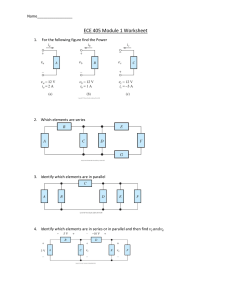
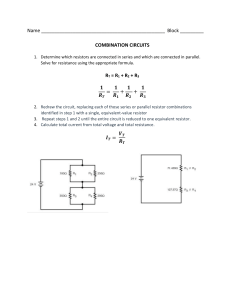
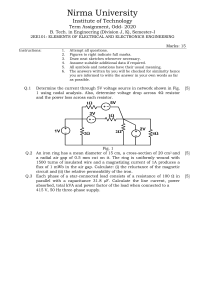
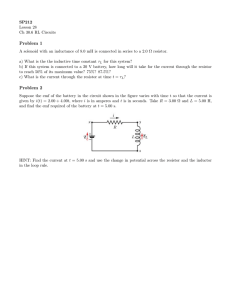
Laboratory Expirement Sheet on the Fundamentals of Electricity and Electronics (ECE 112)
advertisement

Republic of the Philippines E A S T E R N V I S AYA S STATE UNIVERSITY Tacloban City COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT Laboratory Experiment Sheet on the Fundamentals of Electricity and Electronics (ECE112) Part 1 Components Actual/Available (On-hand) Recommended Resistance Value (Using Multimeter) 470Ω Resistor 1kΩ Resistor 3.3kΩ Resistor 10kΩ Resistor 33kΩ Resistor 100kΩ Resistor 1MΩ Resistor 50kΩ Variable Resistor 0.005μF Disc Capacitor 0.047μF Disc Capacitor 10μF Electrolytic Capacitor 100μF Electrolytic Capacitor Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) Activity 1. The Light Bulb After fixing your setup according to the given diagram: While the switch is off: 1. 2. 3. 4. Measure the voltage across the Battery (VT) Measure the voltage across the LED (VLED) Measure the voltage across the Resistor (R1) Measure the current along the circuit (IT) While the switch is on, do steps 1-4 above…. Replace the 10k resistor with any other resistor of your choosing, 1 higher, 1 lower, then do step 1-4 again. Actual Data: @ Off state (10k resistor) @ On state (10k resistor) VT VLED R1 IT Verify the data above by computation: @ On state (____ resistor) @ On state (____ resistor) (You may insert your solutions here) Computed Value: @ Off state (10k resistor) @ On state (10k resistor) @ On state (____ resistor) @ On state (____ resistor) VT VLED R1 IT Questions: (You may insert your answers in between questions) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. How do your turn on the LED? Why does the LED light up when you connect it based on the circuit diagram? What happened when you replaced the 10k resistor? How does the value of the resistor affect the brightness of the LED? Is there any difference between the actual and computed values? Documentation (Insert pictures while performing experiment) Activity 2. The Brightness Control Isolate the potentiometer: 1. Measure the resistance of the potentiometer by connecting the black probe of your multimeter to the middle terminal of the potentiometer, turn the potentiometer to the left, and connect the red probe to the left terminal, then right terminal. Gradually turn the dial and record each of the resistance reading. Dial Position Maximum Left Left – Middle Reading Right – Middle Reading Maximum Right Proceed to fixing your setup according to the given diagram: While switched on, using your multimeter tabulate the Voltage across the LED, and the Resistance value of the potentiometer, turn the dial at random positions. Repeat until you complete the table below. Compute the supposed resistance value of the potentiometer for each dial position you chose. (You may insert your solutions here) Data: Dial Positio n VLED Potentiometer Resistance Computed Resistance 1 2 3 4 5 Questions: (You may insert your answers after questions) 1. What happens to the brightness of the LED when you turn the dial of the variable resistor to the left? To the right? (For Activity 3-6, tabulate the data just like the previous activities and compare the actual vs computed values. The final format should be like the previous activities). Activity 3. 1. Describe the brightness of the LED. 2. What happened when you replaced the 100k resistor with a 10k resistor? 3. Remove one of the resistors in the circuit. What happened to the LED? Activity 4. Parallel Pipes 1. Describe the brightness of the LED. 2. What happened when you replaced the 100k resistor with a 10k resistor? 3. Remove one of the resistors in the circuit. What happened to the LED? Activity 5. Comparison of Parallel Current 1. Compare the brightness of the left and right LED. Activity 6. Combined Circuit Data: Dial Position 1 2 3 4 5 VLED1 (Actual) VLED1 (Computed) VLED2 (Actual) VLED2 (Computed) Potentiometer Resistance (Actual) Potentiometer Resistance (Computed) Actual Voltage at 3.3k Resistor Computed Voltage at 3.3k Resistor Actual Voltage at 10k Resistor Computed Voltage at 10k Resistor 1. How does the resistor work in series? In parallel? Activity 7. Water Detector (For Activity 7, measure the Voltage of the LED and compute the resistance of water as you add salt, tabulate data) 1. 2. 3. 4. Describe the brightness of the LED when the water is halfway through the cup. Describe the brightness of the LED as you add more water. What happened to the LED when you added table salt to the water. Why does the water affect the brightness of the LED?