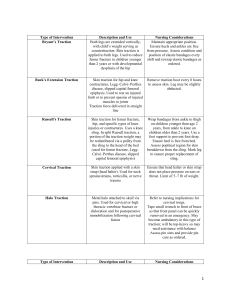
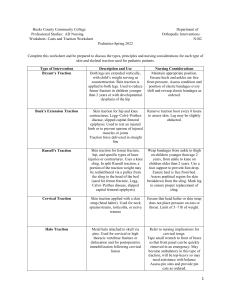
Case Study Discussion Questions 1 Virtual Clinical #5 Case Study Holy Family University Discussion Questions Case Study Discussion Questions 2 1. What does N.E.’s diagnosis of a closed, complete, oblique fracture of the left femur mean? A closed break means that the skin has not been disrupted. A complete break means that the break goes completely through the bone and oblique means that the direction of the break extends in an oblique direction, or at an angle. 2. What is the primary purpose of applying Buck’s traction? What interventions do you employ to maintain the traction system? The primary purpose of the Buck's traction is to immobilize the break in the left femur. Other uses include preventing soft tissue damage and reducing pain and muscle spasms. To prevent external rotation of the left hip from the Buck's traction, a pillow, sandbag, or rolled-up draw sheet is placed along the greater trochanteric region of the left femur. Ensure that he is in the proper position in the bed and the weights are always hanging freely. 3. What specific assessments do you need to be performed? Palpate left posterior tibial and dorsalis pedis pulses to assess circulation. Determine dorsiflexion and plantar flexion to assess motor function of the lower extremity. Assess sensory innervation on the peroneal nerve on the dorsal part of the foot between the web space of the great and second toes. Assess tibial nerve. Assess N.E.'s skin frequently for redness and ulcers. Neurovascular assessment of the injured extremity is a priority with musculoskeletal injuries. The neurovascular assessment should consist of a peripheral vascular assessment and a peripheral neurologic assessment. Case Study Discussion Questions 3 4. What potential complications is N.E. at risk for due to his reduced mobility? Describe interventions to include in his plan of care to prevent each complication. N.E. would be at a high risk for a fall due to the leg fracture and any pain medications given. To prevent falls N.E. needs to be given the instruction to call for help before getting up, he needs to be wearing non-slip socks, and have his call light in reach 5. What additional assessments do you need to make at this time? A neurovascular assessment on the left leg, consisting of a peripheral vascular assessment to assess color, temperature, capillary refill, peripheral pulses, and edema and a peripheral neurologic assessment to assess sensation, motor function, and pain. 6. N.E. states that he has some numbness and tingling in his left foot. What do you suspect and what should you do? Notify the orthopedic surgeon immediately because the patient may have developed compartment syndrome. 7. Using SBAR, outline the information you would provide the surgeon when you call? S: I am nurse Adams. I am calling about patient N.E because he has severe pain that appears to be uncontrolled, and the pain is now below the site of injury. B: N.E. is a 32-year-old male who sustained a closed, complete, oblique fracture of the left femur in a single vehicle motor vehicle accident. He is being admitted to the orthopedic floor from the ED and is scheduled to have surgery tomorrow afternoon. He states he had asthma as a child and denies any other health problems. Patient pain has changed in the last two hours, he previously reported 4/10 pain and it is now 10/10 and below the site of injury after receiving 2mg of morphine. Case Study Discussion Questions 4 A: I think the problem is compartment syndrome and I have already given a 2mg of morphine twice. R: I need you to come and see the patient as soon as you can. Is there is anything I can do in the meantime? Case Study Discussion Questions 5 References Harding, M., In Kwong, J., In Roberts, D., In Hagler, D., & In Reinisch, C. (2020). Lewis's medical-surgical nursing: Assessment and management of clinical problems Assessment Technologies Institute. (2019). In Content mastery series: Review module, RN adult medical-surgical nursing (11th ed., pp. 469-473).