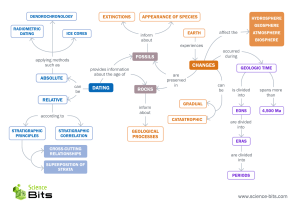
DATING METHODS AND PRINCIPLES (RADIOMETRY, ELECTRON SPIN RESONANCE, THERMOLUMINISCENCE AND PALEOMAGNETISM) BY DIDI CHEKWUBE NNAMDI PAU-UI-0704 DEPARTMENT OF PETROLEUM GEOSCIENCES PAULESI, IBADAN, NIGERIA DATE: 28-07-2022 PRESENTATION OUTLINE • INTRODUCTION • TYPES OF DATING • APPLICATION OF DATING • SIGNIFICANCE • CONCLUSION INTRODUCTION • How Old Is the Earth? • How Can We Determine Earth’s Geologic History? • How Can We Determine the Age of Geologic Events? THE EARTH TYPES OF DATING • Two Primary Means of Dating Rocks 1) Relative Dating Relative Dating • Determines the temporal order of rock forming events • Does not give numeric ages • Use of stratigraphic principles and fossils • Cheap Cheap 2) Absolute Dating Absolute Dating • Determines the numeric age of rock forming events • Only appropriate for ages of igneous rocks and minerals • Primary method is the radiometric technique • Used in conjunction with stratigraphic principles and fossils • Expensive Relative Versus Absolute Dating Relative Dating • Stratigraphic principles • Fossil Succession • Emphasis on Sed Rocks Absolute Dating • Radio-Isotopic techniques • Emphasis on Igneous Rocks SOURCE: Ray Rector How Can We Figure Out the Age Sequence of Geologic Events? The Stratigraphic Principles 1. Superposition - Oldest layer occurs at base of a layered sequence and is overlain by progressively younger rock layers. 2. Cross-Cutting Relations - If a body or discontinuity cuts across a rock structure, it must have formed after that stratum. 3. Law of Inclusions - Rock fragments (in another rock) must be older than the rock containing the fragments. 4. Law of Fossil Succession - Unique fossil groups were succeeded by other fossil groups through time. 5. Original Horizontality - All sedimentary rocks are originally deposited horizontally. Sedimentary rocks that are no longer horizontal have been tilted from their original position. 6. Lateral Continuity - Sedimentary and volcanic rocks are laterally continuous over large areas. The Stratigraphic Principles Principle of Superposition Principle of Fossil Succession Principle of Cross-Cutting Relations Principle of Inclusions Index Fossils 1) Narrow time range 2) Worldwide distribution 3) Preserve in a wide range of depositional settings 4) Very Abundant Index fossils Original horizontality Principle of Lateral Continuity Principle of Unconformities Q? ABSOLUTE DATING Absolute dating is usually based on the physical, chemical, and life properties of the materials. RADIOMETRY, ELECTRON SPIN RESONANCE, THERMOLUMINISCENCE, OPTICAL STIMULATING LUMINESCENCE, PALEOMAGNETISM ABSOLUTE DATING Name of Method Age Range of Application Material Dated Methodology Radiocarbon 1 - 70,000 years Organic material such as bones, wood, charcoal, shells Radioactive decay of 14C in organic matter after removal from bioshpere K-Ar dating 1,000 - billion of years Potassium-bearing minerals and glasses Radioactive decay of 40K in rocks and minerals Uranium-Lead 10,000 - billion of years Uranium-bearing minerals Radioactive decay of uranium to lead via two separate decay chains ABSOLUTE DATING Name of Method Age Range of Application Material Dated Methodology Uranium series 1,000 - 500,000 years Uranium-bearing minerals, Radioactive decay of 234U corals, shells, teeth, CaCO3 to 230Th Fission track 1,000 - billion of years Uranium-bearing minerals and glasses Measurement of damage tracks in glass and minerals from the radioactive decay of 238U Luminescence (optically or thermally stimulated) 1,000 - 1,000,000 years Quartz, feldspar, stone tools, pottery Burial or heating age based on the accumulation of radiation-induced damage to electron sitting in mineral lattices ABSOLUTE DATING Name of Method Age Range of Application Material Dated Methodology Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) 1,000 - 3,000,000 years Uranium-bearing materials in which uranium has been absorbed from outside sources Burial age based on abundance of radiationinduced paramagnetic centers in mineral lattices Cosmogenic Nuclides 1,000 - 5,000,000 years Typically quartz or olivine from volcanic or sedimentary