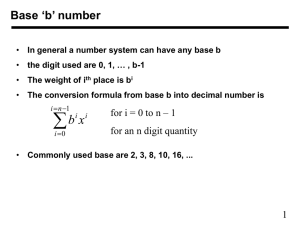
Practical class № 1 Subject: «The role of ICT in key sectors of the development of society. Standards in the field of ICT, Number systems. Transfer numbers from one number system to another. Arithmetic in the number systems.» Purpose: To acquire the skills of operations in different number systems. There are many methods or techniques which can be used to convert numbers from one base to another. We'll demonstrate here the following Basic Concepts: Information and communications technology (ICT) is an extended term forinformation technology (IT) which stresses the role of unified communicationsand the integration of telecommunications (telephone lines and wireless signals), computers as well as necessary enterprise software, middleware, storage, and audio-visual systems, which enable users to access, store, transmit, and manipulate information. Information and communications technologies (ICT) are a diverse set of technological tools and resources used to communicate, and to create, disseminate, store, and manage information. Information Communications and Technology (ICT) is a term that refers to all the hardware and software that people use to send and receive information. Social networking sites such as Facebook, Twitter and MySpace, computers, phones and tablets make up the term ICT. Over the past few years, the ICT sector has grown substantially with a lot of new companies releasing new gadgets to improve how we communicate. Information and communication technologies for development (ICT4D) refers to the use of information and communication technologies (ICTs) in the fields of socioeconomic development, international development, and human rights. The theory behind this is, more and better information and communication furthers the development of a society. World experience of ICT development Beginning in the 1980s, during the rise of the level of use of personal computers, as well as a consequence of increased demand for software products and completing formation of the different approaches of state policy towards the development of the ICT sector. Next, the transition to digital telecommunications in the 1990s and the subsequent formation of the Internet, the impetus to promote the further development of ICT in the world. A lot of approaches to ICT development conventionally divided into two directions: the first - the development of ICT production and services (computers, software, devices, telecommunications and others.), In order to increase output and to strengthen ICT industry - "ICT as a manufacturing sector "; the second - the introduction of ICTs in different sectors of the economy, to maximize the information society and economy - "ICT as a tool of information society." Within these two areas can be classified in the following levels of strategic approaches: the development of the ICT sector, export-oriented; ICT sector development, oriented to the domestic market; approach global positioning; ICT as a tool for social and economic development. Consider these approaches on country practices. In modern society ICT is everpresent, with over three billion people having access to the Internet. With approximately 8 out of 10 Internet users owning a smartphone, information and data are increasing by leaps and bounds. This rapid growth, especially in developing countries, has led ICT to become a keystone of everyday life, in which life without some facet of technology renders most of clerical, work and routine tasks dysfunctional. The most recent authoritative data, released in 2014, shows "that Internet use continues to grow steadily, at 6.6% globally in 2014 (3.3% in developed countries, 8.7% in the developing world); the number of Internet users in developing countries has doubled in five years (2009-2014), with two thirds of all people online now living in the developing world. Favorably, the gap between the access to the Internet and mobile coverage has decreased substantially in the last fifteen