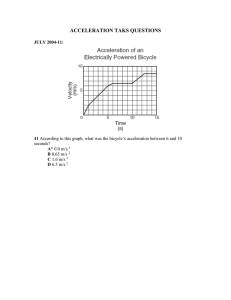
GRADES 1 to 12 Daily Lesson Log School Teacher Teaching Date / Time Ramon Avanceña National High School Ms. Shane Catherine T. Besares Grade Level Grade 8 Learning Area Science Quarter First(Physics) DAY: I. OBJECTIVES A. Content Standards B. Performance Standards The learners demonstrate an understanding of Newton’s three laws of motion and uniform circular motion. The learner shall be able to develop a writer plan and implement a “Newton’s Olympics”. S8FE –Ib-17 Demonstrate how a body responds to changes in motion. C. Learning Competencies / Objectives Write the LC code for each Objective: Solve problems involving the interrelationships of net force, mass and acceleration Module I: FORCE AND MOTION Lesson 5: THREE LAWS OF MOTION The Law of Acceleration: Computation II. CONTENT III. LEARNING RESOURCES A. B. References 1. Teacher's Guide Pages pp. 13- 16 2. Learner's Materials Pages pp. 15 - 17 3. Textbook Pages 4. Additional Materials from Learning Resource (LR) portal Other Learning Resource Physics ( Science and Technology Textbook- NPSBE Edition) EASE Physics, Module 10. Lesson 3 Lesson Guide G8 First Quarter pp. 20 - 22 IV. PROCEDURES A. Reviewing previous lesson or presenting the new lesson Ask the students to restate the second law into a simple statement. Derivation of Formula: From the statement that acceleration is directly proportional to force at constant mass. Mathematically a = kF where nK = B. Establishing a purpose for the Lesson mass (eq. 1) Acceleration also varies with mass. As the mass of the object increases with the same amount of force applied, its acceleration decreases thus: a= k(1/m) where K=net force (eq.2) Combining the two equations, we have a α F and a α 1/m Therefore, a = F/m Mathematically, a = F/m where a= acceleration m= mass F= force Give and discuss at least two examples of situation/problems on the C. Presenting examples / instances of the new lesson Law of Acceleration 1. A huge stone is pushed with 30 N of force. If there is only 5N of friction and the stone’s mass is 88 kg. What is the acceleration of? the table? 2. A car is being towed. If its mass is 1750 kg and it accelerated at 5m/s2, how much net force is involved? D. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills #1 Do the Activity Worksheet prepared by group and use the formula of Acceleration. E. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills #2 Presentation of the outcomes. F. Developing mastery (Leads to Formative Assessment 3) Discuss the answers in the exercise given. G. Finding practical applications of concepts and skills in daily living Engineers at the Johnson Space Center must determine the net force needed for a rocket to achieve an acceleration of 70 m/s2. If the mass of the rocket is 45,000 kg, how much net force must the rocket develop. Mathematically, second law of motion can be expressed: A = F/m F = ma M = F/a H. Making generalizations and abstractions about the lesson If the unit of Fnet ( Fn) is in Newton, mass(m) is in kilogram (kg) and acceleration is in meter per second/second (m/s2) Since force is a vector quantity and mass is a scalar quantity, acceleration is also a vector quantity where acceleration follows the direction of the net force The unit of acceleration can be derived also from N/kg, since 1N = 1 kg.m/s2 therefore, N/kg = kg.m/s2 /kg = m/s2 Direction: Solve problems involving the Law of acceleration then write the letter of the correct answer. 1. What is the mass of a truck if it produces a force of 14,000N while accelerating at a rate of 5 m/s2? A. 280 kg *B. 2800kg C. 70,000kg 2. Which is the correct unit of acceleration? A. m/s *B. m/s2 C. kg.m/s I. Evaluating Learning D. 7000kg D. kg.m/N 3. Suppose that a sled is accelerating at a rate of 2m/s2 . If the net force is tripled and the mass is halved, what then is the new acceleration of the sled? A. decrease by half B. doubled *C. tripled D. quadrupled 4. Suppose a ball of mass 0.60 kg is hit with a force of 12 N. Its acceleration will be: *A. 20 m/s2 B. 40 m/s2 C. 10 m/s2 D. 20 m/s 5. If the ball in question no. 4 is increased by 24 N, what is the increased in acceleration? A. 20 m/s2 B. 30 m/s2 *C. 4 0 m/s2 D. 50 m/s2 J. Additional activities for application or remediation Give additional information regarding: balance and unbalance forces. V. REMARKS 2 of 3 VI. REFLECTION A. B. C. No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation who scored below 80% Did the remedial lessons work? No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson D. No. of learners who continue to require remediation E. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did these worked? F. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve? G. What innovation or localized materials did I Use or discover which I wish to share with other teachers? Prepared by: SHANE CATHERINE T. BESARES Teacher I Checked by: LILIAN A. SUMAMPONG Department Head 3 of 3