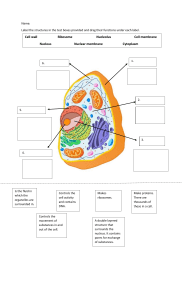
The History of Cells and Cell Theory OBJECTIVES: In this lesson, you will learn: • how cells were first discovered, • how the cell theory was developed, and • the main components of the cell theory CABBAGE PAPER GAME CELL THEORY HISTORICAL TIMELINE HANS and ZACHARIAS JANSSEN • Around the year 1590, two Dutch lens makers by the name of Hans and Zacharias Janssen invented the first compound microscope when they put two of their lenses together in a tube. A Dutch father-son team named Hans and Zacharias Janssen invented the first so-called compound microscope in the late 16th century when they discovered that, if they put a lens at the top and bottom of a tube and looked through it, objects on the other end became magnified Hans and Zacharias Janssen are known for inventing the compound optical microscope. They made it in the 1590's. This contributed to "The Cell Theory" by making it easier and more practical whilst observing cells. ROBERT HOOKE • In 1665, an English scientist, Robert Hooke discovered and came up with the name “cells” while looking through a microscope at a piece of cork. • Supposedly, the cork (which was made of dead oak tree tissues) reminded him of the small rooms that the monks lived in at the monasteries. ● Hooke's cells Robert Hooke • While observing cork through his microscope, Hooke saw tiny boxlike cavities, which he illustrated and described as cells. He had discovered plant cells! Hooke's discovery led to the understanding of cells as the smallest units of life—the foundation of cell theory • ANTON VAN Not longLEEUWENHOEK after Hooke (around 1683), a Dutch amateur scientist by the name of Anton Van Leeuwenhoek observed some of the first living cells under a simple (1 lens) microscope. • He named these small organisms “animalcules”. • It is now believed that some of the living cells he saw were actually protozoa. • He was the first person to examine many cells, including red blood cells. He was also the first person to see the nucleus of these blood cells. Before him, the notion of cells as the building blocks of living things was not widely accepted. MATTHIAS JACOB SCHLEIDEN In 1838 a German botanist by the name of Matthias Schleiden viewed plant parts under microscope discovered that plant parts are made of cells. THEODORE SCHWANN In 1839 German zoologist by the name of Theodore Schwann viewed plants and animals under a microscope and discovered that plants and animals are both made of cells. RUDOLPH VIRCHOW In 1855 a Prussian (modern day German) physician by the name of Rudolph Virchow collaborated his ideas with the other two scientists and they developed the Cell Theory. Q The Cell Theory 1. All organisms are made of cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of life in all living things. 3. All cells come from existing cells. THIS IS IMPORTANT BECAUSE IT SHOWS THAT ALL LIVING THINGS SHARE A SIMILAR STRUCTURE Cells: The Basic Units of Life Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. Examples of Cells Amoeba Proteus Plant Stem Bacteria Red Blood Cell Nerve Cell How big is a cell? • http://www.cellsalive.com/howbig.htm Two Types of Cells All cells, whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, have some common features Organelles Organelles are structures that enable the cell to live, grow and reproduce. Two Types of Cells Prokaryotic Cells: • Have no membrane covered nucleus • Have no membrane - covered organelles • Have circular DNA • Are bacteria Prokaryotic Cells ● Prokaryotic cell – Unicellular organisms like bacteria. Notice the DNA is not found in a nucleus and organelles are absent (except ribosomes). Two Types of Cells Eukaryotic Cells: • Have a nucleus • Have a membrane covered organelles • Have linear DNA • Are all other cells Organelles Organelles are structures that enable the cell to live, grow and reproduce. Cell Membrane • Outer layer of cell • Allows nutrients into the cell and wastes outside of the cell “Gate into the city” Cell Membrane Cytoplasm • Cytoplasm a jelly-like fluid contained in the cell that holds the organelles. The Nucleus DNA • The control center of the cell • Contains the Cell’s DNA Nucleolus Nuclear Membrane “Mayor’s office” Mitochondria Outer Membrane • Power center of cell • Provides the energy the cell needs to move, divide, etc. Inner Membrane “Electric company of the cell” Ribosomes • Site where proteins are made • Cell parts are made of proteins “Factories of the cell” Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosomes • Transportation system of cell • Rough ERribosome's attached • Smooth ER- no ribosome's “Roadways of the cell” Golgi Complex • Packaging house of cell • Packages, processes, and ships out the stuff the cell makes “UPS of the cell” Lysosomes • Digests food particles and cell parts – “Garbage men” • Protects cell by digesting foreign invaders – “Police men Vacuole Vacuole • Stores water, food & wastes Vacuole is largest organelle in plant cell Cell Wall • Found only in plant cells • Protects and supports the cell Chloroplasts • Found only in plant cells • Contains chlorophyll (makes plants green) • Where photosynthesis takes place “Typical” Plant Cell http://waynesword.palomar.edu/images/plant3.gif • A "raphide crystal" is found in plant cells and has the primary purpose of "repelling animals away from plants". The needle-like crystals are made of calcium oxalate and are shaped like needles. • How are raphides different from plastids? Rhapides are elongated, crystals that function in storage and protection. Plastids create and store food and pigments and are membrane bound organelles. • Raphides seem to be a defense mechanism against plant predators, as they are likely to tear and harm the soft tissues of the throat or esophagus of a plant predator chewing on the plant's leaves. Plants with Raphide Crystals A druse is a group of crystals of calcium oxalate,[1] silicates, or carbonates present in plants, and are thought to be a defense against herbivory due to their toxicity. Plant or Animal Cell? Found in Plant and Animal cells: • Nucleus • Golgi Complex • Mitochondrion • Lyosomes • Endoplasmic Reticulum • Cell Membrane • Ribosomes • Vacuoles Found only in Plant Cells: • Chloroplasts • Cell Wall