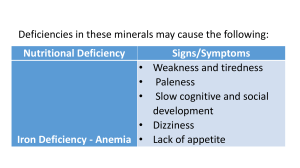
INTRODUCTION DEFINITION Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis (CVST) is a type of rare blood clot that forms in the venous sinuses in your brain. This is a system of veins found between the layers of the dura mater -- the tough outer layer of your brain that lies directly under your skull. causes • Thrombophilia, a tendency to develop blood clots due to abnormalities in coagulation, e.g. factor V Leiden, deficiency of protein C, protein S or antithrombin, or related problems. • Nephrotic syndrome, a kidney problem causing protein loss in the urine. • Chronic inflammatory diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease, lupus and Behçet's disease. • Pregnancy and puerperium (the period after giving birth). • Particular blood disorders, especially polycythemia vera and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. • Use of estrogen-containing forms of hormonal contraception. causes •Meningitis and infections of the ear, nose and throat area such as mastoiditis and sinusitis. •Direct injury to the venous sinuses. •Medical procedures in the head and neck area. •Sickle cell anemia. •Dehydration, primarily in infants and children. •Homocystinuria. Risk factors • Pregnancy and the first few weeks after delivery • Problems with blood clotting; for example, antiphospholipid syndrome, protein C and S deficiency, antithrombin III deficiency, lupus anticoagulant, or factor V Leiden mutation • Cancer • Collagen vascular diseases like lupus, Wegener’s granulomatosis, and Behcet syndrome • Obesity • Low blood pressure in the brain (intracranial hypotension) • Inflammatory bowel disease like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis • Risk factors for children and infants include: • Problems with the way their blood forms clots • Sickle cell anemia • Chronic hemolytic anemia • Beta-thalassemia major • Heart disease — either congenital (you're born with it) or acquired (you develop it) • Iron deficiency • Certain infections • Dehydration • Head injury • For newborns, a mother who had certain infections or a history of infertility SIGNS AND SYMTOMS •Headache •Blurred vision •Fainting or loss of consciousness •Loss of control over movement in part of the body •Seizures •Coma SURGERY AND POST OF CARE was based on the location and size of the venous infarct and . A bone flap larger than the venous infarct was made and the dura was widely opened and patched with the pericranium. The wound was closed in layers over a drain. , patients were monitored in the ICU and were mechanically ventilated in most cases. Twelve hours after surgery, anticoagulation with either heparin infusion or LMWH was resumed and subsequently changed to oral anticoagulation with warfarin. Oral anticoagulation was continued for at least 6 months. Patients with a craniectomy had a cranioplasty performed 3-6 months following the decompressive surgery COMPLICATION • Impaired speech • Difficulty moving parts of the body • Problems with vision • Headache • Increased fluid pressure inside the skull • Pressure on nerves • Brain injury • Developmental delay • Death PREVENTION • Respond quickly to symptoms like headaches, blurry vision, fainting, losing control of a part of your body, and seizures. • If you have the above symptoms, have someone take you immediately to the emergency room or call 911 for help. • Take your medicines as prescribed, and check with your health are provider to make sure that none of your medicines increase your risk of havi • Lead a healthy lifestyle which includes eating a low-fat diet made up mostly of fruits and vegetables, low-fat meats and proteins, low-fat dairy products, and whole-fiber grains, breads, cereals, and pasta. • Exercise daily and avoid smoking. NURSING MANAGEMENT • Monitor the vital sings,GCS,pupils, • monitor intake output to the patient. • Head end elevation 30-40 degree to be maintained • Provide comportable position • provide acitrom diet • provide good nutrient diet • provide 2nd hourly position to prevent bedsore • psycological support to the attenders NURSING DIAGNOSIS • Acute pain related to decrease blood circulation in the brain • ineffective cerebral tissue perfusion related to clot formation in to the brain • Impaired physical mobility related to current immobility • ineffective airway clearance related to increase secreation • Imbalance nutrition(less than boby requirment) related to insufficient intake of food • Risk for infection • self care deficit related to immobility • anxiety related to chance in health status and situational crisis. • knowledge deficient regarding health condition and self care. THANK YOU