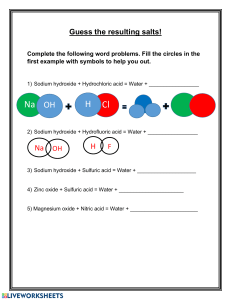
Neutralisation Definition Neutralisation is a chemical reaction between a base and an acid to form salt and water. Neutralisation reactions are exothermic. 𝐴𝑐𝑖𝑑 + 𝐵𝑎𝑠𝑒 → 𝑆𝑎𝑙𝑡 + 𝑊𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟 e.g. Both the acid and alkali are aqueous solutions. Remember to write the state when you write the equation Acid (aq) Alkali (aq) General Word Equation Acid(aq) + Alkali(aq) Salt(aq) + Water(l) Examples: Sulfuric Acid + Potassium Hydroxide Potassium Sulfate + Water H₂SO₄ + 2KOH K₂SO₄ + 2H₂O Hydrochloric Acid + Ammonium Hydroxide Ammonium Chloride + Water HCl + NH₄OH NH₄Cl + H₂O Write Word Equation 1. Hydrochloric Acid and Potassium Hydroxide 2. Sulfuric Acid and Calcium Hydroxide 3. Sulfuric Acid and Sodium Hydroxide 4. Nitric Acid and Barium Hydroxide 5. Hydrochloric Acid and Magnesium Hydroxide Write Symbol Equation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. For the previous 5 equations, write the symbol equations. Answers 1. Hydrochloric Acid and Potassium Hydroxide HCl + KOH H₂O + KCl 2. Sulfuric Acid and Calcium Hydroxide H₂SO₄ + Ca(OH)₂ 2H₂O + CaSO₄ 3. Sulfuric Acid and Sodium Hydroxide H₂SO₄ + 2NaOH 2H₂O + Na₂SO₄ 4. Nitric Acid and Barium Hydroxide 2HNO₃ + Ba(OH)₂ 2H₂O + Ba(NO₃)₂ 5. Hydrochloric Acid and Magnesium Hydroxide 2HCl + Mg(OH)₂ 2H₂O + MgCl₂