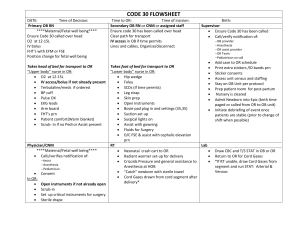
[MATERNAL AND CHILD CARE NURSING] /LEOPOLDS MANEUVER/ Preparation -It is a systematic way to determine ACTION the position of a fetus inside the a.Explain the procedure to the client uterus. b.Instruct the client to empty the -it utilizes palpation and observation bladder which provides information about the c.Place a small pillow under the number of fetuses, identity of the client’s head presenting part, fetal line and d.Position the woman supine with attitude. knees slightly flexed. Place a small -Named after the gynecologist pillow or rolled towel under her left Christian Gerhard Leopold side. -Maneuver is preferably performed e.Drape the client properly after 24 weeks gestation when fetal Note: If the Nurse is R handed, stand outline can be already palpated at the woman’s R side facing her for -The maneuvers are not truly the first 3 steps, then turn and face diagnostic. her feet for the last step (L handed, -Actual position can only be stand at left side) determined by ultrasound performed f. Wash your hand using warm water by a competent technician or g. Observe the woman’s abdomen for professional. longest diameter and where the fetal movement is apparent Purposes RATIONALE 1. Systematically observing and a.Explanation reduces anxiety and palpating the abdomen to: enhances cooperation b.Doing so promotes comfort and determine of what is in the allows for more productive palpation fundus because a distended bladder will evaluate the fetal back and obscure fetal contour. extremities c.To provide comfort for the client. palpate the presenting part d.Flexing the knees relaxes the above the symphysis abdominal muscles determine the direction and e.To provide client’s privacy degree of flexion of the head f. Hand washing prevents the spread 2. To aid in location of fetal of possible infection. Using warm heart rates water aids in client’s comfort and 3. To determine single versus prevents tightening of the abdominal multiple gestation muscles 4. The data provide the general g. The longest diameter (axis) is the and specific information that length of the fetus, the location of can be used to plan care activity most likely reflects the during the antepartum and position of the feet. intrapartum periods. Factors Affecting Performing The Procedure 1. Difficult to perform in Obese patients. 2. Women with hydramnios 3. Women with full bladder Implementation FIRST MANEUVER 1)Stand on the foot of the bed facing her, and placing both hands flat on her abdomen. 2) Palpate the surface of the fundus, determine the consistency, shape and mobility. 3) Expecting to palpate a soft, irregular mass in the upper quadrant of the maternal abdomen. (Also known as the Fundal Grip) FINDINGS -The fetal head is round and hard, and moves independently of the trunk. -The soft mass is the fetal buttocks, it is symmetric, and has small bony processes; unlike the head, it moves with the trunk. SECOND MANEUVER 1)Face the client and place the palms of each hand on either side of the client’s abdomen 2) While the right hand is placed steady, palpate the opposite side of the abdomen from top to bottom using the left hand. 3) Do the same to the other side of the abdomen using the right hand to palpate the side while the left palm is place steady. (Known also as Lateral and Umbilical Grip) FINDINGS -On one side of the abdomen, you will palpate round nodules; these are the fists and feet of the fetus (Kicking and movement are expected to be felt). -The other side of the abdomen feels smooth; this is the fetus’s back THIRD MANEUVER 1)While facing the client Gently grasp the lower portion of the abdomen just above the symphysis pubis between the thumb and the third finger together (to determine the presenting part). 2)Determine any movement whether the part is soft or firm (also known as Pawlick’s Grip) FINDINGS -The unengaged is round, firm, and ballottable -The buttocks are soft and irregular -Soft, presenting part at the symphysis pubis indicates Breech presentation. [MATERNAL AND CHILD CARE NURSING] FOURTH MANEUVER /LABOR WATCH/ 1)Face the client’s feet. -To monitor the progress of women’s 2)Place your hand on the client’s labor abdomen, and point your fingers -REMEMBER!!!! toward the mother’s feet. You will need a watch, or clock, with a 3)Then try to move the hands toward second hand and a laboring woman! each other while applying downward =Contractions pressure. -a rhythmic tightening of the (Pelvic Grip) musculature of the upper uterine FINDINGS segment that begins mildly and -If the hands move together easily, becomes very strong late in labor the fetal head has not descended into -The duration of the uterine the maternal pelvic inlet contraction is the time from the -If the hands do not move together beginning of one contraction to the and stop to resistance met, the fetal end of that same contraction head is engaged into the pelvic inlet. -During labor, the duration of the -If you palpated the buttocks in the contractions will start out short (25 to fundus, then you should feel for the 35 seconds long) and ultimately get to head. 70 – 90 seconds long. -If one cannot feel the head, then it =Duration probably has descended into the -With this progression from shorter pelvic inlet. contractions to longer contractions, a mother can figure out if this is real labor, or simply Braxton Hicks contractions. Braxton Hicks contractions remain irregular and do not get progressively longer as time passes. =Frequency -The frequency of the contractions is measured from the beginning of one contraction to the beginning of the very next - This not only includes the duration of one contraction, but also the rest period between the two. So if you have a contraction at 8 pm and it lasts for 60 seconds, and then