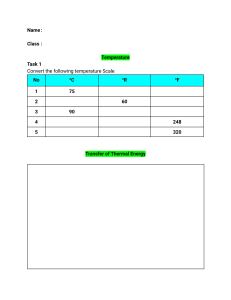
Unit 2: Energy & Energy Management – In this unit I will learn that there are different categories and forms of energy and that these forms of energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed - The Law of Conservation of Energy. I will also increase my knowledge of how thermal energy is exchanged between substances through heat transfer by conduction, convection, and radiation. Forms of Energy All forms of energy fall under two categories Kinetic Energy (Motion) Potential Energy (Stored/Position) Electrical Radiant Chemical Nuclear Thermal Sound Mechanical TEK 6.9A – investigate methods of thermal energy transfer, including conduction, TEK 6.8A – compare and convection and radiation. contrast potential and kinetic energy TEK 6.9B verify through investigations that thermal energy moves in a predictable pattern from warmer to cooler… The height of an object’s position, its mass and the field of gravity affects the object’s potential energy. The mass and the velocity of an object affect the object’s kinetic energy. Heat (Thermal Energy) always moves from a warmer substance to a cooler substance. Heat moves until a Thermal Equilibrium has occurred (Where a common/equal temperature has been reached.) Gravitational nuclear energy: holds protons TEK 6.9C – and neutrons in the TEK 6.7A – research and together demonstrate energy nucleus of an atom, the debate the advantages and transformations energy disadvantages of using coal, such as energy in a oil, natural gas, nuclear flashlight can be battery power, biomass, wind, changes releasefrom hydropower, geothermal, and chemical d when energy to solar resources. electrical energy to the light energy nuclei are combin ed or split apart: the sun combin es the nuclei of the one form of Changing hydrogeto another energy n atomform (fusion) and nuclear power plants TEK 6.7B – design a logical plan to manage energy resources in the home, school, or community In this unit I must know this vocabulary… TEKS 6.8A TEKS 6.7A energy renewable resource kinetic energy non-renewable resource potential energy coal gravitational potential energy oil thermal energy petroleum chemical energy natural gas solar (radiant) energy nuclear power electrical energy biomass nuclear energy hydropower mechanical energy hydroelectric geothermal TEKS 6.9 A & B fossil fuel conduction alternative sources of energy convection radiation TEKS 6.9C energy transformation heat TEKS 6.7B energy efficiency After completing this unit I should I be able to do this… I can compare and contrast potential and kinetic energy. I can define and provide examples of conduction, convection and radiation. I can describe the movement of thermal energy. I can give several examples of energy transformation. I can describe the advantages and disadvantages of using renewable and non-renewable resources. I can provide examples of how to conserve energy at home or school. law of conservation of energy After completing this unit I should I be able to answer these questions… 1. A pendulum swings back and forth. What would be the easiest way to increase its potential energy? TEKS 6.8A 2. A door separates two small rooms in a house. The air in one room is at a temperature of 25°C, while the air in the other room is at 30°C. If the 3. Describe the relationship between potential and kinetic door is left open for several energy at each point on the roller coaster. TEKS 6.8A hours, what is most likely to happen and what type of 4. Where is the kinetic energy the greatest? Where is the thermal energy transfer is potential energy the greatest? occurring? TEKS 6.9A & 6.9B 5. Describe the energy transformation(s) that occurs when: a) a battery operated remote is used to control a toy car; and b) falling water runs through a hydroelectric power plant, turning giant turbines in the plant which produces electricity that is carried by wires into homes where it powers electric heaters. Describe the energy transformations that have taken place. TEKS 6.9C