Cellular Respiration Worksheet: Aerobic & Anaerobic Processes
advertisement

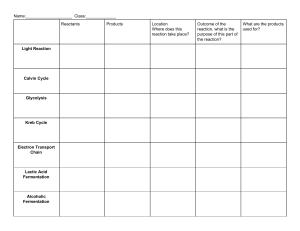
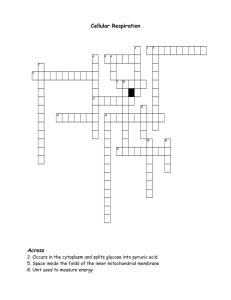
NAME: _____________________ CLASS: ________ DATE:_____________ CHAPTER CELLULAR RESPIRATION KSSM BIO F4 7.1 Energy Production through Cellular Respiration The main substrate in energy production Cellular respiration is carried out to generate the energy needed by all living cells. Cellular respiration is the oxidation process of organic molecules to release energy. The main substrate for cellular respiration is glucose. Chemical energy found in glucose is released to produce energy required by cells. In humans and animals, glucose is obtained through the digestion of carbohydrates from the food eaten. In green plants, light energy can be trapped by chlorophyll for the photosynthesis process to produce glucose. Types of cellular respiration Aerobic respiration-occurs in the presence of oxygen. Anaerobic respiration-occurs in the absence of oxygen. (In fermentation, the breakdown of glucose is incomplete in conditions of limited oxygen or without oxygen.) Formative Practice 7.1 (p.114) 1 Give five examples of the necessity of energy in a metabolic process. • Maintaining body temperature at the optimal temperature of ____________ • Muscle contractions to enable __________________. • ______ _____________whereby new cells are produced for growth and development. • Absorption of digested food through ________________ transport. • Synthesis of lipids, hormones, proteins and enzymes. 7.2 Aerobic Respiration Aerobic respiration is the breakdown of glucose involving oxygen to produce chemical energy. Oxygen is used to oxidise glucose to produce carbon dioxide, water and energy. The aerobic respiration process begins with the glycolysis process. Glycolysis means the breakdown of glucose by enzymes. This process occurs in the cytoplasm. One glucose molecule is broken down into two pyruvate molecules. The following process occurs in the mitochondrion. Pyruvate produced from glycolysis is then oxidised through a series of reactions to produce carbon dioxide, water and energy. A large amount of this energy is used to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules. (refer p.115) 7.3 Fermentation Fermentation is the incomplete breakdown of glucose in conditions of limited oxygen or without oxygen. Fermentation is different from aerobic respiration in its metabolic pathway after the glycolysis stage. After glycolysis, the pyruvate produced will undergo either alcohol fermentation or lactic acid fermentation. 1 (refer Alcohol Fermentation p.118 and Lactic Acid Fermentation p.119) ALCOHOL FERMENTATION The incomplete breakdown of glucose to ethanol, carbon dioxide and energy. -happens in yeast and some plant cells when there is lack of oxygen. LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION The breakdown of glucose into lactic acid and energy. -happens in bacteria such as a Lactobacillus and human muscle cells when there is lack of oxygen. Human muscle cells: During vigorous training, the rate of oxygen used exceeds the oxygen supplied by the blood circulatory system. The muscle is in an oxygen-deficiency state and is said to undergo oxygen debt. During this process, glucose cannot break down completely. The produced lactic acid accumulates until it reaches a level of concentration that can cause fatigue and muscle cramps. Comparison between aerobic respiration and fermentation (refer Figure 7.2 p.121) Homework: Copy the similarities and differences into foolscap paper. Formative Practice 7.3 (p.121) 2 Give three examples of microorganisms and food produced by the fermentation process. Organism: Saccharomyces Organism: Aspergillus Organism: Acetobacter 3 Product of fermentation: CO2, ethanol Product of fermentation: lactic acid Product of fermentation: acetic acid Example: ________ Example: ________ Example: ________ While helping your father to cut the grass at the farm, you come across a snake. Terrified, you run away from the snake. Explain the cellular respiration that takes place in the muscle cells of your legs. When you sprint, the lungs and blood supply are unable to supply ___________ quickly enough to meet the demands of the muscles to produce ATP. In this condition, the muscle cells undergo _________________ process, whereby ATP is produced without oxygen. Fermentation in muscle cells produces ___________ ______. 4 State FOUR differences between aerobic respiration and fermentation.(refer Table 7.1 p.121) • Aerobic respiration involves the complete breakdown of organic substances in the presence of ___________ whereas fermentation involves incomplete breakdown of organic substances in the presence of limited ___________ or absence of ___________. • Aerobic respiration takes place in _____________ and ________________ but fermentation only takes place in the _______________ only. • Aerobic respiration produces ____________ whereas fermentation does not. • In aerobic respiration, glucose is oxidised completely into ___________ _____________ and _________ whereas in fermentation, glucose is oxidised to ____________ or _______ ______. 2