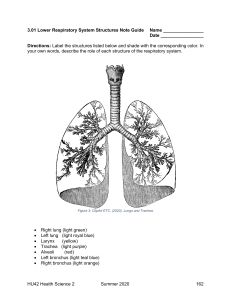
9/12/2022 Chapter 25 Assessment: Respiratory System Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Structures and Functions of Respiratory System (1 of 18) Primary purpose: gas exchange Transfer of oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) between atmosphere and blood Two parts (Fig. 25-1) Upper respiratory tract Lower respiratory tract Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 2 Structures and Functions of Respiratory System (2 of 18) Fig. 25-1 Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 3 1 9/12/2022 Structures and Functions of Respiratory System (3 of 18) Upper respiratory tract Nose • Warm, filter, humidify Mouth Pharynx Epiglottis Larynx Trachea • Carina—bifurcation Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 4 4 Structures and Functions of Respiratory System (4 of 18) Lower respiratory tract Bronchi Bronchioles Alveolar ducts Alveoli Lung lobes • Right—3 • Left—2 Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 5 5 Structures and Functions of Respiratory System (5 of 18) Structures of the lower airways Trachea and bronchi— anatomic dead space (VD); no gas exchange Bronchioles—smooth muscle constricts and dilates Alveoli—terminal part of respiratory tract; gases exchange Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 6 6 2 9/12/2022 Structures and Functions of Respiratory System (6 of 18) Alveoli Primary site for gas exchange with pulmonary capillaries Pores of Kohn Interconnections between alveoli Allow air to pass; also bacteria Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 7 7 Structures and Functions of Respiratory System (7 of 18) Surfactant Lipoprotein secreted by alveoli when stretched Reduces surface tension to make alveoli less likely to collapse Atelectasis—collapsed alveoli Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 8 8 Structures and Functions of Respiratory System (8 of 18) Blood supply Pulmonary circulation—gas exchange • Artery—deoxygenated blood from right ventricle • Capillaries—exchange gases at alveoli • Veins—return oxygenated blood to left atrium Bronchial circulation • Arteries—oxygen to bronchi and lung tissues • Azygos vein—deoxygenated blood to superior vena cava Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 9 9 3 9/12/2022 Structures and Functions of Respiratory System (9 of 18) Chest wall Ribs and sternum Mediastinum Pleura • Thoracic cage—protect lungs and heart • Heart, aorta, and esophagus • Parietal—chest cavity • Visceral—lungs • Intrapleural space: 20 to 25 mL fluid provides lubrication; facilitates expansion Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 10 10 Structures and Functions of Respiratory System (10 of 18) Chest wall Diaphragm—major muscle of respiration • Inspiration—contracts toward abdomen; increases intrathoracic volume • Works with intercostal and scalene muscles • Innervated by right and left phrenic nerves; arise from cervical vertebrae 3 to 5 Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 11 11 Structures and Functions of Respiratory System (11 of 18) Physiology of respiration Oxygenation—O2 from atmosphere to organs and tissues • Oxygen dissolved in plasma = Partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood (PaO2); normal 80 to 100 mm Hg • Oxygen bound to hemoglobin = Arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2); normal greater than 95% Diffusion—O2 and CO2 exchange at alveolar-capillary membrane; move from high to low concentration until equal Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 12 12 4 9/12/2022 Structures and Functions of Respiratory System (12 of 18) Physiology of respiration Ventilation Inspiration and expiration occur due to intrathoracic pressure changes and muscle action Expiration—passive • Elastic recoil—lungs return to original size after expansion Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 13 Structures and Functions of Respiratory System (13 of 18) Physiology of respiration Compliance—measures ease of lung expansion; elasticity and elastic recoil Decreased—hard for lungs to inflate Increased—hard for lungs to recoil Resistance—airflow impeded during inspiration and/or expiration; altered airway diameter Narrowed by constriction or secretions Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 14 14 Structures and Functions of Respiratory System (14 of 18) Control of respiration Medulla is respiratory center • In brainstem • Responds to chemical and mechanical signals • Sends impulses from spinal cord and phrenic nerve to respiratory muscles Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 15 15 5 9/12/2022 Structures and Functions of Respiratory System (15 of 18) Control of respiration Chemoreceptors Respond to changes in PaCO2 and pH in surrounding fluid Central chemoreceptors—medulla Increase H+ concentration—acidosis results in increased RR and VT Decrease H+ concentration—alkalosis results in increased RR and VT Increased PaCO2 results in increased H2CO3 resulting in decreased pH of CSF resulting in increased RR Decreased PaCO2 results in decreased H2CO3 resulting in increased pH of CSF resulting in decreased RR Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 16 16 Structures and Functions of Respiratory System (16 of 18) Control of respiration Chemoreceptors Peripheral chemoreceptors—carotid bodies and aortic bodies • Respond to decreased PaO2, decreased pH, and increased PaCO2 • Stimulate respiratory center to increase RR COPD—chronically increased PaCO2 does not stimulate increased RR; hypoxic drive Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 17 17 Structures and Functions of Respiratory System (17 of 18) Control of respiration Mechanical receptors Located conducting upper airways, chest wall, diaphragm, and alveolar capillaries Three types respond to stimuli • Irritant • Stretch—Hering-Breuer reflex • j-receptors—juxtacapillary receptors Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 18 18 6 9/12/2022 Structures and Functions of Respiratory System (18 of 18) Respiratory defense mechanisms Protect lungs Filtration of air Mucociliary clearance system -escalator Cough reflex Reflex bronchoconstriction Alveolar macrophages Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 19 19 Gerontologic Considerations: Effects of Aging on Respiratory System Structural changes Defense mechanisms Respiratory control Reduced chest expansion and functional alveoli Reduced immune function More gradual responses to changes in O2 and CO2 levels See Table 25-2 Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 20 20 Assessment of Respiratory System (1 of 16) Health history and physical examination Subjective data Consider degree of respiratory distress Important health information • Past health history—respiratory, allergies, other body systems • Medications—prescription, OTC, Illicit, O2 • Surgery or other treatments Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 21 21 7 9/12/2022 Assessment of Respiratory System (2 of 16) Subjective data Functional health patterns (Table 25-3) • Health perception–health management pattern Smoking history/exposure to smoke Change in respiratory status; respiratory problems; characteristics of cough and sputum; international travel Immunizations • Genetic risk Family history of cystic fibrosis, COPD, asthma Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 22 22 Assessment of Respiratory System (3 of 16) Subjective data Functional health patterns • Nutritional–metabolic pattern Weight changes; fluid intake • Elimination pattern Incontinence; constipation • Activity–exercise pattern Dyspnea limitations (Table 25-4) Positions make better or worse ADLs Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 23 23 Assessment of Respiratory System (4 of 16) Subjective data Functional health patterns • Sleep–rest pattern Awakened during night; HOB increase; apnea; night sweats • Cognitive–perceptual pattern Neurologic changes; pain with breathing Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 24 24 8 9/12/2022 Assessment of Respiratory System (5 of 16) Subjective data Functional health patterns • Self-perception–self-concept pattern Social interactions; body image; self-esteem • Role–relationship pattern Family, job, social life Work—exposure to fumes, toxins, asbestos, coal, fibers, or silica Hobbies—exposure to dust or allergens Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 25 25 Assessment of Respiratory System (6 of 16) Subjective data Functional health patterns • Sexuality–reproductive pattern Change in sexual activity; positions • Coping–stress tolerance pattern Anxiety-dyspnea cycle; support group or pulmonary rehab referral • Value-belief pattern Adherence to treatment; explore constraints Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 26 26 Assessment of Respiratory System (7 of 16) Objective data Physical examination • VS with pulse oximetry • Nose Patency, inflammation, deformity, symmetry, discharge • Mouth and pharynx Color lesions, masses, gums, dentition, bleeding • Neck Symmetry, tenderness, swollen nodes Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 27 27 9 9/12/2022 Assessment of Respiratory System (8 of 16) Objective data Physical examination • Thorax and lungs Inspection Palpation Percussion Auscultation Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 28 28 Assessment of Respiratory System (9 of 16) Inspection Appearance: position; evidence of respiratory distress Shape, symmetry, and movement Respiratory rate, depth, and rhythm Skin and nails: cyanosis, clubbing Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 29 29 Assessment of Respiratory System (10 of 16) Palpation Tracheal position Expansion Fremitus Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 30 30 10 9/12/2022 Assessment of Respiratory System (11 of 16) Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 31 31 Assessment of Respiratory System (12 of 16) Sequence of examination Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 32 32 Assessment of Respiratory System (13 of 16) Percussion Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 33 33 11 9/12/2022 Assessment of Respiratory System (14 of 16) Percussion Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 34 34 Assessment of Respiratory System (15 of 16) Auscultation: Three normal sounds Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 35 35 Assessment of Respiratory System (16 of 16) Abnormal/adventitious breath sounds Crackles • Fine • Coarse Wheezes Stridor Pleural friction