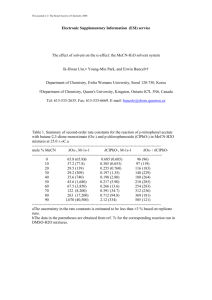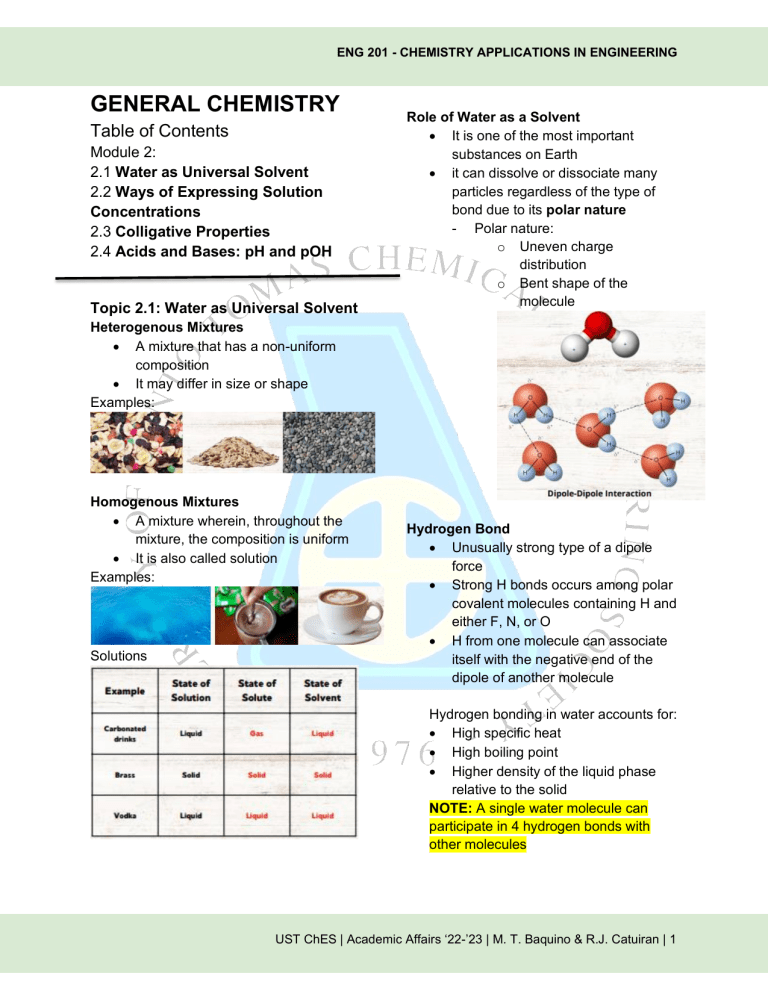
ENG 201 - CHEMISTRY APPLICATIONS IN ENGINEERING GENERAL CHEMISTRY Table of Contents Module 2: 2.1 Water as Universal Solvent 2.2 Ways of Expressing Solution Concentrations 2.3 Colligative Properties 2.4 Acids and Bases: pH and pOH Topic 2.1: Water as Universal Solvent Role of Water as a Solvent • It is one of the most important substances on Earth • it can dissolve or dissociate many particles regardless of the type of bond due to its polar nature - Polar nature: o Uneven charge distribution o Bent shape of the molecule Heterogenous Mixtures • A mixture that has a non-uniform composition • It may differ in size or shape Examples: Homogenous Mixtures • A mixture wherein, throughout the mixture, the composition is uniform • It is also called solution Examples: Solutions Hydrogen Bond • Unusually strong type of a dipole force • Strong H bonds occurs among polar covalent molecules containing H and either F, N, or O • H from one molecule can associate itself with the negative end of the dipole of another molecule Hydrogen bonding in water accounts for: • High specific heat • High boiling point • Higher density of the liquid phase relative to the solid NOTE: A single water molecule can participate in 4 hydrogen bonds with other molecules UST ChES | Academic Affairs ‘22-’23 | M. T. Baquino & R.J. Catuiran | 1 ENG 201 - CHEMISTRY APPLICATIONS IN ENGINEERING Topic 2.2: Ways of Expressing Solution Concentrations Unsaturated Solution • a solution in which more solute can be dissolved. Example: Saturated Solution • A solution in which the maximum amount of solvent has been dissolved. • Any more solute added will sit as crystals on the bottom of the container. Example: Supersaturated • A solution that contains more than the average solvent that can be dissolved at a given temperature. Example: Concentration Units • Molarity (M) • Mole Fraction (X) • Mass Percent • Molality (m) Molarity • is the amount of a substance in a certain volume of solution. 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑡𝑦 (𝑀) = 𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑠 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 • Preparation of a solution to a specified molarity can be attained using the dilution equation. 𝑀1 𝑉1 = 𝑀2 𝑉2 UST ChES | Academic Affairs ‘22-’23 | M. T. Baquino & R.J. Catuiran | 2 ENG 201 - CHEMISTRY APPLICATIONS IN ENGINEERING Mole Fraction • Is the ratio of the number of moles of one component of a solution or other mixture to the total number of moles representing all the components. 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒 𝑓𝑟𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 (𝑥) = • 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑖 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 By adding up the mole fractions of all components of a solution, the sum should always be 1 𝑋𝑎 + 𝑋𝐵 + ⋯ = 1 Molality • is the amount of a substance dissolved in a certain mass of solvent. 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑎𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑦 (𝑚) = 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 𝑘𝑔 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡 Conversions Between Concentration Units Mass Percent • Is the ratio of the mass of solute that is present in a solution, relative to the mass of the solution, as a whole 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 = • 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 When the amount of solute is very small, the concentration is often expressed as parts per million (ppm) or parts per billion (ppb) 𝑔 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 𝑥 106 𝑔 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑔 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 1 𝑝𝑝𝑏 = 𝑥 109 𝑔 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 1 𝑝𝑝𝑚 = UST ChES | Academic Affairs ‘22-’23 | M. T. Baquino & R.J. Catuiran | 1 ENG 201 - CHEMISTRY APPLICATIONS IN ENGINEERING Sample Problems 1. Copper sulfate is widely used as a dietary supplement for animal feed. A lab technician prepares a “stock” solution of CuSO4 by adding 79.80 g of CuSO4 to enough water to make 500.0 mL of solution. An experiment requires a 0.1000 M solution of CuSO4. MW of CuSO4 is 159.6 g/mol (a) What is the molarity of the CuSO4 “stock” solution prepared by the technician? (b) How would you prepare 1.500 L of 0.1000 M solution from the stock solution? 