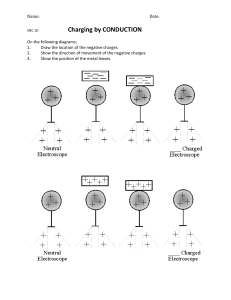
Republic of the Philippines Department of Education REGION VIII – EASTERN VISAYAS SCHOOLS DIVISION OF CATBALOGAN CITY SAMAR NATIONAL SCHOOL Catbalogan City DETAILED LESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 7 QUARTER 3 Content Standard: Charges and the different charging processes Performance Standard: Suggest proper lighting in various activities. I. OBJECTIVE: A. Most Essential Learning Competency Describe the different types of charging processes (S7LT-IIIj-13). B. Instructional Objectives: 1. Identify the types of charges: 2. Describe the different charging processes: 3. Perform activities involving charging processes. II. SUBJECT MATTER Topic: Electric Charges and the Charging Process KBI: Cooperation, teamwork, critical thinking III. Learning Resources A. Materials: Audiovisual set (laptop, projector and speakers), picture of sorts, illustrations. B. References: Grade 7 Science Learner’s Module pages 262-276 Grade 7 Science Teacher’s Material pages 306-314 IV. PROCEDURE Teacher’s Activity 1. Preliminary Activities Learner’s Activity May we all stand for the prayer. Who can lead the prayer? A student leads the prayer Good morning class! Good morning, ma’am! You may now take your seat. Thank you, ma’am. Let me check the attendance first. Make sure that you are in your proper seats so that you will not be marked absent. Very Good! Everybody is present. (Check attendance using a seat plan) Since we’re in pandemic let’s observe health protocol; First, wear your face mask. Second, observe social distancing. Third, always sanitized your hands. 2. Developmental Activity A. Drill Please read the following: Student will read in chorus Electrostatic Law- Like charges repel and unlike charges attract Law of Conservation of charge- Charges cannot be created nor destroyed, but can be transferred from one material to another. Positively charge- Charge of material that is losing electrons Conductor- A material that permits charges to flow freely. Charging by friction- Charging process involved when rubbing of material to another. Negatively charge- Charge of material that is gaining electrons. Charging by induction- Charging process without actual contact to any other charged object. Electric force- Force which acts on charges. Triboelectric series- An arrangement of materials/substances according to their ability to gain or lose electrons. Insulator- Materials that hinder the free flow charges within it. Charging by conduction- Charging process which involves the contact of a charged object to a neutral object. Attraction and Repulsion- Two kinds of electric forces. Thank you! These are the term that we will encounter along with our lesson class. A. Elicit In your previous lesson, you have learned about heat as a form of energy that can be transferred through conduction, convection and radiation. To refresh your understanding of the previous lesson, answer these following questions: Teacher will call the student randomly to answer these following questions. COMPLETION Directions: Fill in the blanks with appropriate word/s to complete the paragraph. Choose your answer from the word box below. (1) ___________ is a thermal energy that is in transit. (2) ___________ takes place due to the vibrating and colliding particles of objects that are in contact. It can take place in solids, liquids, and gases but it takes place best in solids. (3) ___________takes place in fluids because their particles can move around. While heat transfer by (4) ___________ does not need particles or a medium to take place. Also (5) ________ takes place between objects of different temperature. Heat Convection Conduction Radiation Heat transfer Students possible answer (1) Heat is a thermal energy that is in transit. (2) Conduction takes place due to the vibrating and colliding particles of objects that are in contact. It can take place in solids, liquids, and gases but it takes place best in solids. (3) Convection takes place in fluids because their particles can move around. While heat transfer by (4) Radiation does not need particles or a medium to take place. Also (5) Heat Transfer takes place between objects of different Very Good! It seems that you learned something about heat temperature. transfer. B. Engage Who among you here has a hairbrush or hair comb? Kindly get your hairbrush or comb and try to brush your hair for 2 minutes. Then, put the hairbrush near the tiny bits of paper. What have you observed? The paper stick to the hair brush or comb. How is this possible? Student’s answer may vary Yes, and that is our topic for today, Electric Charges and the Charging Process. So, class, before we start our lesson for today let us first know what are we achieving today. Please read our Instructional Objectives. Thank you. Students are reading the instructional objectives. Instructional Objectives: 1. Identify the types of charges: 2. Describe the different charging processes: 3. Perform activities involving charging processes. C. Explore Let us do an activity first. Directions: Every group assigned a different activity. All you have to do is perform the activity according to the procedures and report your observation in front by answering the guide question. You have 10 minutes to perform the activity. Students are starting doing their group activity. Group 1 Activity 1 Charged interactions Materials Needed: Acetate Tissue Small strips of paper Procedure: 1. Rub the tissue against the acetate. 2. Place the rubbed acetate above the strips of paper. Q1. Is there any sign of interaction between the acetate and strips of paper? 