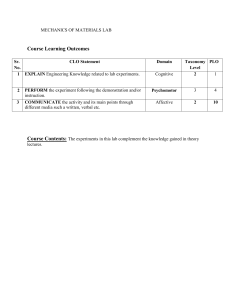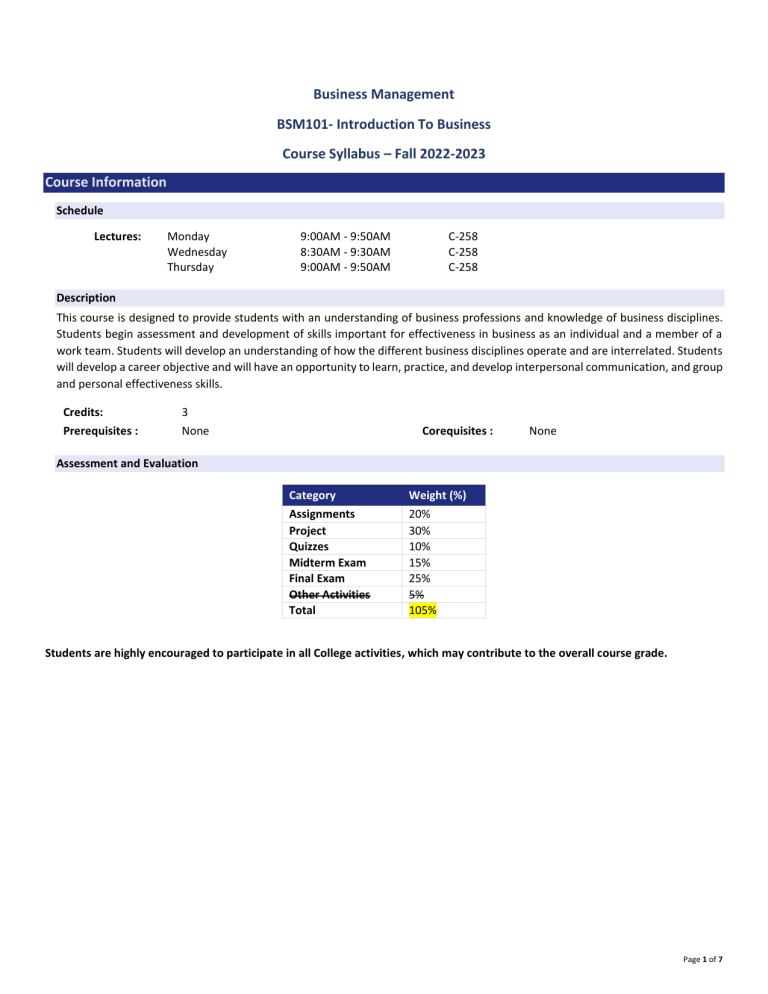
Business Management BSM101- Introduction To Business Course Syllabus – Fall 2022-2023 Course Information Schedule Lectures: Monday Wednesday Thursday 9:00AM - 9:50AM 8:30AM - 9:30AM 9:00AM - 9:50AM C-258 C-258 C-258 Description This course is designed to provide students with an understanding of business professions and knowledge of business disciplines. Students begin assessment and development of skills important for effectiveness in business as an individual and a member of a work team. Students will develop an understanding of how the different business disciplines operate and are interrelated. Students will develop a career objective and will have an opportunity to learn, practice, and develop interpersonal communication, and group and personal effectiveness skills. Credits: 3 Prerequisites : None Corequisites : None Assessment and Evaluation Category Weight (%) Assignments Project Quizzes Midterm Exam Final Exam Other Activities Total 20% 30% 10% 15% 25% 5% 105% Students are highly encouraged to participate in all College activities, which may contribute to the overall course grade. Page 1 of 7 Teaching Resources Required Textbook: Required e-book(s): O.C. Ferrell. H. Geoffrey. L. Ferrell. Business foundations A changing world. 12th edition. McGraw-Hill education. E-book. Tools: NOTE TO HODs: Please choose the relevant statements for your course, then delete this sentence. Microsoft Teams will be the main platform used for instructor-based recordings of live sessions. Students must make sure to follow their registered schedule. Recordings are made available for students to review their live classes and are not a replacement for students’ in-person class attendance. Moodle is the main platform of study, where resources are kept, and assessments may occur. Pearson Education (MyLab platform) is the primary site of study and assessment in this course. Other Useful Resources: Books: Glencoe McGraw-Hill Introduction to Business, Students edition Glencoe_McGraw-Hill (2008). William G. Nickels, James M. McHugh, Susan M. McHugh, “Understanding Business”, 10th Edition, Boston, Irwin/McGraw Hill, 2010. Articles/Case studies: Girgis, D. and Ramadhan, D., 2018. Status of SMEs in the GCC: Policies, Institutions, and the Way Forward. KUWAIT FOUNDATION FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF SCIENCES, IV. Ashoor, A., 2013. The structure of SMEs in the GCC and how are they promoted. Arab-EU Business Facilitation Network. Public Authority for SME Development. 2013. Guide for Services in English. National Center for Statistics and Information, Third Publication, https://riyada.om/en-us/Pages/Home.aspx. Accessed on 4/5/2017. Course Learning Outcomes (CLO) CLO-1 Understand the concepts of business management. CLO-2 Understand the environments in which businesses operates. CLO-3 Understand the role of ethics and social responsibility in business. CLO-4 Examine the roles of major functional areas of business and the interrelationships among them. CLO-5 Understand and gain the skills related to business management, decision making, financial analysis, operation management, entrepreneurship, and marketing. Attendance: Attendance to all lectures and laboratories is necessary. By registering for a course, you have made a commitment to participate regularly with your instructor and fellow classmates. Page 2 of 7 1st Absence Warning 2 hours 3 hours 4 hours Number of Credits 2 Credits 3 Credits 4 Credits 2nd Absence Warning 4 hours 6 hours 8 hours FA – Course Dismissal 5 hours 9 hours 12 hours 5 excused absence submissions – submitted within 5 business days by email to Students who are 10 minutes late to class may attend but will be marked absent. Midterm/Final Exam approved excuses: Death of a first degree relative, or hospital admission. Students with chronic illness that require frequent appointments must submit their medical report to the Office of Student Advising. Students who have missed 2 consecutive weeks of classes from the day of their registration, will be considered as “No Show” student’s and will receive an “FA” grade for the course. Part-time (working) students must notify Office of Student Advising during the first week of class. Course Outline Week Module Topics & Activities Topics: CLO Achievement CLO-1, CLO-2 Define basic concepts such as business, product, profit, and economics. 