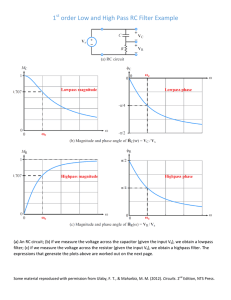
Don Honorio Ventura Technological State University College of Engineering and Architecture Department of Electronics Engineering Bacolor, Pampanga INDIVIDUAL REPORT Course Code: COMMS 1 (LAB) Course Title: COMMUNICATIONS THEORY 1 (LABORATORY) Year and Section: BS ECE- 2B Room/Time/Date: ECE LABORATORY / 07:30-10:30 a.m. / JAN. 07, 2020 Experiment No.: EXPERIMENT 1 Experiment Title: FILTERS Date Experiment Performed: JANUARY 07, 2020 Date Experiment Final Due: JANUARY 07, 2020 Group Number: 4 Experiment Leader: GONZALES, DANE MACKLYN Y. Experiment Members: MERCADO, KIMBERLY JOY Y. SIYTOO, JAILAH JOY V. Instructor: Engr. Enmar T. Tuazon Date Final Received: Day Late: VILLEGAS, CHESKA MAE B. INTRODUCTION: In electronic circuits systems, it is often helpful to separate a specific range of frequencies from the total spectrum. It is a type of circuit that passes a specific range of frequencies while rejecting other frequencies. A passive filter consists of passive circuit elements such as capacitors, inductors and resistors. Further, it is a device that changes the amplitude of an AC voltage as the frequency of the input voltage changes. Filters have two terminals, the input terminals take in the input voltage, which passes through the filter and onto the output terminals, where the resulting output waveform can be observed. Typically in electronic systems such as filters and communication channels, cutoff frequency applies to an edge in a lowpass, highpass, bandpass, or band-stop characteristic , a frequency characterizing a boundary between a passband and a stopband. From a graph, it can be find the by finding the frequency where the magnitude of the output voltage is 70.7% off from the maximum value. In another way, the frequency when the signal magnitude is Vpp/sqrt(2). It can also be calculated from the R and C values as: 𝑓𝑐𝑜 = 1 2𝜋𝑅𝐶 There are several types of filters, but in the experiment, we will be looking at three types. A low-pass filter is a filter that allows a signal of a low frequency (i.e. a low amount of oscillations per second) to pass through it. Consequently, it attenuates (reduces) the amplitude of an input signal whose frequency is higher than the cutoff frequency. R = 10kW Vin C = 47nF Vout A high-pass filter is a filter that passes high frequencies well, but attenuates (or reduces) frequencies lower than the cutoff frequency. C = 47nF Vin R = 10kW Vout A band-pass filter is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects (attenuates) frequencies outside that range. L = 10mH C = 47nF Vin R = 1kW Vout DISCUSSION: We started the experiment by constructing the given low-pass filter in the simulation software Multisim, consisting of a resistor and a capacitor. The input is connected in series with the resistor, and the output is the voltage across the capacitor. The input and output have one common terminal, which is the low (ground, or reference) side of each. We then set up the function generator so that it produces a sinusoidal waveform, with a peak to peak voltage of 10V and put the oscilloscope to verify this and a multimeter to measure the voltages. Next, we use Channel 1 of the scope to display Vin, and Channel 2 to display Vout. Starting at 50Hz, we vary the frequency of the input signal up to 2500Hz (2.5kHz) in a sufficient number of intervals and record the peak to peak voltage of the output for each frequency, and tabulate the data obtained. Lastly, we plot a graph of the amplitude of Vout against the frequency and calculated for the cut-off frequency. Low-Pass Graph Moreover, we constructed an RC network that behaves as a high-pass filter on the Multisim, and the high-pass filter is the same as the low-pass filter, but with the positions of the resistor and capacitor interchanged. Here the input is in series with the capacitor and the output voltage is taken across the resistor. We just repeated the steps we did on the low-pass filter, but, this time we started our frequency readings at 100Hz and work our way up to 10kHz, and recorded the data obtained. High-Pass Graph Lastly, we constructed the circuit for band-pass filter on the simulation software, the output voltage is taken across the resistor and the input is in series with the inductor and the capacitor. We then also repeat the same procedures we did on the previous filters but started frequencies from 2kHz up to 30kHz and recorded the data obtained and plotted them on a graph. Band-Pass Graph CONCLUSION: The discrepancies between the theoretical and measured value are relatively small. The cut cut-off frequency can be changed by adjusting the value of either the resistor or the capacitor as can be noticed from the formula. Meanwhile, a potentiometer is an alternative way to be utilized for varying, adjusting, or tuning circuits. Low-pass filter allows the frequencies below the cut-off frequency to pass and attenuates those above its cut-off frequency. Conversely, high-pass filter allows the frequencies above the cut-off frequency to pass and attenuated those below it. On the other hand, a band-pass filter allows certain range of frequencies around the center frequency to pass and rejects those above and below the center frequency. Applications of low-pass and high-pass are audio amplifiers and speaker systems. Band-pass filters are used for wireless transmitters. Additionally, low pass filter inhibits that when a greater frequency is set up, the lower the voltage, high-pass filter shows that a greater frequency, the greater voltage obtained. Meanwhile, band-pass filter demonstrates that as the frequency increases, the voltage approaches the amplitude but as it reach closer to the amplitude, it decreases. Reference: Experiment Manual