rocks Radioactive decay of cosmic-ray generated nuclides in surficial environments Magnetostratigraphy 20,000 - billion of years Sedimentary and volcanic rocks Measurement of ancient polarity of the earth's magnetic field recorded in a stratigraphic succession ABSOLUTE DATING Name of Method Age Range of Application Material Dated Methodology 100 - billions of years Volcanic ejecta Uses chemistry and age of volcanic deposits to ephrochronology establish links between distant stratigraphic successions ABSOLUTE DATING GENERAL WORKING PRINCIPLE FOR • Thermoluminescence, • Optical stimulating luminescence and • Electron spin resonance RADIOACTIVE DECAY (RADIOCATIVE ELEMENT) RADITAION EXCEPTION RANGE Applicable to materials that are up to about 100,000 years old ABSOPTION (NON RADIOACTIVE ELEMENTS) EXCEPTION RANGE No accumulation of electron when the rock or fossil is older than 100,000 years because the trap is full ELECTRON DISPLACEMENT TRAP OR IMPERFECTION ELECTRON ACCUMULATION AGE RADIOMETRY RADIOCARBON DATING RADIOCARBON DATING • Once an organism dies, it ceases to obtain more 14C • 14C decays reducing the concentration within organism after death • 14C decays by beta emission, emission of an electron and a neutron changing into a proton, thus reverting back into nitrogen 14C ---> 14N + ß + neutrino The emitted beta particles (ß) are what is counted in Libby's "gas proportional“ method of 14C dating RADIOCARBON DATING Determining the Starting Amount Two types of carbon used in the dating process: 12C and 14C • 12C • When an organism is alive it has the same ratio (12C to 14C) that is found in the atmosphere (1-trillion to 100-trillion) is a stable isotope (it does not decay) Same ratio Different ratio RADIOCARBON DATING The C-14 dating method relies on measuring the amount of 14C in the material Two Things Need to Know to determine how many half-lives have expired 1. How fast it decays (measured in half-lives). This is known (5,730 years --> Cambridge half life). 2. The starting amount of C-14 in the fossil. A Critical Detail RADIOCARBON DATING How the 12C / 14C Ratio Works PALEOMAGNETISM The Earth is like a gigantic magnet. It has a magnetic north and south pole and its magnetic field is everywhere. Magnetic needle in a compass points toward magnetic north, Small magnetic minerals that occur naturally in rocks point toward magnetic north, approximately parallel to the Earth's magnetic field. Because of this, magnetic minerals in rocks are excellent recorders of the orientation, or polarity, of the Earth's magnetic field. PALEOMAGNETISM CONT’D ORIGIN OF THE EARTH’S MAGNETISM • Core • Core current MAGNETIC POLARITY DEPENDENT • Core current direction • Mantle current direction MAGNETIC POLARITY magnetic north marries geographical north • REVERSE POLARITY: Magnetic north marries geographical south PALEOMAGNETISM CONT’D What is paleomagnetism method? Radiometric dates and measurements of the ancient magnetic polarity in volcanic and sedimentary rocks Geologists have been able to determine precisely when magnetic reversals occurred in the past. Combined observations of this type have led to the development of the geomagnetic polarity time scale (GPTS) The GPTS is divided into periods of normal polarity and reversed polarity. PALEOMAGNETISM CONT’D • Earth’s magnetic field: earth’s magnetic field that any earth’s magnetic material aligns to • Geomagnetic polarity time scale (GPTS): Black bands indicate times of normal polarity and white bands indicate times of reversed polarity. CONCLUSION Using a variety of methods, geologists are able to determine the age of geological materials to answer the question: "how old is this fossil?" Relative dating methods are used to describe a sequence of events. These methods use the principles of stratigraphy to place events recorded in rocks from oldest to youngest. Absolute dating methods determine how much time has passed since rocks formed by measuring the radioactive decay of isotopes or the effects of radiation on the crystal structure of minerals. Paleomagnetism measures the ancient orientation of the Earth's magnetic field to help determine the age of rocks. THANK YOU