1 The Dynamics of Business & Economics Identify the main participants and activities of business. Explain why studying business is important. Activity: Get to know You Assignment Book/Chapter: Chapter 1 Topics: CLO-3 Describe the importance of business ethics and social responsibility. Detect some of the ethical issues that may arise in business. Specify how businesses can promote ethical behavior. Evaluate an organization’s social responsibilities to owners, employees, consumers, the environment, and the community. Evaluate the ethics of a business’s decision. Activity: 3 Business Ethics and Social Responsibility Case Study Submission Book/Chapter: Chapter 2 Project implications: You should start thinking of a business idea for your project. Start by addressing the following questions: 4 What markets in Kuwait are thriving? Is there a gap in those markets? Is there a problem that requires a solution? Topics: CLO-6 Describe the legal forms of organizations in Kuwait. Page 3 of 7 Week Module Options for organizing business Topics & Activities CLO Achievement Describe the advantages and disadvantages of the sole proprietorship form of organization. Describe the types of business partnership and their advantages and disadvantages. Describe the corporate form of organization and its advantages and disadvantages. Assess the advantages and disadvantages of mergers, acquisitions, and leveraged buyouts. Propose an appropriate organizational form for a startup business. Demonstrate how to license your business in Kuwait. Activity: Options for Organizing a Business Assignment Book/Chapter: Chapter 4 Project implications: You should start thinking of a business idea for your project. Start by addressing the following questions: What legal form would you choose for your business and why? Topics: CLO-4, CLO-5, CLO-6 Define entrepreneurship and small business. Explain the importance of small business in the Kuwaiti. economy and why certain fields attract small business. Specify the advantages of small-business ownership. Analyze the disadvantages of small-business ownership and the reasons why many small businesses fail. Activity: 5 Small business, entrepreneurship, and franchising Success Vs. Failure Story Assignment Book/Chapter: Chapter 5 Project implications: Start thinking of your business plan in detail: a precise statement of the rationale for the business and a step-by-step explanation of how it will achieve its goals. You will be introduced to a business plan template in which you can use to fulfill your project requirements. Topics: CLO-4, CLO-5, CLO-6 Describe how to start a small business and what resources are needed. Evaluate the demographic, technological, and economic trends that are affecting the future of small business. 6 Small business, entrepreneurship, and franchising Explain why many large businesses are trying to “think small.” Assess two entrepreneurs’ plans for starting a small business. Activity: Quiz 2 Book/Chapter: Page 4 of 7 Week Module Topics & Activities CLO Achievement Chapter 5 Project implications: Students must submit part 1 of their project which will include information about topics we discussed in previous weeks. Detailed guidelines will be distributed prior. Part 1 Deliverable Due on: 27/10/2022 Topics: CLO-4, CLO-5, CLO-6 Define operations management. Differentiate between operations and manufacturing. Explain how operations management differs in manufacturing and service firms. Describe the elements involved in planning and designing an operations system. Specify some techniques managers may use to manage the logistics of transforming inputs into finished products. Assess the importance of quality in operations management. 