3. Try this with another object. Q2. Is there any sign of interaction between the acetate and this object? 4. Remove the strips of paper by wiping the acetate with tissue. 5. Touch the rub portion of acetate after one minute. 6. Place the rubbed acetate above the strips of paper. Q3. Do you still observe any interaction? Group 2 Activity 2 To charge or not to charge Materials Needed: Acetate Tissue Aluminum foil Coper wire Jar Adhesive tape Procedure: 1. Make a cover for the glass jar through the acetate. 2. Cut the cover from the acetate. 3. Punch a hole to the center of the cover using the copper wire. 4. Hook two pieces of aluminum strip at the bottom end of the wire. 5. 6. 7. 8. Secure the copper wire with adhesive tape. Put the cover to the top of the jar. Rub the tissue against the acetate. Bring the rubbed acetate close to the copper wire without touching it. 9. Remove your hand and observe how the balloon and the can will interact. Q1. What do you think is the charge acquired by the acetate after rubbing it against the tissue? Q2. What is the purpose of touching the can in step #4? Q3. Were you able to charge the soft drink can? Explain how this happened. Q4. Based on your answer in Q1, what do you think is the charge of the soft drink can? Group 3 Activity 3 Pass the charge Materials Needed: 2 Styrofoam cup 2 Soft drinks can 2 Balloon Procedure: Very Good everyone D. Explain Based on your presentation let us answer the following questions: Activity 1 Q1. Is there any sign of interaction between the tape and the finger? 1. Repeat all steps in Activity 2. 2. Let the charged can set-up touch a neutral can set-up as shown in the figure. 3. Separate the two set-ups then observe how the charged balloon interacts with the first and second set-up. Q2. Is there any sign of interaction between the Q1. Were you able to charge the can in the second set-up? tape and this object? Explain how this happened. Q2. Is it necessary for the two cans to come into contact Q3. Do you still observe any interaction? for charging to happen? Why or why not? Q3. From your observation in step 3, infer the charge Very good! acquired by the can in the second set-up. How about on the activity 2? Q1. What do you think is the charge acquired by the balloon after rubbing it against your hair? Student’s answers may vary. Yes ma’am, strips of paper is attracted to the rubbed Q2. What is the purpose of touching the can in step acetate. #4? Once again, students will observe an attraction between the acetate and the object. Q3. Were you able to charge the soft drink can? Interactions observed earlier will be greatly reduced or will be non-existent. Explain how this happened. Q4. Based on your answer in Q1, what do you think is the charge of the soft drink can? And lastly, Activity 3 The hair will give up electrons thus the balloon will acquire a negative charge. Q1. Were you able to charge the can in the second By touching the can, a path was provided for the charges set-up? Explain how this happened. to be transferred. This is an example of grounding. Q2. Is it necessary for the two cans to come into contact for charging to happen? Why or why not? Ideally, the soft drink can will be charged. The hand provided a path for negative charges to move away from the can thus when the hand was removed the can was left Q3. From your observation in step 3, infer the with a net charge. charge acquired by the can in the second set-up. The soft drink can have acquired a net positive charge. E. Elaborate You have learned in previous modules that all matter is made up of atoms or combinations of atoms called compounds. The varying atomic composition of different materials gives them different electrical properties. One of which is the ability of a material to lose or gain electrons when they come into contact with a different material through friction. Ideally, the can in the second set up will be charged since excess charges has been transferred to it from the can in the first set up. The contact between the cans is necessary since it is this contact that has provided a path for the charges to be transferred. This is possible because both cans are good In activity 1, how the tape acquired a net charge electrical conductors. when the tape was pulled vigorously from the The can in the second set up has acquired a net positive table? charge. Very good! And how will you differentiate positively charged from negatively charged based on your activity 1? Very good! The process involved is usually referred to as charging up the material, and in this particular activity What do you think is charging process Student’s answers may vary. used? It is important to remember that during the When you pulled the tape vigorously from the table, some charging process, ideally, the amount of charge lost of the electrons from the table’s surface were transferred by the table is equal to the amount of charge gained to the tape. by the tape. This is generally true in any charging process. Based on activity 1, the table become positively charged because it has lost some electrons while the tape has This idea is also known as… gained electrons which made it negatively charged. When you brought your finger (and the other object) near the charged tape, what have you Charging by friction which simply means rubbing of observed on the tape? material to another. Very good! We learned from the previous activity that the tape is negatively charged. The excess negative charge in the tape allowed it to interact with your finger and the other object. The Law of Conservation of Charge Charges cannot be created nor