years, in which "2015 is the deadline for achievements of the UN Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), which global leaders agreed upon in the year 2000, and the new data show ICT progress and highlight remaining gaps."ICT continues to take on new form, with nanotechnology set to usher in a new wave of ICT electronics and gadgets. ICT newest editions into the modern electronic world include smart watches, such as the Apple Watch, smart wristbands such as the Nike+ FuelBand, and smart TVs such as Google TV. With desktops soon becoming part of a bygone era, and laptops becoming the preferred method of computing, ICT continues to insinuate and alter itself in the ever-changing globe. Standards in the field of ICT A new generation of components and systems ICT1 – 2016: Smart Cyber-Physical Systems ICT2 – 2016: Thin, Organic and Large Area Electronics ICT3 – 2016: SSI – Smart System Integration ICT4 – 2017: Smart Anything Everywhere Initiative ICT5 – 2017: Customized and low energy computing ICT6 – 2016: Cloud Computing Number systems. Decimal to Other Base System Other Base System to Decimal Other Base System to Non-Decimal Shortcut method - Binary to Octal Shortcut method - Octal to Binary Shortcut method - Binary to Hexadecimal Shortcut method - Hexadecimal to Binary Decimal to Other Base System Steps Step 1 - Divide the decimal number to be converted by the value of the new base. Step 2 - Get the remainder from Step 1 as the rightmost digit (least significant digit) of new base number. Step 3 - Divide the quotient of the previous divide by the new base. Step 4 - Record the remainder from Step 3 as the next digit (to the left) of the new base number. Repeat Steps 3 and 4, getting remainders from right to left, until the quotient becomes zero in Step 3. The last remainder thus obtained will be the most significant digit (MSD) of the new base number. Example Decimal Number: 2910 Calculating Binary Equivalent: Remaind Step Operation Result er Step 1 29/2 14 1 Step 2 14/2 7 0 Step 3 7 / 2 3 1 Step 4 3 / 2 1 1 Step 5 1 / 2 0 1 As mentioned in Steps 2 and 4, the remainders have to be arranged in the reverse order so that the first remainder becomes the least significant digit (LSD) and the last remainder becomes the most significant digit (MSD). Decimal Number: 2910 = Binary Number: 111012. Other base system to Decimal System Steps Step 1 - Determine the column (positional) value of each digit (this depends on the position of the digit and the base of the number system). Step 2 - Multiply the obtained column values (in Step 1) by the digits in the corresponding columns. Step 3 - Sum the products calculated in Step 2. The total is the equivalent value in decimal. Example Binary Number: 111012 Calculating Decimal Equivalent: Step Binary Number Step 1 111012 Step 2 111012 Step 3 111012 Decimal Number ((1 x 24) + (1 x 23) + (1 x 22) + (0 x 21) +(1x 20))10 (16+8+4+0+1)10 2910 Binary Number: 111012 = Decimal Number: 2910 Other Base System to Non-Decimal System Steps Step 1 - Convert the original number to a decimal number (base 10). Step 2 - Convert the decimal number so obtained to the new base number. Example Octal Number: 258 Calculating Binary Equivalent: Step 1: Convert to Decimal Step Octal Number Decimal Number Step 1 258 ((2 x 81) + (5 x 80))10 Step 2 258 (16 + 5 )10 Step 3 258 2110 Octal Number: 258 = Decimal Number: 2110 Step 2: Convert Decimal to Binary Step Operation Result Remainder Step 1 21/2 10 1 Step 2 10/2 5 0 Step 3 5 / 2 2 1 Step 4 2 / 2 1 0 Step 5 1 / 2 0 1 Step 1 - Divide the binary digits into groups of three (starting from the right). Step 2 - Convert each group of three binary digits to one octal digit. Example Binary Number: 101012 Calculating Octal Equivalent: Step Binary Octal Number Number Step 1 101012 010 101 Step 2 101012 28 58 Step 3 101012 258 Step 1 - Convert each octal digit to a 3 digit binary number (the octal digits may be treated as decimal for this conversion). Step 2 - Combine all the resulting binary