7 Managing Operations & Supply Chains Propose a solution to a business’s operations dilemma. Activity: Russian Invasion of Ukraine Assignment Book/Chapter: Chapter 8 Project implications: Does your business involve any type of manufacturing? Does your business involve customization? Is outsourcing a solution for you? 8 Midterm Examination Week Define Marketing & Market Describe the exchange process. CLO-4, CLO-5 Specify the functions of marketing. Explain the marketing concept and its implications for developing marketing strategies. Examine the development of a marketing strategy, including market segmentation and marketing mix. 9 Customer-driven Marketing Describe how marketers conduct marketing research and study buying behavior. Activity: Quiz 3 Case Study Book/Chapter: Chapter 11 Project implications: Who is your customer? During these lectures you should focus on understanding the behavior of your consumers. Page 5 of 7 Week Module Topics & Activities Topics: CLO Achievement CLO-4, CLO-5, CLO-6 Describe the role of product in the marketing mix, including how products are developed, classified, and identified. Explain the importance of price in the marketing mix, including various pricing strategies a firm might employ. Identify factors affecting distribution decisions, such as marketing channels and intensity of market coverage. Specify the activities involved in promotion, as well as promotional strategies and promotional positioning. 10 Dimensions of a marketing strategy Activity: Quiz 4 Book/Chapter: Chapter 12 & 13 Project implications: Your marketing plan should come together at this point with clear promotional strategies. Students must submit part 2 of their project which will include information about topics we discussed in previous weeks. Detailed guidelines will be distributed prior. Part 2 Deliverable Due on 27/11/2022 Topics: CLO-4, CLO-5, CLO-6 Describe the different uses of accounting information. Demonstrate the accounting process. Examine the various components of an income statement in order to evaluate a firm’s “bottom line.” Accounting & Financial Statements Interpret a company’s balance sheet to determine its current financial position. Activity: 11 Quiz 5 Book/Chapter: Chapter 14 Project implications: 95% of start-ups fail mainly because of insufficient cash management. Think of how you will maintain sustainable financial management. Topics: CLO-4, CLO-5, CLO-6 Analyze financial statements, using ratio analysis, to evaluate a company’s performance. 12 Accounting & Financial Statements Assess a company’s financial position using its accounting statements and ratio analysis. How to apply this information to your business plan Activity: Assess a company’s financial statement assignment Page 6 of 7 Week Module Topics & Activities CLO Achievement Book/Chapter: Chapter 14 Project implications: Students must submit the final part of their project (part 3) of their project which will include information about topics we discussed in previous weeks. Detailed guidelines will be distributed prior. Part 3 Deliverable Due on 11/12/2022 Project implications: 13 Project Presentations CLO-4, CLO-5, CLO-6 Shark Tank Presentations This week will be dedicated to your presentations. Be prepared to present your project all presentation requirements will be provided to you prior. Topics: Final Exam Review Activity: 14 Final Exam Review In-Class Assignments Book/Chapter: All Chapters covered on this syllabus 15 Final Examination Week This course outline is subject to change if the course instructor deems it necessary. Guidelines Students with Special Needs: Plagiarism/Cheating: Plagiarism is cheating by taking or copying another person’s work and submitting it as your own work. Instances of plagiarism are treated very seriously, and penalties may include dismissal from the college. Plagiarism includes but is not limited to: o An individual claiming any part of another’s work as their own, regardless of whether the work has been published or whether permission to use the work has been granted by the author. o Using material without correctly citing the source. o Paying or arranging with another person to complete your work and then submitting it as your own. o Downloading material from the internet and submitting it as your own work. Page 7 of 7