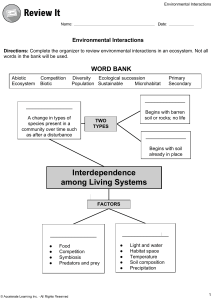
Ecological Studies 2 Objectives: ● To treat and analyse the results of sampling methods. ● Use sampling methods to determine the most ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ ❖ Dominant Abundant Common Frequent Occasional Rare Species Treatment of Results from sampling methods From Quadrats A scalemap should be drawn showing the positions of the quadrats thrown. The results of the quadrat can be used to obtain: ● Species density: The average number of individuals of each species per m2 ● Species Cover: the percentage of the ground covered by a species; used if individual organisms were difficult to count ● Species frequency: The percentage of quadrats in which a particular species is found. These results can then be recorded in tables and charts Example Histograms showing a. Species density and b. Species cover Terms to remember ❖ Dominant: The species that predominates in an ecological community, particularly when they are most numerous or has the greatest effect on the environment ❖ Abundant: the number of individuals per species ❖ Common: describe the population status of a species whether there is a large number of organisms in a specific species or not ❖ Frequent: The species most frequently found in every sample obtained ❖ Occasional: The species least frequently found in every sample obtained ❖ Rare Species: A group of organisms that are rarely encountered Line Transects Information from line transects could be shown on profile diagrams One group of students uses a 1 m2 quadrat to determine the distribution of three plant species in the area behind lhe mangroves. The results are shown in Table 1. 1. Complete the table by calculating the total population, species density and species frequency for each species. TABLE 1: RESULTS FROM QUADRAT THROWS Plant Organisms Quadrat Numbers 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Small flowering shrub 5 2 3 2 2 1 2 1 3 1 Grass growing in clumps 4 2 3 2 0 1 2 4 0 0 Succulent plants 10 10 12 15 20 25 15 22 5 18 Total Population of species Species Density Species Frequency 2. Complete the following table and answer the questions on the next slide SPECIES 1 A B QUADRAT SIZE: 1m² QUADRAT NUMBER (No. of individuals) 2 3 4 5 6 7 2 20 % 25% C 2 3 3 4 3 D 10 % 50 % 5% 45 % 20 % 8 9 6 2 30 % 5% 5 2 2 0 20 % 10 % 30 % 10 Total Populati on 10 20 % 0 Species Density (Individual s per m2) 1 80% 24 190 % Species Frequency % 30 50 2.4 Spec ies Cove r 8% 80 80 19 % Which species is the Most 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Dominant? Abundant? Frequent? Occasional Rare? Outline how the quadrat is to obtain the results in the table Type your answer here Abiotic Factors in Ecological Study Objectives: ● Identify the abiotic elements associated with an ecosystem ● Determine the Relationship between the distribution of species to abiotic factors EUTROPHICATION??? Importance of Abiotic Factors Climate and Vegetation How to measure Climatic factors Temperature: Thermometer Humidity: Wetand Dry bulb thermometer Light Intensity: Photographic Light Meter Rainfall: Rain Guage Wind Speed :Anemometer Wind direction: Wind Vane Edaphic Factors Objectives: ● Define Soil ● Describe the process of soil formation ● Identify the components of soil ● Identify the types of soil ● Describe the characteristics of each type of soil Components of Soil and Their Importance Soil Profile Particles of clay soil are tightly packed Particles are large and spaced CONSTANTS: Amount of water added. Amount of soil EVALUATION Create a blank document and answer the following questions: ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Name FOUR abiotic factors that influence the distribution and survival of living organisms. List FOUR reasons why soil is important to plants. Why are sandy soils better aerated than clay soils? What is humus and how does it get into the soil? List THREE advantages of having plenty of humus in a soil. What are the problems of trying to cultivate a clay soil? How may a sandy soil be improved?