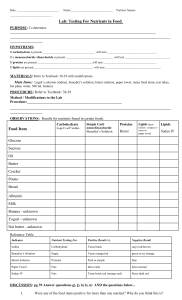
Biuret & Emulsion Tests (Protein & Lipids) Biuret Test • Biuret test is used to test for the presence of proteins by: • Detecting the presence of peptide bonds Biuret Test Procedure 1. Add the sample to be tested to a clean test tube. Biuret Test Procedure 2. Add Biuret A (sodium hydroxide) to the test tube. • This is to make the solution alkaline. Biuret Test Procedure 3. Add Biuret B [copper (II) sulphate] to the test tube. 3.1. Mix the solution gently. Biuret Test Procedure 4. Record results • If proteins are present: colour change from blue purple • If proteins are absent: no colour change. Emulsion Test • Used to detect the presence of lipids. A fine dispersion of minute droplets of one liquid in another in which it is not soluble. What is an emulsion? Emulsion Test • Lipids are nonpolar molecules that do not dissolve in water • BUT, will dissolve in organic solvent such as ethanol. • This is a qualitative test: does not give a quantitative value of how much lipid may be present. Emulsion Test Procedure 1. Add the sample to be tested to a clean test tube. Emulsion Test Procedure 2. Add ethanol to the test tube. • Mix solution thoroughly to dissolve any lipids. Emulsion Test Procedure 3. Add water to the test tube. • Mix solution gently. Emulsion Test Procedure 4. Record results. • If lipids are present: cloudy white • If lipids are absent: no change Emulsion Test Reasoning • Reason for cloudy white substance: • Lipids dissolve in ethanol. • When water is added, lipids separate to form lipid globules. • Lipids are hydrophobic. Learning Check Question 1 • Explain why the Biuret test is a qualitative test. Learning Check Question 1 • Name the bond that is found between adjacent amino acids. Learning Check Question 1 • Name the bond that is found between adjacent amino acids.