destroyed, but can be When you placed the two charged tapes near each transferred from one material to another. The total charge other, What have you observe? in a system must remain constant. These observations tell us that there are two kinds of electric force which arises from the fact that The tape was drawn towards your finger as if being pulled there also two kinds of electrical charges. by an invisible force. This force is called electric force which acts on charges. What do you think are they? An uncharged or neutral object that has balanced positive and negative charges cannot experience this force. Yes, this interactions between the charges are summarized through electrostatic law. Anyone who has an idea about electrostatic Law? But how will you know if an object will either gain or lose electrons? They seem to push each other away. The behavior of a charged material depends on its ability to allow charges to flow through it. A material that permits charges to flow freely within it, is… Force of Repulsion and Force of Attraction. In contrast to conductors, insulators are… Electrostatic Law Like charges repel and unlike charges attract. By using the Triboelectric series were in it is an arrangement of materials/substances according to their Based on your observation in activity 2, which do ability to gain or lose electrons. you think that used in materials in the activity are conductors and which are insulators? The observations you made had in Activity 2 a good electrical conductor. A good conducting material depended on the fact that the balloon and the will allow charges to be distributed evenly on its surface. Styrofoam are good insulators while the soft drink Metals are usually good conductors of electricity. can and you are good conductors. are materials that hinder the free flow charges within it. If How do you think that the can was charged? charge is transferred to an insulator, the excess charge will remain at the original location of charging. This means that Very good! charge is seldom distributed evenly across the surface of And the charging process used in this activity is an insulator. Some examples of insulators are glass, porcelain, plastic and rubber. called? Very good! How about in activity 3, what do you think is the The materials in the activity that are conductors is soft drinks and me while the insulator are the balloon and charging process you performed? Styrofoam Very good Class, in what learning area/field of study this lesson be applied? Again class, what are the types of charging The can has become charged after we touched one of its ends. processes? How do you feel about our lesson today? Charging by induction where in an object can be charged without actual contact to any other charged object. E. Evaluate Okay, since there are no questions lets have a quiz. Charging by conduction which involves the contact of a charged object to a neutral object. Get ¼ sheet of paper. And answer the following. Test 1: Where I Belong! Student’s answer may vary. Charging by friction Charging by induction Charging by conduction Student’s answer may vary. Test 1: Where I Belong! Directions: Complete the table below. Identify the process of charging presented. Write your answer Directions: Complete the table below. Identify the before the number. process of charging presented. Write your answer before the number. Test 2. Multiple Choice Directions: Choose the letter of the correct answer. Test 2. Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is NOT a process of Directions: Choose the letter of the correct answer. charging? a. Induction 1. Which of the following is NOT a process of charging? b. Friction a. Induction c. Convection b. Friction d. Conduction c. Convection d. Conduction 2. What do you call the process of transferring charges between objects by rubbing? 2. What do you call the process of transferring charges a. Proton transfer between objects by rubbing? b. Static discharge a. Proton transfer c. Charging by friction b. Static discharge d. Charging by induction c. Charging by friction d. Charging by induction 3. What do you call the process of charging which involves the contact of a charged object to a neutral object? a. Proton transfer b. Charging by Conduction c. Charging by friction d. Charging by induction 4. What do you call the process of charging where an object can be charged without actual contact to any other charged object? a. Proton transfer b. Charging by Conduction c. Charging by friction d. Charging by induction 5. What do you call the attraction or repulsion between electric charges? a. Friction b. Conduction c. Electric field d. Electric force 3. What do you call the process of charging which involves the contact of a charged object to a neutral object? a. Proton transfer b. Charging by Conduction c. Charging by friction d. Charging by induction 4. What do you call the process of charging where an object can be charged without actual contact to any other charged object? a. Proton transfer b. Charging by Conduction c. Charging by friction d. Charging by induction 5. What do you call the attraction or repulsion between electric charges? a. Friction b. Conduction c. Electric field d. Electric force After 3 minutes. Let’s check. Exchange your paper with your seatmate. Very good F. Extend Cite another sample where charging processes is present? Write your answer in a 1 whole sheet of paper. That’s all for today Good bye, class Thank you and good bye, teacher. V. Remarks VI. Reflection Prepared by: EDESSA D. MASINAS SST I NOTED: BRIGIDA C. SINGZON Science Head Teacher RUTH D. CABANGANAN Principal