groups (of 3 digits each) into a single binary number. Step Octal Number Step 1 258 Step 2 258 Step 3 258 Binary Number 210 510 0102 1012 0101012 Step 1 - Divide the binary digits into groups of four (starting from the right). Step 2 - Convert each group of four binary digits to one hexadecimal symbol. Example Binary Number: 101012 Calculating hexadecimal Equivalent: Step Binary Hexadecimal Number Number Step 1 101012 0001 0101 Step 2 101012 110 510 Step 3 101012 1516 Step 1 - Convert each hexadecimal digit to a 4 digit binary number (the hexadecimal digits may be treated as decimal for this conversion). Step 2 - Combine all the resulting binary groups (of 4 digits each) into a single binary number. Example Hexadecimal Number: 1516 Calculating Binary Equivalent: Step Hexadecimal Binary Number Number Step 1 1516 110 510 Step 2 1516 00012 01012 Step 3 1516 000101012 Hexadecimal Number: 1516 = Binary Number: 101012 Тasks. 1. This figure in the decimal system to translate into binary, octal and hexadecimal numbers. 2. Set this a number on the decimal system. 3. Add the numbers. 4. Perform subtraction of numbers 5. perform the multiplication operation. Variant 1 1. а) 860(10); б) 785(10); в) 149,375(10); г) 953,25(10); д) 228,79(10). 2. а) 1001010(2); б) 1100111(2); в) 110101101,00011(2); г) 111111100,0001(2); д) 775,11(8); е) 294,3(16). 3. а) 1101100000(2) + 10110110(2); б) 101110111(2) + 1000100001(2); в) 1001000111,01(2)+100001101,101(2); г) 271,34(8)+1566,2(8); д) 65,2(16)+3CA,8(16). 4. а) 1011001001(2) – 1000111011(2); б) 1110000110(2) – 101111101(2); в) 101010000,10111(2) – 11001100,01(2); г) 731,6(8) – 622,6(8); д) 22D,1(16) – 123,8(16). 5. а) 1011001(2) ´ 1011011(2); б) 723,1(8) ´ 50,2(8); в) 69,4(16) ´ A,B(16). 6. а) 250(10); б) 757(10); в) 711,25(10); г) 914,625(10); д) 261,78(10). 7. а) 1111000(2); б) 1111000000(2); в) 111101100,01101(2); г) 100111100,1101(2); д) 1233,5(8); е) 2B3,F4(16). 8. а) 1010101(2)+10000101(2); б) 1111011101(2)+101101000(2); в) 100100111,001(2)+100111010,101(2); г) 607,54(8)+1620,2(8); д) 3BF,A(16)+313,A(16). 9. а) 1001000011(2) – 10110111(2); б) 111011100(2) – 10010100(2); в) 1100110110,0011(2) – 11111110,01(2); г) 1360,14(8) – 1216,4(8); д) 33B,6(16) – 11B,4(16). 10. а) 11001(2) ´ 1011100(2); б) 451,2(8) ´ 5,24(8); в) 2B,A(16) ´ 36,6(16). 11. а) 759(10); б) 265(10); в) 79,4375(10); г) 360,25(10); д) 240,25(10). 12. а) 1001101(2); б) 10001000(2); в) 100111001,01(2); г) 1111010000,001(2); д) 1461,15(8); е) 9D,A(16). 13. а) 100101011(2)+111010011(2); б) 1001101110(2)+1101100111(2); в) 1010000100,1(2)+11011110,001(2); г) 674,34(8)+1205,2(8); д) 2FE,6(16)+3B,4(16). 14. а) 1100110010(2) – 1001101101(2); б) 1110001100(2) – 10001111(2); в) 11001010,01(2) – 1110001,001(2); г) 641,6(8) – 273,04(8); д) 3CE,B8(16) – 39A,B8(16). 15. а) 1010101(2) ´ 1011001(2); б) 1702,2(8) ´ 64,2(8); в) 7,4(16) ´ 1D,4(16). 16. а) 216(10); б) 336(10); в) 741,125(10); г) 712,375(10); д) 184,14(10). 17. а) 1100000110(2); б) 1100010(2); в) 1011010,001(2); г) 1010100010,001(2); д) 1537,22(8); е) 2D9,8(16). 18. а) 101111111(2)+1101110011(2); б) 10111110(2)+100011100(2); в) 1101100011,0111(2)+1100011,01(2); г) 666,2(8)+1234,24(8); д) 346,4(16)+3F2,6(16). 19. а) 1010101101(2) – 110011110(2); б) 1010001111(2) – 1001001110(2); в) 1111100100,11011(2) 101110111,011(2); г) 1437,24(8) – 473,4(8); д) 24A,4(16) – B3,8(16). 20. а) 101011(2) ´ 100111(2); б) 1732,4(8) ´ 34,5(8); в) 36,4(16) ´ A,A(16). 21. а) 530(10); б) 265(10); в) 597,25(10); г) 300,375(10); д) 75,57(10). 22. а) 101000111(2); б) 110001001(2); в) 1001101010,01(2); г) 1011110100,01(2); д) 1317,75(8); е) 2F4,0C(16). 23. а) 1100011010(2)+11101100(2); б) 10111010(2)+1010110100(2); в) 1000110111,011(2)+1110001111,001(2); г) 1745,5(8)+1473,2(8); д) 24D,5(16)+141,4(16). 24. а) 1100101010(2) – 110110010(2); б) 110110100(2) – 110010100(2); в) 1101111111,1(2) – 1100111110,1011(2); г) 1431,26(8) – 1040,3(8); д) 22C,6(16) – 54,2(16). 25. а) 1001001(2) ´ 11001(2); б) 245,04(8) ´ 112,2(8); в) 4B,2(16) ´ 3C,3(16).