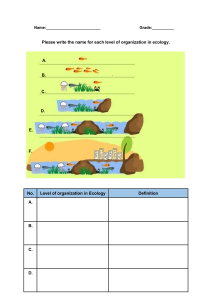
Chapter 1: The Nature of Ecology Learning Objectives • Define ecology • Understand the biological hierarchy in ecology. • Understand the scientific Method • Understand good experimental design What is Ecology? • Ecology – the study of how organisms interact with each other and the environment. Biological Hierarchy • Organism – an individual form of life. • Populations – the number of one species in a given area. • Community – all the populations interacting with one another in a given area. • Ecosystem – the biotic (living) community and abiotic (non-living) environment interacting as a unit. • Biosphere – the layer of earth in which all living organisms exist. Questions that can be asked at each hierarchical level Scientific Method Example of Scientific Method • Observation: Growth of juvenile convict cichlid fish vary. • Question: Is this variation in growth due to food acquisition? • Hypotheses: Variation in growth is directly related to food acquisition capability. • Predictions: If variation in growth is due to the food acquisition, then fish that are given more food will grow faster. • Hypothesis Testing: How would we do this???? • Give one set of fish more food than the other Good Experimental Design • Can easily identify the dependent & independent variables. • The dependent variable is quantifiable. • There are no confounding variables. – Confounding variable – a variable that is not the focus of study, but influences the independent and dependent variable. • There is a control group if appropriate. • It is something feasible to accomplish. • It answers your hypotheses and predictions.