you have another contraction at 8:15 pm, the contractions have a duration of 60 seconds and a frequency of 15 minutes = Intensity *contraction -The intensity of the contractions also changes as labor progresses. Early labor contractions are often described as mild menstrual cramps. Contractions in later labor, have been described by some stand-up comedians as feeling like *frequency your lower lip was stretched up over your head! While this analogy is humorous, it is true that with normal labor, the intensity of the contractions does increase, and this is a good sign that labor is progressing well. Mild - the uterus is contracting but does not become more than minimally tense (tip of the nose) Moderate - the uterus feels firm (chin) Strong - the contraction is so intense that the uterus feels as hard as wood at the peak of contraction (forehead) Procedure 1. Explain the procedure to the patient 2. Assist patient to a comfortable position with pillow on her head. 3. Sit on one side of the bed facing the patient. 4. Rest hand on the abdomen of the women in labor. 5. Do the labor monitoring. Date/ti me Vital signs FHT Frequency / duartion Remarks 7/26/14 @ 8:00 am T - 36.8 C P - 89 bpm R – 18 cpm Bp – 120/80 mmHg 138 bpm ? / 30 sec. mild 8:15 am T - 36.8 C P - 95 bpm R – 18 cpm Bp – 120/80 mmHg 140 bpm 15 min./ 40 sec. moderate [MATERNAL AND CHILD CARE NURSING] /FUNCTIONS AND RESPONSIBILITIES infant’s APGAR Score; hand in the DURING INTRAPARTAL STAGE/ infant to the cord dressing nurse. Handle 15)Deliver the placenta. (Determine 1)Wear complete DR attire including the signs of placental separation). mask, cap and prescribed slippers for 16)Monitor the vital signs, palpate DR during the delivery. fundus for size, consistency, position, 2)Do proper hand washing before the and vaginal bleeding. delivery. 17)Reassure the patient. Provide 3)Prepare sterile sets (OB pack), post-partum instructions. supplies, drapes and equipment 18)Complete the DR records and needed in the delivery. patient’s chart. 4)Place patient on the DR table and 19)Assist in the transport of the assist in lithotomy position. Elevate patient to the ward together with her patient’s legs simultaneously and infant. position in stirrups, adjusting to leg Cord Care length, provide padding to prevent 1)Wear complete DR attire including pressure on popliteal veins and mask, cap and prescribed slippers for nerves, provide hand grips. DR during the delivery. 5)Cleanse the vulva and perineal area. 2)Do proper hand washing before the delivery. 3)Gather equipment and supplies needed for the newborn care. 4)Prepare pre-heated linens/mattress or warmer. 5)Check infant’s weighing scale for correct 6)Do gloving. 6)Prepare the suction machine if 7)Drape the patient aseptically. properly functioning. 8)Catheterize patient if bladder is 7)Receive the baby after cutting the full.( Should have physician’s order) cord and place in a pre-heated crib. 9)Coach patient for most effective 8)Aspirate remaining secretions using pushing using abdominal muscles bulb syringe. upon contractions 9)Dry up the infant thoroughly and 10)Monitor maternal vital signs and change wet linens. fetal heart tones following 10)Evaluate further APGAR score. contractions and pushing. Take vital signs. 11)Deliver the baby’s head, shoulder 11)Perform cord dressing aseptically. and body announcing and showing - Cord is tied off 1 inch from the base the sex of the baby to the mother and expose to air. - Dress the cord while laying on patient’s abdominal with 70 % ethyl alcohol. drape. Note the time of birth 12)Weight the baby 12)Support the perineum during the 13)Measure head, chest and delivery. abdominal circumference in 13)Loosen and slip the loops of cord if centimeters. fetal head has cord coil before the 14)Dress the baby shoulder are delivered. 15)Administer eye prophylaxis. 14)Clamp cord coil with 2 clamps 16)Administer Vitamin K to R anterior during the delivery. ( curve Kelly thigh forceps-towards the mother, Full term - 1 mg IM Straight Kelly forceps - towards the Preterm - 0.5 mg IM baby ) - If no cord coil, cut the cord 8 17)Administer Hepatitis B1 10 inches from the infant’s umbilicus immunization on L anterior thigh. after pulsation ceases. - Evaluate 18)Attach wrist ID band. -Indicating the sex of the baby, Family name, Date and Time of Delivery 19)Assist Pediatrician in the evaluation of Ballard score. 20)Bedded in to mother for breastfeeding. 21)Clean used instruments and pack. 22)Complete the infant’s chart and endorse to NICU staff, or give to the appropriate significant other. Complete DR record. =The Department of Health(DOH Ph) embarked on Essential Newborn Care, a new program to address neonatal deaths in the country. Under the umbrella of the Unang Yakap Campaign, Essential Newborn Care is an evidenced based strategic intervention aimed at improving newborn care and helping cub neonatal mortality. =The Essential Newborn Care package is a four-step newborn care time bound intervention undertaken to lessen newborn death. -Immediate and thorough drying to stimulate breathing after delivery of the baby -Provision of appropriate thermal care through mother and newborn skin-to skin contact maintaining a delivery room temperature of 25-28 degrees centigrade and wrapping the newborn with clean, dry cloth. -Properly timed clamping and cutting of the umbilical cord, (1-3 minutes or until cord pulsation stops) -Non-separation of the newborn and mother for early breast-feeding. Immediate latching on and initiation of breastfeeding within first hour after birth =Post-natal care required within 24 hours after birth also includes *Cord care *NB screening *Breastfeeding *Vitamin K Injection *Eye prophylaxis *Delayed bathing until 6 hours of life *BCG and first dose of Heb B *Immunization