IV Solutions: Isotonic, Hypotonic, Hypertonic Explained
advertisement
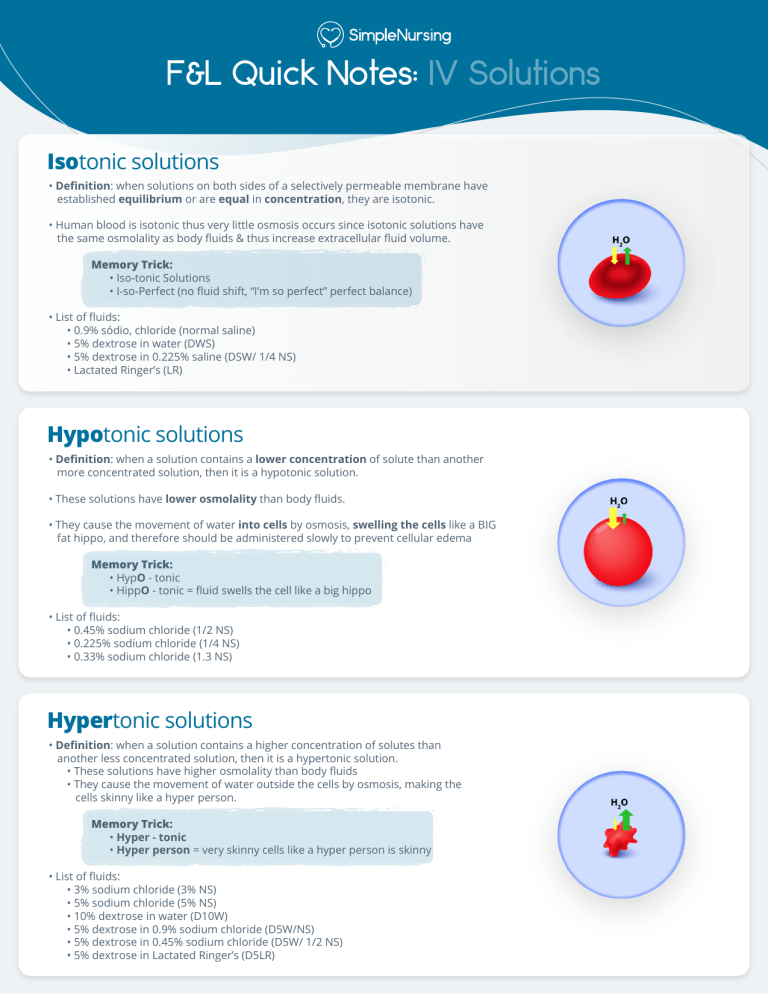
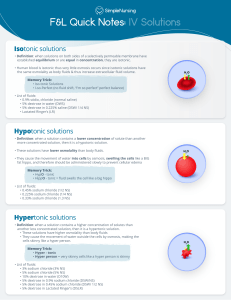
F&L Quick Notes: IV Solutions Isotonic solutions • Definition: when solutions on both sides of a selectively permeable membrane have established equilibrium or are equal in concentration, they are isotonic. • Human blood is isotonic thus very little osmosis occurs since isotonic solutions have the same osmolality as body fluids & thus increase extracellular fluid volume. Memory Trick: • Iso-tonic Solutions • I-so-Perfect (no fluid shift, “I’m so perfect” perfect balance) • List of fluids: • 0.9% sódio, chloride (normal saline) • 5% dextrose in water (DWS) • 5% dextrose in 0.225% saline (DSW/ 1/4 NS) • Lactated Ringer’s (LR) Hypotonic solutions • Definition: when a solution contains a lower concentration of solute than another more concentrated solution, then it is a hypotonic solution. • These solutions have lower osmolality than body fluids. • They cause the movement of water into cells by osmosis, swelling the cells like a BIG fat hippo, and therefore should be administered slowly to prevent cellular edema Memory Trick: • HypO - tonic • HippO - tonic = fluid swells the cell like a big hippo • List of fluids: • 0.45% sodium chloride (1/2 NS) • 0.225% sodium chloride (1/4 NS) • 0.33% sodium chloride (1.3 NS) Hypertonic solutions • Definition: when a solution contains a higher concentration of solutes than another less concentrated solution, then it is a hypertonic solution. • These solutions have higher osmolality than body fluids • They cause the movement of water outside the cells by osmosis, making the cells skinny like a hyper person. Memory Trick: • Hyper - tonic • Hyper person = very skinny cells like a hyper person is skinny • List of fluids: • 3% sodium chloride (3% NS) • 5% sodium chloride (5% NS) • 10% dextrose in water (D10W) • 5% dextrose in 0.9% sodium chloride (D5W/NS) • 5% dextrose in 0.45% sodium chloride (D5W/ 1/2 NS) • 5% dextrose in Lactated Ringer’s (D5LR)