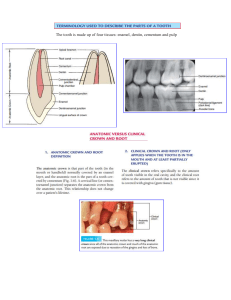
PERIODONTIUM PERIODONTIUM Cementum Pulp cavity Enamel Dentin Gingiva PDL Alveolar bone Cementum Sharpey's fibers Attachment organ Periodontal ligament Root canal Alveolar bone Apical foramen Alveolar vessels & nerves TEETH IN-SITU APICAL FORAMEN Cementum Periodontal Ligament Alveolar bone Gingiva facing the tooth Periodontium is the supporting tissue adjacent to the teeth. It consists of the free gingiva, attached gingiva, the cementum, periodontal ligament and the alveolar bone. ALVEOLAR BONE : Bone of the maxilla and the mandible that houses the sockets for the roots of teeth. PERIODENTAL LIGAMENT : Is a connective tissue which attaches the cementum of the root to the Alveolar bone. GINGIVA : Is the soft tissue that surrounds the tooth. Also called the GUM. 1.Supply annotations to periodontium and tooth below(10): Gingivitis Healthy gingiva Gingivitis is irritation and inflammation of the part of gum around the base of your teeth (gingiva). RED, SWOLLEN, TENDER, BLEEDING WHEN BRUSHING HALITOSIS Brushing your teeth twice a day and flossing once a day removes plaque Gingivitis can be reversed with professional treatment (SCALE AND POLISH) GOOD HOME ORAL CARE: BRUSHING AND FLOSSING ORAL RINSE WITHOUT ALCOHOL STARCH AND SUGAR+ ORAL HYGIENE PLAQUE(sticky film ) (+BACTERIA) HARDEN CALCULUS (TARTAR) POCKETS between gums and teeth, fill with plaque, tartar and bacteria REVERSED WITH PROFESSIONAL TREATMENT: Deep scale, root planing and surgery Swollen or puffy gums Bright red, dusky red or purplish gums Gums that feel tender when touched Gums that bleed easily Gums that pull away from your teeth (recede), making your teeth look longer than normal New spaces developing between your teeth Pus between your teeth and gums Bad breath Loose teeth Painful chewing A change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite Plaque Calculus Medical History Medication (Epilepsy) UNTREATED PERIODONTITIS CAN LEAD TO PROBLEMS IN IMMUNE SYSTEM HEART DISEASE DUE TO CHRONIC BACTERIA IN BLOOD STREAM