2. Hydrogen peroxide is used by some water treatment systems to remove the disagreeable odor of sulfides in drinking water. It is available commercially in a 20.0% by mass aqueous solution. What is the mole fraction of H2O2? MW of H2O2 = 34.02 g/mol MW of H2O = 18.02 g/mol UST ChES | Academic Affairs ‘22-’23 | M. T. Baquino & R.J. Catuiran | 1 ENG 201 - CHEMISTRY APPLICATIONS IN ENGINEERING 3. Glucose, C6H12O6, in water is often used for intravenous feeding. Sometimes sodium ions are added to the solution. A pharmacist prepares a solution by adding 2.0 mg of sodium ions (in the form of NaCl), 6.00 g of glucose, and 112 g of water. (a) What is the molality of the glucose in solution? (b) How many ppm of Na+ does the solution contain? 4. Convert 10 M of H2SO4 into molality. The density of H2SO4 is 1.84 g/mL and the molar mass of H2SO4 is 98.09 g/mol. UST ChES | Academic Affairs ‘22-’23 | M. T. Baquino & R.J. Catuiran | 2 ENG 201 - CHEMISTRY APPLICATIONS IN ENGINEERING Topic 2.3: Colligative Properties Colligative Properties • Properties that depend primarily on the concentration or the relative number of solute particles present rather than their nature. Such properties include: o Vapor pressure lowering o Boiling point elevation o Freezing point depression o Osmotic pressure Vapor pressure lowering • Concentrated aqueous solutions evaporate more slowly than pure water. • Ex: The vapor pressure of water above a 0.10 M solution of either glucose or sucrose at 0 °C is about 0.008 mmHg less than that of pure water Raoult’s Law P1 = 𝑋1 𝑃1𝑜 Freezing Point Depression • the solution of a nonvolatile solute, when cooled, only freezes when its temperature reaches below the freezing point of the solvent ∆Tf = 𝑇𝑓𝑜 − 𝑇𝑓 ∆Tf = 𝐾𝑓 ∗ 𝑚 Wherein: Kf - molal freezing point constant m - molality Boiling Point Elevation • The solution of a nonvolatile solute, when heated, only boils when its temperature exceeds the boiling point of the solvent. The difference in temperature is called the boiling point elevation, ∆Tb ∆Tb = 𝑇𝑏𝑜 − 𝑇𝑏 ∆Tb = 𝐾𝑏 ∗ 𝑚 Wherein: Kb - molal boiling point constant m - molality UST ChES | Academic Affairs ‘22-’23 | M. T. Baquino & R.J. Catuiran | 2 ENG 201 - CHEMISTRY APPLICATIONS IN ENGINEERING • • • Osmotic Pressure The spontaneous passage of a pure solvent into a solution that is separated via semipermeable membrane, wherein solute particles are not allowed to pass through is called osmosis. • • osmotic pressure, then the water flows in the opposite direction. This is called reverse osmosis The pressure that is applied to the solution to stop the influx of solvent is called osmotic pressure (𝛱). If the external pressure (P) exceeds the osmotic pressure, then the water flows in the opposite direction. This is called reverse osmosis π= 𝑛𝑅𝑡 𝑉 π – osmotic pressure n – moles r- gas law constant T- Temperature V- Volume Sample Problems 1. A solution contains 82.0 g of glucose, C6H12O6, in 322 g of water. Calculate the vapor pressure of the solution at 25°C (vapor pressure of pure water at 25°C = 23.76 mm Hg) UST ChES | Academic Affairs ‘22-’23 | M. T. Baquino & R.J. Catuiran | 3 ENG 201 - CHEMISTRY APPLICATIONS IN ENGINEERING 2. An antifreeze solution is prepared containing 50.0 cm3 of ethylene glycol, C2H6O2 (d = 1.12 g/cm3), in 50.0 g of water. Calculate the freezing point of this 50-50 mixture 3. Calculate the osmotic pressure at 15°C of a solution prepared by dissolving 50.0 g of sugar, C12H22O11, in enough water to form one liter of solution. UST