rub Abnormal voice sounds Egophony Bronchophony Whispered pectoriloquy Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 36 36 12 9/12/2022 Diagnostic Studies of Respiratory System (1 of 10) Pulse oximetry—SpO2 = 94% to 99% • Nursing: Be aware of factors affecting accuracy • See Tables 25-9 and 25-10 Arterial blood gases (ABG) • Oxygenation and acid-base balance • PaO2, PaCO2, pH, HCO3− , SaO2 See Table 25-11 • Nursing: No changes to O2 15 minutes before sample; use heparinized syringe; apply pressure Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 37 37 Diagnostic Studies of Respiratory System (2 of 10) CO2 monitoring (capnography) Transcutaneous—electrode on skin End-tidal—sensor analyzes exhaled air Mixed venous blood gases (SvO2) Sample from pulmonary artery using PA catheter or fiberoptic sensor on central line Normal SvO2 = 60% to 80% • Early warning of change in cardiac output or O2 delivery to tissues • See Table 25-12 Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 38 38 Diagnostic Studies of Respiratory System (3 of 10) Sputum studies (See Table 25-13) Expectoration, suctioning, or bronchoscopy for sample; or induced • Nursing: teach effective specimen production Skin tests—intradermal injection Allergies TB (See Table 25-14) • Nursing: read induration, not reddened area for interpretation Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 39 39 13 9/12/2022 Diagnostic Studies of Respiratory System (4 of 10) Bronchoscopy Direct visualization of bronchi through scope Obtain specimens Remove mucous or foreign bodies A Nursing: Fiberoptic bronchoscope Before: verify consent; NPO; sedated After: NPO until gag returns; monitor for hemorrhage or pneumothorax Smaller bronchus B Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 40 40 Diagnostic Studies of Respiratory System (5 of 10) Bronchoscopy Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) Sterile saline injected through scope and withdrawn to examine cells Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 41 41 Diagnostic Studies of Respiratory System (6 of 10) Lung biopsy (Table 25-15)—verify consent Transbronchial Percutaneous/transthoracic needle aspiration (TTNA) Video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) Open lung biopsy Nursing—may include: • Monitor for distress, pneumothorax, or bleeding; obtain chest X-ray; incision or chest tube care; monitor breath sounds; encourage deep breathing Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 42 42 14 9/12/2022 Diagnostic Studies of Respiratory System (7 of 10) Thoracentesis Needle inserted through chest wall to obtain specimens, remove pleural fluid, or instill medication Nursing Before—verify consent, explain procedure During—position and monitor After—monitor breath sounds and for hypoxia and pneumothorax; chest tube Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 43 43 Diagnostic Studies of Respiratory System (8 of 10) Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) Measures lung volumes and airflow Diagnose and monitor disease progression; evaluate treatment; determine disability Spirometer and computer calculate values; coaching from trained personnel • At home—peak flow meter See Tables 25-16 and 25-17 in the textbook Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 44 44 Diagnostic Studies of Respiratory System (9 of 10) Radiology—no metal; check pregnancy Chest x-ray—most common Computed tomography (CT) • Nursing: check allergy to contrast/iodine; renal function; encourage hydration before and after; feel warm and flushed with injection Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) • Nursing: screen for/remove all metal; check implantable devices; address claustrophobia (sedation) Ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scan Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 45 45 15 9/12/2022 Diagnostic Studies of Respiratory System (10 of 10) Radiology Pulmonary angiogram • Nursing: contrast media precautions, pressure dressing to injection site; monitor distal circulation Positron emission tomography (PET) • Nursing: NPO prior; monitor glucose levels; encourage fluids Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 46 46 Audience Response Question (1 of 2) A patient’s arterial blood gas (ABG) results include the following: pH 7.32, PaO2 84 mm Hg, PaCO2 49 mm Hg, and SaO2 84%. For what should the nurse assess the patient? a. Tetany b. Tachypnea c. Pleural friction rub d. Kussmaul respirations Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 47 47 Audience Response Question (2 of 2) Answer: B Tachypnea Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 48 48 16 9/12/2022 Audience Response Question (1 of 2) The nurse would interpret an induration of 5 mm resulting from tuberculin skin testing as a positive finding in which patient? a. A patient with a history of IV drug use b. A patient who immigrated from India 3 months ago c. A patient with diabetes and end-stage kidney disease d. A patient with human immunodeficiency virus- infected Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 49 49 Audience Response Question (2 of 2) Answer: D A patient who is human immunodeficiency virusinfected Copyright © 2020 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. 50 50 17