They supply the body's cells with oxygen. B. They are responsible for the movement of the body. C. They break down food into energy and eliminate waste. D. They send chemical signals throughout the body via hormones.