ChES | Academic Affairs ‘22-’23 | M. T. Baquino & R.J. Catuiran | 2 ENG 201 - CHEMISTRY APPLICATIONS IN ENGINEERING Topic 2.4: Acids and Bases: pH and pOH Definition of Acids and Bases • According to Svante Arrhenius: o an acid is a species that produces H+ ions in water solution o a base is a species that produces OH- ions in water solution o Amphiprotic • a species that can either accept or donate a proton Ex: Water molecule Ion Product of Water • According to Johannes Brønsted and Thomas Lowry: o an acid is a proton (H+ ion) donor o a base is a proton (H+ ion) acceptor o in an acid-base reaction, a proton is transferred from an acid to a base • The Brønsted-Lowry reaction above shows the amphiprotic nature of water. However, it can also be viewed as the ionization of a single water molecule as seen below. • In the equilibrium constant expression for reactions in a solution: o solutes enter as their molarity [] o the solvent, H2O in this case, does not appear. Its concentration is essentially the same in all dilute solutions • In pure water, both ions are formed in equal numbers. Therefore, Brønsted-Lowry Acid-Base Model • • • Conjugate base - the species formed when a proton (H+) is removed from an acid. Conjugate acid - the species formed when a proton (H+) is added to a base UST ChES | Academic Affairs ‘22-’23 | M. T. Baquino & R.J. Catuiran | 2 ENG 201 - CHEMISTRY APPLICATIONS IN ENGINEERING • In most water solutions, H+ and OHconcentrations are not equal. Both ions have an inversely proportional relationship. If [H+] is greater than [OH-], the solution is termed acidic. If [OH-] is greater than [H+], the solution is termed as basic / alkaline. pOH • power of the hydroxide ion\ • • • if pH < 7.0 - acidic solution if pH = 7.0 - neutral solution if pH > 7.0 - basic solution pH and pOH pH • power of the hydrogen ion Note: at 25 °C, pH + pOH = 14 UST ChES | Academic Affairs ‘22-’23 | M. T. Baquino & R.J. Catuiran | 3 ENG 201 - CHEMISTRY APPLICATIONS IN ENGINEERING Sample Problem Calculate, at 25°C: 1. the [H ] and pH of a tapwater sample in which [OH ] = 2.0 X 10E-07. 2. the [H ] and [OH ] of human blood at pH 7.40. 3. the pOH of a solution in which [H ] = (5.0)[OH ] Ans: 1. [H+] = 5.0 X 10^-8 M, pH = 7.30 2. [H ] = 4.0 X 10^-8 M, [OH ] = 2.5 X 10^-7 M 3. pOH = 7.35 UST ChES | Academic Affairs ‘22-’23 | M. T. Baquino & R.J. Catuiran | 4 ENG 201 - CHEMISTRY APPLICATIONS IN ENGINEERING References Admin. (2022, May 13). Supersaturated solution - definition, examples & applications with videos. BYJUS. Retrieved August 17, 2022, from https://byjus.com/chemistry/supersaturated-solution/ Libretexts. (2020, August 11). 7.13: Concentrations: Mass percent. Chemistry LibreTexts. Retrieved August 17, 2022, from https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Heartland_Community_College/CHEM_120%3A_Fun damentals_of_Chemistry/07%3A_Solutions/7.13%3A__Concentrations%3A__Percents#:~ :text=The%20mass%20percent%20of%20a%20solution%20is%20defined%20as%20the,th e%20solution%2C%20as%20a%20whole. Merriam-Webster. (n.d.). Mole fraction definition & meaning. Merriam-Webster. Retrieved August 17, 2022, from https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/mole%20fraction Molarity vs Molality: Formula and definitions. Analysis & Separations from Technology Networks. (n.d.). Retrieved August 17, 2022, from https://www.technologynetworks.com/analysis/articles/molarity-vs-molality-formula-anddefinitions-334119 Saturated solution definition. (n.d.). Retrieved August 17, 2022, from https://groups.molbiosci.northwestern.edu/holmgren/Glossary/Definitions/DefS/saturated_solution.html#:~:text=A%20solution%20in%20which%20the,the%20bottom% 20of%20the%20container. Unsaturated solution. (n.d.). Retrieved August 18, 2022, from https://www.chem.purdue.edu/jmol/gloss/unsoln.html#:~:text=unsaturated%20solution%3 A%20a%20solution%20in%20which%20more%20solute%20can%20be%20dissolved. UST ChES | Academic Affairs ‘22-’23 | M. T. Baquino & R.J. Catuiran | 2