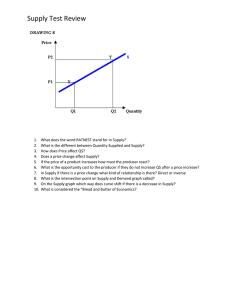
INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING ECONOMY Engineering Economy by Hipolito Sta Maria Fundamental of Engineering Economics by Park Engr Jonathan B. Tungal ECE, MBA 2 Definition of Terms Engineering Economy – uses mathematical formulas to account for the time value of money and to balance current and future revenues and costs. Economics – is the science that deals with the production, allocation and use of goods and services. The two major subdivisions of economics are: a. Macroeconomics is the study of the entire system of economics. b. Microeconomics is the study of how the systems affect one business or parts of the economic system. Necessities and Luxuries Necessities – are products or services that are required to support human and activities that will be purchased in somewhat the same quantity even though the prices vary considerably. Luxuries – are products and services that are desired by humans and will be purchased if money is available after the required necessities have been obtained. Consumer and Producer Goods and Services Goods – is defined as anything that anyone wants or needs. Services – would be the performance of any duties or work for another; helpful or professional activity. Marketing – refers to the distribution of goods and services. Marketing a Product – refers to the advertising, and other efforts to promote a products sale. Different Types of Goods 1. Consumer Goods – are those such as food and clothing that satisfy human wants and needs. 2. Producer Goods – are those such as raw materials and tools, used to make consumer goods. 3. Capital Goods – are the machinery, used in the production of commodities in producer goods. Supply and Demand Supply – refers to how many of a certain good or services are available for people to purchase. Demand – means how many people wish to buy that good or service. Law of Supply and Demand Under conditions of perfect competition, the price at which a given product will be supplied and purchased is the price that will result in the supply and demand being equal. Demand Demand – it refers to the people’s willingness to buy a product or service. Demand Curve – is the plot or graph of the quantity demanded versus the price. Demand Schedule – is the schedule or table listing of the quantity demanded with the corresponding price. Types of Demand 1. Elastic Demand – exists when there is a greater change in quantity demanded as a response to a change in price. 2. Inelastic Demand – exists when there is a lesser change in quantity demanded as a response to a change in price. 3. Unitary Demand – exists when there is an equal change in price and quantity demanded (increase or decrease). Factors that Influence Demand Factors that Influence Demand are: 1. Income 2. Population 3. Taste and preference 4. Price Expectation 5. Price of Related Goods Supply Supply – it is the willingness of a producer to manufacture goods. Supply Curve – is the plot or graph of the quantity supplied versus the price. Supply Schedule – is the schedule or table listing of the quantity supplied with the corresponding price. Factors that Influence Supply Factors that Influence Supply are: 1. Price of Goods 2. Cost of Production 3. Availability of Resources 4. Number of Producer and Sellers 5. Technological Advancement 6. Taxes 7. Subsidies Relationship of Supply and Demand Shortage – the supply is less than the demand. Surplus – the supply exceeds the demand. Equilibrium Point – the supply is equal to the demand. Market Structures Market – is the place where the vendors and buyers meet to transact. Perfect Competition – occurs in a situation where a commodity or service is supplied by a number of vendors and there is nothing to prevent additional vendors entering the market. Perfect Monopoly – exist when a unique product or services is available from a single vendor and that the vendor can prevent the entry of all others into the market. Oligopoly – exist when there are so few suppliers of a product or service that action by one will almost inevitably result in similar action by the others.