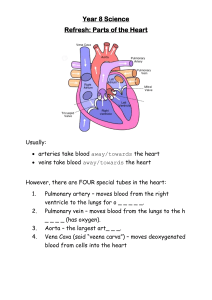
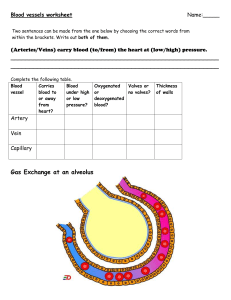
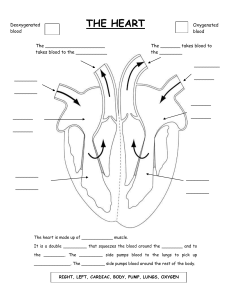
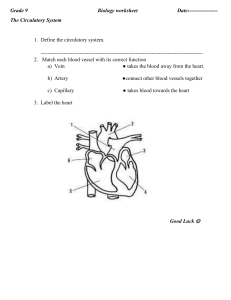
The Transport System in Man Aka Circulatory System/Cardiovascular System Notes Definition of Circulatory System A system comprising of the heart, blood and blood vessels which efficiently transports blood, nutrients and other essential materials to cells while removing waste substances from the body. 3 Major Components: 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels Humans have a closed transport system. This means that blood is transported in a network of blood vessels which separate it from the outer environment. Importance of Circulatory System: Humans have a LOW surface area to volume ratio. The interior cells of humans are too far from the surface of the body surface for diffusion to be relied on to bring oxygen and nutrients to body cells and to remove metabolic waste. List of Substances that Need to be Transported Around the Body • Waste materials: eg. carbon dioxide to lungs, urea to kidneys • Hormones: Adrenaline, insulin from endocrine glands to target organs • Antibodies • Blood proteins • Blood cells • Nutrients The Heart -Muscle made of specialised myocardium cells designed to pump blood around the body 2 types of blood are pumped at the same time: 1. Oxygenated blood 2. Deoxygenated blood Thus, this system is known as a Double Circulatory System. Deoxygenated blood is transported Comprises of 4 spaces called chambers -Upper chambers: Atrium (pl. atria) -Lower chambers: Ventricles -Thick muscle in middle of heart that separates the heart in two sides: Septum These 2 sides are known as the left side and right side of the heart. The left side pumps oxygenated blood to the body cells while the right side pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs to become oxygenated and release waste substance to be breathed out. Oxygenated Blood → Body cells Deoxygenated Blood → Lungs Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from heart to the body cells. EXCEPT! Pulmonary artery: Transports deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs Veins carry deoxygenated blood to the heart from body cells. EXCEPT! Pulmonary vein: Transports oxygenated blood to the heart from lungs Major Blood Vessels in Heart: 1. Vena Cava • • • • Main vein that transports deoxygenated blood back to the heart Comprises of Superior Vena Cava and Inferior Vena Cava Superior (Upper) transports deoxygenated blood from head, neck, arms and chest to the heart Inferior (Lower) transports deoxygenated blood from lower part of body 2. Aorta • Transports oxygenated blood to the body cells 3. Pulmonary Artery • Transports deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs 4. Pulmonary Veins • Transports oxygenated blood to the heart from lungs 5. Coronary Arteries • Heart’s own blood vessels which supply it with blood to maintain its function Major Arteries and Veins in Different Regions of the Body Region of Body Head Arms Lungs Liver Intestines Kidneys Legs Main Artery Carotid Artery Brachial Artery Pulmonary Artery Main Vein Jugular Vein Brachiocephalic Vein Pulmonary Vein Hepatic Artery Hepatic Vein Mesenteric Artery Hepatic Portal Vein Renal Artery Iliac Artery Renal Vein Iliac Vein