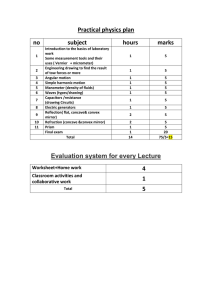
Practical Experiment - Light Waves: Reflection and Refraction. Background information. As we know, light travels from one place to another as waves. We can use equipment such as a light box kit to investigate how light waves interact when reflecting and refracting. Light box kits contain concave (curved inwards) objects, convex (curved outwards) objects, prisms and planes that can be used to demonstrate how light is reflected or refracted. Name: Penelope Tsirogiannis Partners: Vanessa Galea and Jake Farrugia. Aim: The aim of the experiment is to visibly see light waves travelling using reflection and refraction while utilising the lightbox kits and different surfaces. Hypothesis: It is hypothesised that the experiment will demonstrate reflection and refraction with the light waves of energy by using the light box kits to create a beam of light that can reflect or refract depending on the different surfaces used, such as concave, convex, plane, lens or prisms. Materials: - Light box kit - Convex and concave lenses - Prisms and planes - Battery pack - White A4 paper Method: Set up of light box kit. 1. Connect your lightbox to your battery pack as shown by your teacher. 2. Place the black plastic light distributor down with the single open shaft facing downwards. 3. Place a sheet of white paper down in front of the light box. 4. Choose a coloured square of your choice. 5. Close the sides of the box making sure no light escapes. Experiment 1. 6. Place a concave mirror in front of the light box and fill in the table below. 7. Flip over the concave mirror so it faces backwards and fill in the table below. 8. Place down the plane mirror so that it faces the light box and fill in the table below. Experiment 2. 9. Place the concave lense in front of the light box (on the horizontal) and fill in the table below. 10. Place the convex lense in front of the light box (on the horizontal) and fill in the table below. 11. Place down the rectangular plane in front of the light box (on the diagonal) and fill in the table below. 12. Place the prism in front of the light box and fill in the table below. Experiment 3. 13. Start with a convex lens and hold it close to your eye. Slowly move the lense away from your face until your arm is completed outstretched. Record what you see in the space below. The convex lense made the object appear larger through the lens. 14. Repeat the action for concave lenses and describe the difference between the two lenses. The concave lens enlarges the object and makes the object appear upside down. Results: Experiment 1- Light box experiment demonstrating reflection and refraction by using different surfaces: Top view What happened to the Plane, convex or concave rays? Reflection or surface? refraction? The rays are being reflected Concave surface off the concave surface. → → → → → → Experiment 2. The rays are once again being reflected by the concave surface. Concave surface The rays are also being reflected by the plane surface. Plane surface Top view What happens to the rays? Reflection or refraction? The ray went straight through the lens and it refracted. Lens or prism? Convex or concave? Convex lens The rays of light travelled straight through the lens which means that it was refraction. Convex lens The rays went straight through but also reflected some light so therefore it was both reflection and refraction. Rectangular plane The light went through the triangular prism and broke of in two directions which makes it refraction. The light scattered. Triangular prism → → → → → → → → Discussion: Question 1: Describe the difference between reflection and refraction based on what you saw in your results. The difference between reflection and refraction is that with reflection, the light bounces off the object and with refraction, the light rays travel straight through. Question 2: Describe the effect concave and convex lenses have on the light that passes through them. Both the concave and convex lenses had the same effect which was refraction meaning that they both made the light to go straight through. Question 3. Does the distance from the object alter the way the light bends? Explain your response. The distance from the object does indeed alter the way that the light bends because it makes the light sharper and closer together. Question 4. The following image demonstrates what feature of light waves and why? The image shows reflection and also appears to be scattering because the light is travelling in two different directions. Conclusion: (Summarise the experiment, refer to and describe results, state if the hypothesis was support or not and why and acknowledge any errors made and how they could have impacted results). In conclusion, the experiment that was completed in class provided a visual representation of how light waves interact when reflecting and refracting. It was discovered that by using different surfaces or lenses, it affects whether the light reflects or refracts. The predicted hypothesis was correct, and the experiment did indeed demonstrate reflection and refraction whilst using the light box kits and different surfaces/lenses. Using a concave surface enforced the rays to reflect off the concave surface, whereas using a convex surface made the ray travel directly through the lens and it then refracted. An interesting component was that using a triangular prism made the light go through the triangular prism and broke of in two directions which is called scattering and also makes it refraction. It was also identified when looking through the convex and concave lenses, that the convex lens made the object appear larger through the lens whereas the concave lens enlarged the object and made the object appear upside down. The results may have been affected by the scattering of other light sources such as the sky light and other windows in the room, and the colour of the colour cards may have also affected the experiments because different colours would have different opacities.